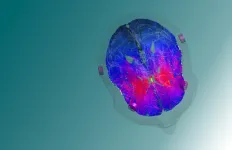
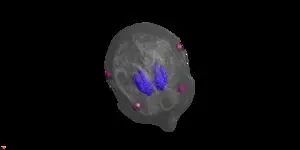
(Press-News.org) Neurological disorders, such as addiction, depression, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), affect millions of people worldwide and are often characterized by complex pathologies involving multiple brain regions and circuits. These conditions are notoriously difficult to treat due to the intricate and poorly understood nature of brain functions and the challenge of delivering therapies to deep brain structures without invasive procedures.
In the rapidly evolving field of neuroscience, non-invasive brain stimulation is a new hope for understanding and treating a myriad of neurological and psychiatric conditions without surgical intervention or implants. Researchers, led by Friedhelm Hummel, who holds the Defitchech Chair of Clinical Neuroengineering at EPFL’s School of Life Sciences, and postdoc Pierre Vassiliadis, are pioneering a new approach in the field, opening frontiers in treating conditions like addiction and depression.
Their research, leveraging transcranial Temporal Interference Electric Stimulation (tTIS), specifically targets deep brain regions that are the control centers of several important cognitive functions and involved in different neurological and psychiatric pathologies. The research, published in Nature Human Behaviour, highlights the interdisciplinary approach that integrates medicine, neuroscience, computation, and engineering to improve our understanding of the brain and develop potentially life-changing therapies.
“Invasive deep brain stimulation (DBS) has already successfully been applied to the deeply seated neural control centers in order to curb addiction and treat Parkinson, OCD or depression,” says Hummel. “The key difference with our approach is that it is non-invasive, meaning that we use low-level electrical stimulation on the scalp to target these regions.”
Vassiliadis, lead author of the paper, a medical doctor with a joint PhD, describes tTIS as using two pairs of electrodes attached to the scalp to apply weak electrical fields inside the brain. "Up until now, we couldn’t specifically target these regions with non-invasive techniques, as the low-level electrical fields would stimulate all the regions between the skull and the deeper zones—rendering any treatments ineffective. This approach allows us to selectively stimulate deep brain regions that are important in neuropsychiatric disorders," he explains.
The innovative technique is based on the concept of temporal interference, initially explored in rodent models, and now successfully translated to human applications by the EPFL team. In this experiment, one pair of electrodes is set to a frequency of 2,000 Hz, while another is set to 2,080 Hz. Thanks to detailed computational models of the brain structure, the electrodes are specifically positioned on the scalp to ensure that their signals intersect in the target region.
It is at this juncture that the magic of interference occurs: the slight frequency disparity of 80 Hz between the two currents becomes the effective stimulation frequency within the target zone. The brilliance of this method lies in its selectivity; the high base frequencies (e.g., 2,000 Hz) do not stimulate neural activity directly, leaving the intervening brain tissue unaffected and focusing the effect solely on the targeted region.
The focus of this latest research is the human striatum, a key player in reward and reinforcement mechanisms. "We're examining how reinforcement learning, essentially how we learn through rewards, can be influenced by targeting specific brain frequencies," says Vassiliadis. By applying stimulation of the striatum at 80 Hz, the team found they could disrupt its normal functioning, directly affecting the learning process.
The therapeutic potential of their work is immense, particularly for conditions like addiction, apathy and depression, where reward mechanisms play a crucial role. "In addiction, for example, people tend to over-approach rewards. Our method could help reduce this pathological overemphasis," Vassiliadis, who is also a researcher at UCLouvain’s Institute of Neuroscience, points out.
Furthermore, the team is exploring how different stimulation patterns can not only disrupt but also potentially enhance brain functions. "This first step was to prove the hypothesis of 80 Hz affecting the striatum, and we did it by disrupting it’s functioning. Our research also shows promise in improving motor behavior and increasing striatum activity, particularly in older adults with reduced learning abilities," Vassiliadis adds.
