(Press-News.org) Pennsylvania has been disproportionately affected by the opioid epidemic, having the fourth highest number of overdose deaths in the country in 2020. Also, the rate of overdose deaths among Black persons is significantly higher than that of white persons in the state. A recent analysis published in Addiction reveals that compared with white people in Pennsylvania, Black individuals are less likely to receive naloxone—a medication that rapidly reverses an opioid overdose.
In the analysis of 2019–2021 data collected from death certificates and the State Unintentional Drug Overdose Reporting System, investigators found that overdose death rates in Pennsylvania were the highest among Black persons in the study population and increased over time (rates per 10,000 population were 4.3 in 2019, 6.1 in 2020, and 6.5 in 2021); rates were lowest among white persons and stayed constant over time (approximately 2.6 per 10,000 population).
Across all years, Black people who died from an overdose had 40–50% lower odds of naloxone administration compared with white people who died. Hispanic decedents had similar odds of naloxone administration to that of white decedents.
“The disparity in overdose rates and differences in naloxone administration emphasize the urgent and continued need for equitable distribution of naloxone and other harm reduction services throughout Pennsylvania, especially among communities of color who are already disproportionately affected by systemic inequalities,” said corresponding author Erin Takemoto, PhD, MPH, of the Pennsylvania Department of Health.
URL upon publication: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/add.16478
Additional Information
NOTE: The information contained in this release is protected by copyright. Please include journal attribution in all coverage. For more information or to obtain a PDF of any study, please contact: Sara Henning-Stout, newsroom@wiley.com.
About the Journal
Addiction publishes peer-reviewed research reports on pharmalogical and behavioural addictions, bringing together research conducted within many different disciplines. The publication is an official journal of the Society for the Study of Addiction, and has been in publication since 1884.
About Wiley
Wiley is a knowledge company and a global leader in research, publishing, and knowledge solutions. Dedicated to the creation and application of knowledge, Wiley serves the world’s researchers, learners, innovators, and leaders, helping them achieve their goals and solve the world's most important challenges. For more than two centuries, Wiley has been delivering on its timeless mission to unlock human potential. Visit us at Wiley.com. Follow us on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn and Instagram.
END
Are there racial inequities in naloxone administration during fatal overdoses?
2024-05-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Does recreational marijuana legalization affect a state’s college enrollment?
2024-05-29
New research has revealed up to a 9% increase in college freshmen enrollments in US states that have legalized recreational marijuana compared with states without such legalization. The study, which is published in Economic Inquiry, found that the increase was from out-of-state enrollments, with early adopter states and public non-research institutions experiencing the most pronounced increases.
Recreational marijuana legalization did not negatively impact degree completion or graduation rate, and it did not affect ...
Is a train’s risk of derailment affected by its length?
2024-05-29
Longer freight trains are more likely to derail compared with shorter trains, according to new research published in Risk Analysis. The increased risk held even after accounting for the need for fewer trains if more cars were on each train.
For the study, investigators assessed information on US freight train accidents between 2013–2022 from Federal Railroad Administration databases. The team found that running 100-car trains would lead to an 11% higher risk of derailment compared with running 50-car trains, even when accounting for the fact that only half as many 100-car trains would need to run. For 200-car trains, the risk was 24% higher than ...
To what extent are pharmaceutical and illicit drugs contaminating city rivers?
2024-05-29
In research published in Environmental Toxicology & Chemistry, investigators sampled water from 19 locations across the Hudson and East Rivers in 2021 and 2022 to identify and quantify the prescribed pharmaceuticals and drugs of abuse that are making their way into New York City’s rivers and to determine the source of these pollutants.
Metoprolol and atenolol (blood pressure medications), benzoylecgonine (the main metabolite of cocaine), methamphetamine (a stimulant), and methadone (an opioid) were the most prevalent drugs, ...
