(Press-News.org) Vaccination remains the most effective strategy for avian influenza prevention and control in humans, despite varying vaccine efficacy across strains.
That’s according to the authors of a new review which delves into existing research into bird flu vaccines for humans.
Published in the peer-reviewed journal Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics, the results of the paper are particularly timely following news last week (Wednesday 22nd May) that the bird flu strain H5N1 had once again, for a second time, jumped from cattle in America to a human – prompting fears of subsequent human-to-human infection, with possible critical consequences.
Instances of the avian influenza were first recognized in US cattle in March. Since then, this strain has mainly spread from cow-to-cow and scientists have discovered very high levels of virus in raw milk (pasteurized milk is safe, having shown viral RNA but not infectious virus). To-date two people, however, are known to have contracted the bird flu virus. Both patients – US farmers – only reported eye symptoms and with treatment they made a full recovery.
Following tests on the first human instance, it was seen that the strain had mutated to be better adapted to mammalian cells, but as long as that human didn’t pass it onto another person it likely stopped the spread at that point.
With the second case, the CDC has released a statement to say it has been monitoring influenza surveillance systems intently, especially in impacted states. “There has been no sign of unusual influenza activity in people, including in syndromic surveillance,” they report.
The concern now, though, is that if H5N1 continues to be given the environment in which to mutate (such as in close quarter cattle farms) – and this continues long enough – it has the potential to find a combination that will easily spread to humans.
The results of this new research, carried out by a team at the University of Georgia, USA, suggests vaccines still remain our “primary defense” against potential spread of avian influenzas such as the H5N1 and others assessed.
“The H5N1, H7N9, and H9N2 subtypes of avian influenza virus pose a dual threat, not only causing significant economic losses to the global poultry industry but also presenting a pressing public health concern due to documented spillover events and human cases,” explains lead author Flavio Cargnin Faccin, who alongside his mentor Dr. Daniel Perez of the University of Georgia, USA, analyzed the current landscape of research into human vaccines for these bird flus.
“This deep delve into the landscape of avian influenza vaccines for humans shows vaccination remains the primary defense against the spread of these viruses.”
The team examined studies of vaccines tested in mice, ferrets, non-human primates, and clinical trials of bird flu vaccines in humans, and assessed both established platforms and promising new directions.
The review carried out suggests inactivated vaccines are a safe and affordable option that primarily activate humoral immunity – the part of our immune system that produces antibodies.
Live attenuated influenza vaccines (LAIVs) are known to induce a wider immune response than inactivated vaccines, activating not only antibody production but also mucosal and cellular defenses. In this review, the authors suggest this broader response may offer greater protection, though, the authors suggest further research is needed to fully understand and harness its potential benefits for both human and agricultural applications.
The review also examined alternatives, such as virus-like particle (VLP) vaccines and messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines, that have emerged more recently. Although VLP vaccines for bird flu have limited clinical trial data in humans, results from studies in mice and ferrets showed promise, the authors found. mRNA vaccines against H5N1 and H7N9 bird flu subtypes also generated a rapid and strong immune response in mice and ferrets, and, while data in humans is scarce, results from a phase 1 study of an H7N9 mRNA vaccine in healthy humans were “encouraging”.
Overall, the team suggests “exploring and employing a diverse range of vaccine platforms”, will be “crucial for enhancing pandemic preparedness and mitigating the threat of avian influenza viruses”.
END
Bird flu: diverse range of vaccines platforms “crucial” for enhancing human pandemic preparedness
New study launches following the discovery of a second case of avian influenza spreading from cows to humans
2024-05-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Marine Protected Areas don’t line up with core habitats of rare migratory fish, finds new research
2024-05-29
62% of Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) designated to protect rare migratory fish species are outside of their core habitats, according to a new modelling study. The findings are published in the British Ecological Society’s Journal of Applied Ecology.
