Reverse electrodialysis heat engine with helium-gap diffusion distillation: Energy efficiency analysis
2024-05-29
(Press-News.org)
The depletion of energy resources poses a significant threat to the development of human society. Specifically, a considerable amount of low-grade heat (LGH), typically below 100 °C, is currently being wasted. However, if harnessed effectively, it has the potential to significantly improve overall energy utilization efficiency and subsequently reduce carbon dioxide emissions.
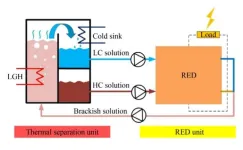
A research group of Junyong Hu from Taiyuan University of Technology has concentrated on developing a new type of reverse electrodialysis heat engine (REDHE). It can efficiently convert LGH into electricity and has emerged as a promising technology in recent years. REDHE incorporates helium-gap diffusion distillation (HGDD) as the thermal separation (TS) unit. The team employed a validated mathematical model to analyze the impact of various operational and structural parameters on the performance of REDHE.
It was found that maintaining a moderate molality of the cold stream, increasing the inlet temperatures of hot and cold streams, lengthening the channels for hot and cold streams, and minimizing the thickness of helium gaps can significantly improve the performance of REDHE. Especially, the REDHE achieved a maximum energy conversion efficiency of 2.96% by reducing the thickness of helium gaps to 3 mm and extending the length of the stream channels to 5 m.
This research is significant as it provides a new technological approach to the effective utilization of low-grade heat energy. The development of the novel REDHE not only helps alleviate energy shortages but also reduces carbon emissions, offering substantial practical application value and environmental benefits for promoting sustainable energy development.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-05-29
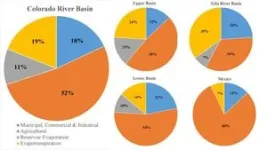
The Colorado River is a lifeline for many cities and farms in the Southwest United States. It flows for about 1,448 miles before reaching the Gulf of California in Mexico and supplies water to numerous cities and farms along the way.
However, over the past 60 years, the amount of water in the Colorado River has been shrinking. In fact, in some years, the river’s water has been used up completely before it reaches the gulf.
Landon Marston, assistant professor in civil and environmental engineering, teamed up with researchers from multiple universities and ...
2024-05-29
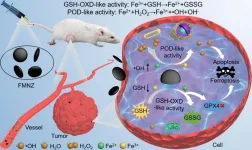
According to a recent study published in Chemical Engineering Journal, a collaborative research team led by Professor WANG Hui from High Magnetic Field Laboratory, Hefei Institutes of Science of Chinese Academy of Sciences developed magnetite nanozyme (MNZs) with dual enzymatic activities through structural engineering, and proved its structure-dependent behavior in the process of tumor treatment.
MNZs, as a substitute for natural enzymes, has been widely studied in the field of tumor catalytic therapy. However, the catalytic efficiency of traditional MNZs in tumor microenvironment (TME) is often limited, which is mainly due to the low production rate of hydroxyl radical ...
2024-05-29
People have various relationships in society including those with family, friends, and coworkers. While these relationships play a significant role in our lives, it's crucial to maintain a healthy distance as being too close can lead to intense emotions or conflicts. Interestingly, a recent study in the field of chemistry demonstrates that maintaining such distance can enhance battery performance in electric vehicles.
In this research, Professor Soojin Park, Dr. Sungjin Cho and Youngjin Song, a PhD student, from the Department of Chemistry at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) in collaboration with the team of Professor Sung Gap Im ...
2024-05-29
May 28, 2024
For more information, contact:
Nicole Fawcett, nfawcett@umich.edu
EMBARGOED for release at 6:30 p.m. ET May 28, 2024
Altering cancer treatment dosing could reduce climate impact, study finds
Model estimates potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by delivering treatment every 6 weeks
ANN ARBOR, Michigan — Changing how often a popular cancer therapy is delivered would reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve environmental impact without decreasing cancer survival, according to a new analysis from researchers at the University of Michigan Health Rogel ...
2024-05-29
Corals play an essential role in ocean ecosystems, and like many organisms, they are under threat from climate change and other human activities. To better protect coral, it’s first necessary to understand them, in particular their reproductive life cycle, which only happens once a year. For the first time, researchers have produced a model for coral spawning, based on various environmental factors. They achieved this by tapping an often overlooked source of aquatic knowledge, an aquarium.
Given their branching shapes or waving tendrils, you would be ...
2024-05-29
Research led by the University of Plymouth has shown that a new deep learning AI model can identify what happens and when during embryonic development, from video.
Published today (Wednesday 29 May) in the Journal of Experimental Biology, the study highlights how the model, known as Dev-ResNet, can identify the occurrence of key functional developmental events in pond snails, including heart function, crawling, hatching and even death.
A key innovation in this study is the use of a 3D model that uses changes occurring between frames of the video, and enables the AI to learn from these features, as opposed to the more traditional use of still images.
The ...
2024-05-29
Primates, including humans, have larger brains than most other mammals, but why? Scientists searching for the answer have long followed a trail pointing to diet—specifically fruit—as the reason for why primates evolved larger brains. A team from the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior and the Smithsonian Institute of Tropical Research tested this idea for the first time—finding that the fruit-diet theory might be out of juice. The researchers used drone imaging, GPS tracking, and fine-scale behavioral analyses to test how four species of fruit-eating mammals solved the same natural foraging puzzle in a Panamanian rainforest. They ...
2024-05-29
A new paper published in The Quarterly Review of Biology examines the question of what Darwinism is and how its nonscientific uses relate to the scientific theory of evolution.
Charles Darwin published On the Origin of Species in 1859 as a work in biology. However, in the past century and a half, Darwin’s ideas have impacted a broad range of domains and stimulated scientists and scholars to advance "evolutionary approaches" in domains as diverse as economics, engineering, psychology, and history. The ideas have been used (and abused) to undermine religiously inspired ideas about the origin of humans and their status concerning other species, ...
2024-05-29
AUSTIN, Texas — Wifi-enabled washing machines. Voice-controlled microwaves. App-enabled TVs, vacuum cleaners, and even window blinds you can control from the comfort of your couch.
Many of the technological features now included in everyday products are useful and accessible. But research has shown that having too many can overwhelm potential buyers, making them less likely to make a purchase.
In new research, Wayne Hoyer, marketing professor and James L. Bayless/William S. Farrish Fund Chair for Free Enterprise at Texas McCombs, digs into the phenomenon of “feature creep” and its impact on consumer sentiment. ...
2024-05-29
A new study by researchers from Arizona State University and their colleagues highlights a dietary strategy for significant health improvement and weight management.
Participants following an intermittent fasting and protein-pacing regimen, which involves evenly spaced protein intake throughout the day, saw better gut health, weight loss and metabolic responses. These benefits were notably greater than those seen with simple calorie restriction.
The findings, reported today in the journal Nature ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Reverse electrodialysis heat engine with helium-gap diffusion distillation: Energy efficiency analysis