Hummel, a trained neurologist, sees this technology as the beginning of a new chapter in brain stimulation, offering personalized treatment with less invasive methods. "We're looking at a non-invasive approach that allows us to experiment and personalize treatment for deep brain stimulation in the early stages," he says. Another key advantage of tTIS is its minimal side effects. Most participants in their studies reported only mild sensations on the skin, making it a highly tolerable and patient-friendly approach.
Hummel and Vassiliadis are optimistic about the impact of their research. They envision a future where non-invasive neuromodulation therapies could be readily available in hospitals, offering a cost-effective and expansive treatment scope.
END
Hitting the target with non-invasive deep brain stimulation: Potential therapy for addiction, depression, and OCD
Researchers at EPFL have successfully tested a novel technique for probing deep into the human brain, without surgery, for potential therapeutic purposes.
2024-05-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The mind after midnight: Study shows disrupted sleep increases risk for suicide and homicide
2024-05-29
An analysis by researchers in the Department of Psychiatry at the University of Arizona College of Medicine – Tucson showed that risks for death by suicide and homicide peak at night, with nocturnal wakefulness, age, alcohol use and relationship conflicts being especially prevalent as contributing factors.
Nearly 19% of suicides and 36% of homicides occur at night. Suicide and homicide share little in common, but their highly concordant overnight risk patterns suggest a common feature: nocturnal ...
Health risk from global warming predictor of city climate action during COVID-19
2024-05-29
City officials were more likely to maintain climate action during the pandemic in places with more climate-related health issues affecting residents.
Cities around the world were more likely to maintain climate action and enact ‘green recovery’ long-term plans after the pandemic if local decision-makers were more alert to the health risks of climate change, a new global study has shown.
The health benefits of tackling climate change, such as cleaner air and more access to green spaces, were key ...
Are there racial inequities in naloxone administration during fatal overdoses?
2024-05-29
Pennsylvania has been disproportionately affected by the opioid epidemic, having the fourth highest number of overdose deaths in the country in 2020. Also, the rate of overdose deaths among Black persons is significantly higher than that of white persons in the state. A recent analysis published in Addiction reveals that compared with white people in Pennsylvania, Black individuals are less likely to receive naloxone—a medication that rapidly reverses an opioid overdose.
In the analysis of 2019–2021 data collected from death ...
Does recreational marijuana legalization affect a state’s college enrollment?
2024-05-29
New research has revealed up to a 9% increase in college freshmen enrollments in US states that have legalized recreational marijuana compared with states without such legalization. The study, which is published in Economic Inquiry, found that the increase was from out-of-state enrollments, with early adopter states and public non-research institutions experiencing the most pronounced increases.
Recreational marijuana legalization did not negatively impact degree completion or graduation rate, and it did not affect ...
Is a train’s risk of derailment affected by its length?
2024-05-29
Longer freight trains are more likely to derail compared with shorter trains, according to new research published in Risk Analysis. The increased risk held even after accounting for the need for fewer trains if more cars were on each train.
For the study, investigators assessed information on US freight train accidents between 2013–2022 from Federal Railroad Administration databases. The team found that running 100-car trains would lead to an 11% higher risk of derailment compared with running 50-car trains, even when accounting for the fact that only half as many 100-car trains would need to run. For 200-car trains, the risk was 24% higher than ...
To what extent are pharmaceutical and illicit drugs contaminating city rivers?
2024-05-29
In research published in Environmental Toxicology & Chemistry, investigators sampled water from 19 locations across the Hudson and East Rivers in 2021 and 2022 to identify and quantify the prescribed pharmaceuticals and drugs of abuse that are making their way into New York City’s rivers and to determine the source of these pollutants.
Metoprolol and atenolol (blood pressure medications), benzoylecgonine (the main metabolite of cocaine), methamphetamine (a stimulant), and methadone (an opioid) were the most prevalent drugs, ...