Solving the problems of proton-conducting perovskites for next-generation fuel cells
2024-05-29
As a newly developed perovskite with a large amount of intrinsic oxygen vacancies, BaSc0.8W0.2O2.8 achieves high proton conduction at low and intermediate temperatures, report scientists at Tokyo Tech. By the donor doping of large W6+, this material can take up more water to increase its proton concentration, as well as reduce the proton trapping through electrostatic repulsion between the dopant and proton. These findings could pave the way to the rational design of novel perovskites for protonic ceramic fuel cells (PCFCs) and electrolysis cells (PCECs).
In line with global efforts towards cleaner energy technologies, fuel cells may soon become an indispensable ...
Bird flu: diverse range of vaccines platforms “crucial” for enhancing human pandemic preparedness
2024-05-29
Vaccination remains the most effective strategy for avian influenza prevention and control in humans, despite varying vaccine efficacy across strains.
That’s according to the authors of a new review which delves into existing research into bird flu vaccines for humans.
Published in the peer-reviewed journal Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics, the results of the paper are particularly timely following news last week (Wednesday 22nd May) that the bird flu strain H5N1 had once again, for a second time, jumped from cattle in America to a human – prompting fears of subsequent human-to-human infection, with possible critical consequences.
Instances ...
Marine Protected Areas don’t line up with core habitats of rare migratory fish, finds new research
2024-05-29
62% of Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) designated to protect rare migratory fish species are outside of their core habitats, according to a new modelling study. The findings are published in the British Ecological Society’s Journal of Applied Ecology.
A team of researchers in France from the “Pole MIAME” that gathers diadromous fish experts from multiple research institutions (OFB, INRAE, Institut Agro and UPPA) have developed a new modelling approach that accurately predicts core and unsuitable habitats of rare and data-poor ...
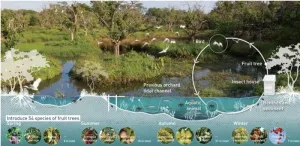
Ecological designed experiment method based on pragmatism: A case study of Haizhu Wetland Restoration Project in Guangzhou, China
2024-05-29
The advancement of urbanization and globalization has impacted every corner of the Earth, human activities have transformed over one-third of the planet’s ecosystems, including agricultural lands and urban areas. Thus, there is an urgent need to define and achieve the equilibrium of novel ecosystems.
This study employed pragmatic designed experiments as its core method, integrating methodologies from empiricism, positivism, and romanticism to propose a semi-empirical ecological design framework that emphasizes learning by doing and research through practice. ...
Scientists call for using consumption-based accounting of carbon emissions to increase fairness
2024-05-29
A new study by Chinese scientists, released on May 29 in Shanghai, has called for the use of consumption-based accounting (“CBA”) emissions in calculating global carbon emissions in order to help make allocating responsibility for reducing emissions just and fair.
The study, “Research Report on Consumption-based Carbon Emissions (2024)” (“the Report”), was jointly completed by scientists from several institutes under the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) as well as from Tsinghua University.
The ...
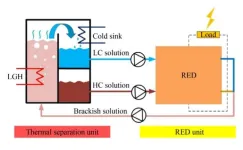
Reverse electrodialysis heat engine with helium-gap diffusion distillation: Energy efficiency analysis
2024-05-29
The depletion of energy resources poses a significant threat to the development of human society. Specifically, a considerable amount of low-grade heat (LGH), typically below 100 °C, is currently being wasted. However, if harnessed effectively, it has the potential to significantly improve overall energy utilization efficiency and subsequently reduce carbon dioxide emissions.
A research group of Junyong Hu from Taiyuan University of Technology has concentrated on developing a new type of reverse electrodialysis ...
Research to uncover the impact of water use in the Colorado River Basin
2024-05-29
The Colorado River is a lifeline for many cities and farms in the Southwest United States. It flows for about 1,448 miles before reaching the Gulf of California in Mexico and supplies water to numerous cities and farms along the way.
However, over the past 60 years, the amount of water in the Colorado River has been shrinking. In fact, in some years, the river’s water has been used up completely before it reaches the gulf.
Landon Marston, assistant professor in civil and environmental engineering, teamed up with researchers from multiple universities and ...