Electrochromic films — like sunglasses for your windows?
2024-05-29
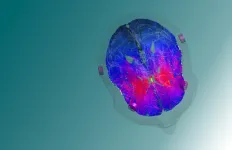
(Press-News.org) Advances in electrochromic coatings may bring us closer to environmentally friendly ways to keep inside spaces cool. Like eyeglasses that darken to provide sun protection, the optical properties of these transparent films can be tuned with electricity to block out solar heat and light. Now, researchers in ACS Energy Letters report demonstrating a new electrochromic film design based on metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) that quickly and reliably switch from transparent to glare-diminishing green to thermal-insulating red.
Hongbo Xu and colleagues used MOFs in their electrochromic film because of the crystalline substances’ abilities to form thin films with pore sizes that can be customized by changing the length of the organic ligand that binds to the metal ion. These features enable improved current flow, more precise control over colors and durability. In demonstrations, Xu’s MOF electrochromic film took 2 seconds to switch from colorless to green with an electric potential of 0.8 volts, and 2 seconds to switch to dark red with 1.6 V. The film maintained the green or red color for 40 hours when the potential dropped, unless a reverse voltage was applied to return the film to its transparent state. The film also performed reliably through 4,500 cycles of switching from colored to clear. With further optimization, the researchers say their tunable coatings could be used in smart windows that regulate indoor temperatures, as well as in smaller scale intelligent optical devices and sensors.
In addition to Xu’s MOF-based electrochromic film, several other research groups have reported electrochromic coating designs, including a UV-blocking but visually transparent radiative cooling film, a colorful plant-based film that gets cooler when exposed to sunlight, and a temperature-responsive film that turns darker in cold weather and lighter when it’s hot.
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province and the Scientific Research Startup Project of Quzhou University.
The paper will be available on May 29 at 8 a.m. Eastern time here: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsenergylett.4c00492
###
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Note: ACS does not conduct research, but publishes and publicizes peer-reviewed scientific studies.
Follow us: X, formerly Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-05-29
What makes chocolate taste and smell so delicious? Chemistry, of course! A variety of molecules work together to create that unmistakable aroma, but those same molecules might carry some unwanted health effects if there are too many around. According to research published in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, while many of the compounds appeared in chocolate in low enough concentrations to be safe, higher amounts were found in some baked sweet treats.
When making chocolate, cocoa beans are roasted to help their chocolatey flavors shine. During this process, new molecules ...
2024-05-29
New York, NY, May 29, 2024 — The New York Academy of Sciences and the Leon Levy Foundation announced today the 2024 cohort of Leon Levy Scholars in Neuroscience, continuing a program initiated by the Foundation in 2009 that has supported 170 fellows in neuroscience.
This highly regarded postdoctoral program supports exceptional young researchers across the five boroughs of New York City as they pursue innovative neuroscience research and advance their careers toward becoming independent principal investigators. Nine scholars were competitively selected for a three-year term from a broad pool of applications from more than a dozen ...
2024-05-29
The number of refugees has sharply increased in recent decades, reaching 37.8 million in 2022. Amidst this surge, host communities—locals residing in areas where refugee camps are situated—are also positively and negatively impacted by the refugee influxes. The negative impacts include competition over scarce resources and in the unskilled labor market. While the international media and aid organizations put the spotlight on assisting refugees, the challenges faced by host communities are frequently sidelined.
In 2017, over ...
2024-05-29
If we want cleaner air, fewer forest fires, and less severe climate change, a new UC Riverside study shows we must reduce aerosol pollution and greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide at the same time.
The study found that boreal forests in the northern hemisphere are particularly vulnerable to negative effects of cleaning up aerosol pollution. This includes forests in Canada, Alaska, northern Europe, and northern Russia.
Aerosols are small particles like dust and sea salt as well as airborne chemicals produced by fossil fuel combustion. They are responsible for poor air quality. The UCR study, published in the journal ...
2024-05-29
A small interfering RNA (siRNA) investigational therapy that inhibits a gene involved in lipoprotein metabolism has been shown in a clinical trial led by Mount Sinai researchers to significantly reduce levels of different types of cholesterol and triglycerides in individuals with mixed hyperlipidemia, a condition in which fats build up in the blood.
In addition to seeing promising preliminary results related to safety and efficacy in clinical trials, the Mount Sinai researchers found the RNA interference (RNAi)-based therapy zodasiran to be a potentially promising option for substantially reducing a number of atherogenic lipoproteins while requiring less frequent ...
2024-05-29
Spend any time scrolling through social media or news sites and it feels like America is a nation in constant argument. Off-hand remarks often spark fierce screaming matches. Partisanship is up, Gallup tells us, while trust in institutions is down.
However, a new study co-authored by Berkeley Haas Assistant Professor Erica R. Bailey suggests this perception may not accurately reflect the nature and frequency of political debates among everyday Americans. In three studies involving nearly 3,000 participants, researchers found most debates ...
2024-05-29
By Dylan Walsh
Some of human history’s greatest atrocities—genocide, slavery, ethnic cleanings—are rooted in our ability to dehumanize people from other social, political, or cultural groups.
Whereas prior research has traced dehumanization to the belief that others think or feel less than we do, new research co-authored by Haas professor Sameer Srivastava shows that our tendency to dehumanize can also be influenced by how we think others view important facets of the world. The greater ...
2024-05-29
Research Highlights:
The benefits gained from better heart health may be related to a process involved in the aging of the body and its cells, researchers found in a study of more than 5,000 adults with a mean age of 56 years.
People with rapid cell aging may offset the increased risk of heart disease, stroke and death by managing their heart disease risk factors and adopting more heart-healthy behaviors, researchers said.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Wednesday, May 29, 2024
DALLAS, May 29, 2024 — The benefit of better heart health may be associated with the positive impact of heart healthy lifestyle factors on biological aging (the age of the body and its ...
2024-05-29
Neurological disorders, such as addiction, depression, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), affect millions of people worldwide and are often characterized by complex pathologies involving multiple brain regions and circuits. These conditions are notoriously difficult to treat due to the intricate and poorly understood nature of brain functions and the challenge of delivering therapies to deep brain structures without invasive procedures.
In the rapidly evolving field of neuroscience, non-invasive brain stimulation is a new hope for ...
2024-05-29
An analysis by researchers in the Department of Psychiatry at the University of Arizona College of Medicine – Tucson showed that risks for death by suicide and homicide peak at night, with nocturnal wakefulness, age, alcohol use and relationship conflicts being especially prevalent as contributing factors.
Nearly 19% of suicides and 36% of homicides occur at night. Suicide and homicide share little in common, but their highly concordant overnight risk patterns suggest a common feature: nocturnal ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Electrochromic films — like sunglasses for your windows?