Solving the problems of proton-conducting perovskites for next-generation fuel cells
2024-05-29
As a newly developed perovskite with a large amount of intrinsic oxygen vacancies, BaSc0.8W0.2O2.8 achieves high proton conduction at low and intermediate temperatures, report scientists at Tokyo Tech. By the donor doping of large W6+, this material can take up more water to increase its proton concentration, as well as reduce the proton trapping through electrostatic repulsion between the dopant and proton. These findings could pave the way to the rational design of novel perovskites for protonic ceramic fuel cells (PCFCs) and electrolysis cells (PCECs).
In line with global efforts towards cleaner energy technologies, fuel cells may soon become an indispensable ...
Bird flu: diverse range of vaccines platforms “crucial” for enhancing human pandemic preparedness
2024-05-29
Vaccination remains the most effective strategy for avian influenza prevention and control in humans, despite varying vaccine efficacy across strains.
That’s according to the authors of a new review which delves into existing research into bird flu vaccines for humans.
Published in the peer-reviewed journal Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics, the results of the paper are particularly timely following news last week (Wednesday 22nd May) that the bird flu strain H5N1 had once again, for a second time, jumped from cattle in America to a human – prompting fears of subsequent human-to-human infection, with possible critical consequences.
Instances ...
Marine Protected Areas don’t line up with core habitats of rare migratory fish, finds new research
2024-05-29
62% of Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) designated to protect rare migratory fish species are outside of their core habitats, according to a new modelling study. The findings are published in the British Ecological Society’s Journal of Applied Ecology.
A team of researchers in France from the “Pole MIAME” that gathers diadromous fish experts from multiple research institutions (OFB, INRAE, Institut Agro and UPPA) have developed a new modelling approach that accurately predicts core and unsuitable habitats of rare and data-poor ...
Ecological designed experiment method based on pragmatism: A case study of Haizhu Wetland Restoration Project in Guangzhou, China
2024-05-29
The advancement of urbanization and globalization has impacted every corner of the Earth, human activities have transformed over one-third of the planet’s ecosystems, including agricultural lands and urban areas. Thus, there is an urgent need to define and achieve the equilibrium of novel ecosystems.
This study employed pragmatic designed experiments as its core method, integrating methodologies from empiricism, positivism, and romanticism to propose a semi-empirical ecological design framework that emphasizes learning by doing and research through practice. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Fecal transplants from older mice significantly improve ovarian function and fertility in younger mice
Delight for diastereomer production: A novel strategy for organic chemistry
Permafrost is key to carbon storage. That makes northern wildfires even more dangerous
Hairdressers could be a secret weapon in tackling climate change, new research finds
Genetic risk for mental illness is far less disorder-specific than clinicians have assumed, massive Swedish study reveals
A therapeutic target that would curb the spread of coronaviruses has been identified
Modern twist on wildfire management methods found also to have a bonus feature that protects water supplies
AI enables defect-aware prediction of metal 3D-printed part quality
Miniscule fossil discovery reveals fresh clues into the evolution of the earliest-known relative of all primates
World Water Day 2026: Applied Microbiology International to hold Gender Equality and Water webinar
The unprecedented transformation in energy: The Third Energy Revolution toward carbon neutrality
Building on the far side: AI analysis suggests sturdier foundation for future lunar bases
Far-field superresolution imaging via k-space superoscillation
10 Years, 70% shift: Wastewater upgrades quietly transform river microbiomes
Why does chronic back pain make everyday sounds feel harsher? Brain imaging study points to a treatable cause
Video messaging effectiveness depends on quality of streaming experience, research shows
Introducing the “bloom” cycle, or why plants are not stupid
The Lancet Oncology: Breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women worldwide, with annual cases expected to reach over 3.5 million by 2050
Improve education and transitional support for autistic people to prevent death by suicide, say experts
GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic could cut risk of major heart complications after heart attack, study finds
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
Machine learning advances non targeted detection of environmental pollutants
ACP advises all adults 75 or older get a protein subunit RSV vaccine
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
[Press-News.org] Hitting the target with non-invasive deep brain stimulation: Potential therapy for addiction, depression, and OCDResearchers at EPFL have successfully tested a novel technique for probing deep into the human brain, without surgery, for potential therapeutic purposes.