A team of researchers in France from the “Pole MIAME” that gathers diadromous fish experts from multiple research institutions (OFB, INRAE, Institut Agro and UPPA) have developed a new modelling approach that accurately predicts core and unsuitable habitats of rare and data-poor ...
Ecological designed experiment method based on pragmatism: A case study of Haizhu Wetland Restoration Project in Guangzhou, China
2024-05-29
The advancement of urbanization and globalization has impacted every corner of the Earth, human activities have transformed over one-third of the planet’s ecosystems, including agricultural lands and urban areas. Thus, there is an urgent need to define and achieve the equilibrium of novel ecosystems.
This study employed pragmatic designed experiments as its core method, integrating methodologies from empiricism, positivism, and romanticism to propose a semi-empirical ecological design framework that emphasizes learning by doing and research through practice. ...
Scientists call for using consumption-based accounting of carbon emissions to increase fairness
2024-05-29
A new study by Chinese scientists, released on May 29 in Shanghai, has called for the use of consumption-based accounting (“CBA”) emissions in calculating global carbon emissions in order to help make allocating responsibility for reducing emissions just and fair.
The study, “Research Report on Consumption-based Carbon Emissions (2024)” (“the Report”), was jointly completed by scientists from several institutes under the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) as well as from Tsinghua University.
The ...
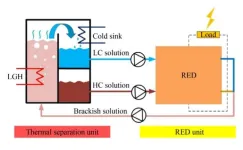
Reverse electrodialysis heat engine with helium-gap diffusion distillation: Energy efficiency analysis
2024-05-29
The depletion of energy resources poses a significant threat to the development of human society. Specifically, a considerable amount of low-grade heat (LGH), typically below 100 °C, is currently being wasted. However, if harnessed effectively, it has the potential to significantly improve overall energy utilization efficiency and subsequently reduce carbon dioxide emissions.
A research group of Junyong Hu from Taiyuan University of Technology has concentrated on developing a new type of reverse electrodialysis ...
Research to uncover the impact of water use in the Colorado River Basin
2024-05-29
The Colorado River is a lifeline for many cities and farms in the Southwest United States. It flows for about 1,448 miles before reaching the Gulf of California in Mexico and supplies water to numerous cities and farms along the way.
However, over the past 60 years, the amount of water in the Colorado River has been shrinking. In fact, in some years, the river’s water has been used up completely before it reaches the gulf.
Landon Marston, assistant professor in civil and environmental engineering, teamed up with researchers from multiple universities and ...
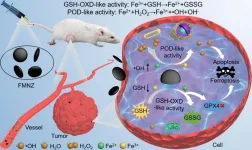
Structural engineering unlocks potent tumor treatment with dual-function magnetite nanozymes
2024-05-29
According to a recent study published in Chemical Engineering Journal, a collaborative research team led by Professor WANG Hui from High Magnetic Field Laboratory, Hefei Institutes of Science of Chinese Academy of Sciences developed magnetite nanozyme (MNZs) with dual enzymatic activities through structural engineering, and proved its structure-dependent behavior in the process of tumor treatment.
MNZs, as a substitute for natural enzymes, has been widely studied in the field of tumor catalytic therapy. However, the catalytic efficiency of traditional MNZs in tumor microenvironment (TME) is often limited, which is mainly due to the low production rate of hydroxyl radical ...
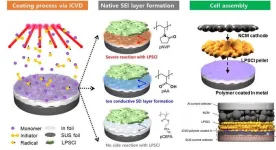
Polymeric films protect anodes from sulfide solid electrolytes!
2024-05-29
People have various relationships in society including those with family, friends, and coworkers. While these relationships play a significant role in our lives, it's crucial to maintain a healthy distance as being too close can lead to intense emotions or conflicts. Interestingly, a recent study in the field of chemistry demonstrates that maintaining such distance can enhance battery performance in electric vehicles.
In this research, Professor Soojin Park, Dr. Sungjin Cho and Youngjin Song, a PhD student, from the Department of Chemistry at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) in collaboration with the team of Professor Sung Gap Im ...
Altering cancer treatment dosing could reduce climate impact, study finds
2024-05-29
May 28, 2024
For more information, contact:
Nicole Fawcett, nfawcett@umich.edu
EMBARGOED for release at 6:30 p.m. ET May 28, 2024
Altering cancer treatment dosing could reduce climate impact, study finds
Model estimates potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by delivering treatment every 6 weeks
ANN ARBOR, Michigan — Changing how often a popular cancer therapy is delivered would reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve environmental impact without decreasing cancer survival, according to a new analysis from researchers at the University of Michigan Health Rogel ...
The secret sex life of coral revealed
2024-05-29
Corals play an essential role in ocean ecosystems, and like many organisms, they are under threat from climate change and other human activities. To better protect coral, it’s first necessary to understand them, in particular their reproductive life cycle, which only happens once a year. For the first time, researchers have produced a model for coral spawning, based on various environmental factors. They achieved this by tapping an often overlooked source of aquatic knowledge, an aquarium.
Given their branching shapes or waving tendrils, you would be ...
New deep learning model is ‘game changer’ for measuring embryo development
2024-05-29
Research led by the University of Plymouth has shown that a new deep learning AI model can identify what happens and when during embryonic development, from video.
Published today (Wednesday 29 May) in the Journal of Experimental Biology, the study highlights how the model, known as Dev-ResNet, can identify the occurrence of key functional developmental events in pond snails, including heart function, crawling, hatching and even death.
A key innovation in this study is the use of a 3D model that uses changes occurring between frames of the video, and enables the AI to learn from these features, as opposed to the more traditional use of still images.
The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Vision sensing for intelligent driving: technical challenges and innovative solutions
To attempt world record, researchers will use their finding that prep phase is most vital to accurate three-point shooting
AI is homogenizing human expression and thought, computer scientists and psychologists say
Severe COVID-19, flu facilitate lung cancer months or years later, new research shows
Housing displacement, employment disruption, and mental health after the 2023 Maui wildfires
GLP-1 receptor agonist use and survival among patients with type 2 diabetes and brain metastases
Solid but fluid: New materials reconfigure their entire crystal structure in response to humidity
New research reveals how development and sex shape the brain
New discovery may improve kidney disease diagnosis in black patients
What changes happen in the aging brain?
Pew awards fellowships to seven scientists advancing marine conservation
Turning cancer’s protein machinery against itself to boost immunity
Current Pharmaceutical Analysis releases Volume 22, Issue 2 with open access research
Researchers capture thermal fluctuations in polymer segments for the first time
16-year study finds major health burden in single‑ventricle heart
Disposable vapes ban could lead young adults to switch to cigarettes, study finds
Adults with concurrent hearing and vision loss report barriers and challenges in navigating complex, everyday environments
Breast cancer stage at diagnosis differs sharply across rural US regions
Concrete sensor manufacturer Wavelogix receives $500,000 grant from National Science Foundation
California communities’ recovery time between wildfire smoke events is shrinking
Augmented reality job coaching boosts performance by 79% for people with disabilities
Medical debt associated with deferring dental, medical, and mental health care
AAI appoints Anand Balasubramani as Chief Scientific Programs Officer
Prior authorization may hinder access to lifesaving heart failure medications
Scholars propose transparency, credit and accountability as key principles in scientific authorship guidelines
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop DDINet for accurate and scalable drug-drug interaction prediction
IEEE researchers achieve 20x signal boost in cerebral blood flow monitoring with next-generation interferometric diffusing wave spectroscopy
IEEE researchers achieve low-power ultrashort mid-IR pulse compression
Deep-sea natural compound targets cancer cells through a dual mechanism
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
[Press-News.org] Bird flu: diverse range of vaccines platforms “crucial” for enhancing human pandemic preparednessNew study launches following the discovery of a second case of avian influenza spreading from cows to humans