(Press-News.org) (Toronto, May 28, 2024) A new study in JMIR Cardio, published by JMIR Publications, shows that a fully digital, artificial intelligence (AI)–driven lifestyle coaching program can effectively reduce blood pressure (BP) in adults with hypertension. This AI-based program leverages data from wearable activity trackers and BP monitors as well as a mobile app questionnaire to tailor lifestyle guidance. The research team, led by Jared Leitner of the University of California, San Diego, used this innovative intervention to help manage hypertension and enhance patient engagement, offering a promising alternative to traditional coaching models.
The researchers employed a single-arm nonrandomized trial to evaluate the effects of the program’s personalized lifestyle guidance, which was delivered to 141 participants through SMS text messages and a mobile app. Over 24 weeks, participants with stage 2 hypertension showed significant reductions in both systolic and diastolic BP. At 12 weeks, systolic BP decreased by an average of 9.6 mm Hg and diastolic BP by 5.7 mm Hg. These reductions were even more pronounced at 24 weeks, with systolic BP dropping by 14.2 mm Hg and diastolic BP by 8.1 mm Hg.
This precision coaching program led to an increase in participants achieving BP control and a decrease in participants with stage 2 hypertension. The study also highlighted high participant engagement and minimal need for manual clinician outreach. This indicates that the AI-driven approach not only enhances BP control but also substantially reduces the workload for health care providers.
“By pinpointing the top lifestyle contributors to patients’ hypertension and providing precise guidance, the AI-powered lifestyle coaching was able to maintain high patient engagement leading to improved patient outcomes. This study demonstrates how an AI-based, autonomous approach to hypertension-related lifestyle coaching can increase scalability and accessibility to effective blood pressure management,” remarked Dr. Leitner.
This research underscores the potential for digital health innovations to transform hypertension management, providing scalable, cost-effective, and personalized care options for patients.
Please cite as:
Leitner J, Chiang PH, Agnihotri P, Dey S.
The Effect of an AI-Based, Autonomous, Digital Health Intervention Using Precise Lifestyle Guidance on Blood Pressure in Adults With Hypertension: Single-Arm Nonrandomized Trial.
JMIR Cardio 2024;8:e51916
URL: https://cardio.jmir.org/2024/1/e51916/
doi: 10.2196/51916
###
About JMIR Publications:
JMIR Publications is a renowned publisher with a long-standing commitment to advancing digital health research and progressing open science. Our portfolio includes a wide array of prestigious open access, peer-reviewed journals dedicated to the dissemination of high-quality research in the field of digital health. JMIR Publications is celebrating its 25th anniversary in 2024 as the leading open access, digital health publisher.
To learn more about JMIR Publications, please visit jmirpublications.com or connect with us via Twitter, LinkedIn, YouTube, Facebook, and Instagram.
Head office: 130 Queens Quay East, Unit 1100, Toronto, ON, M5A 0P6 Canada
Media contact: communications@jmir.org
The content of this communication is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work, published by JMIR Publications, is properly cited.
END
A team of researchers at the University of Waterloo have developed a new machine-learning method that detects hate speech on social media platforms with 88 per cent accuracy, saving employees from hundreds of hours of emotionally damaging work.
The method, dubbed the Multi-Modal Discussion Transformer (mDT), can understand the relationship between text and images as well as put comments in greater context, unlike previous hate speech detection methods. This is particularly helpful in reducing false positives, which are often ...
A new method of drug delivery using proline, an amino acid found in chicken feathers and skin tissue, could be used to limit the side effects of chemotherapy and repair important enzymes, new research suggests.
Published in the journal Chem today, researchers have designed a cage (a box made of single molecules) from biologically compatible peptides, short amino acids that form the basis of proteins. These cages can house drugs of different sizes and transport them in the body with high levels of precision.
The negative ...
It’s every driver’s nightmare: a pedestrian stepping out in front of the car seemingly out of nowhere, leaving only a fraction of a second to brake or steer the wheel and avoid the worst. Some cars now have camera systems that can alert the driver or activate emergency braking. But these systems are not yet fast or reliable enough, and they will need to improve dramatically if they are to be used in autonomous vehicles where there is no human behind the wheel.
Quicker detection using less computational ...
Graphene has been called “the wonder material of the 21st century.” Since its discovery in 2004, the material—a single layer of carbon atoms—has been touted for its host of unique properties, which include ultra-high electrical conductivity and remarkable tensile strength. It has the potential to transform electronics, energy storage, sensors, biomedical devices, and more. But graphene has had a dirty little secret: it's dirty.
Now, engineers at Columbia University and colleagues at the University of Montreal and the National Institute of Standards and Technology are poised to clean things up with an oxygen-free chemical vapor ...
In a study of Medicare beneficiaries, researchers from Brigham and Women’s Hospital found that one year after hospitalization for heart failure, 6 percent of patients had progressed to dialysis.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Study led by Brigham researchers found that among older adults hospitalized for heart failure, nearly 3 in 4 were discharged with reduced kidney function.
Lower kidney function was associated with substantially higher risk of kidney complications and other adverse clinical outcomes among older adults, with more than 1 in 20 progressing to dialysis within one year after heart failure hospitalization.
These findings emphasize the need ...
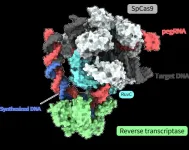
Joint research led by Yutaro Shuto, Ryoya Nakagawa, and Osamu Nureki of the University of Tokyo determined the spatial structure of various processes of a novel gene-editing tool called “prime editor.” Functional analysis based on these structures also revealed how a “prime editor” could achieve reverse transcription, synthesizing DNA from RNA, without “cutting” both strands of the double helix. Clarifying these molecular mechanisms contributes greatly to designing gene-editing tools accurate enough for gene therapy treatments. The findings were published in the journal Nature.
The ...
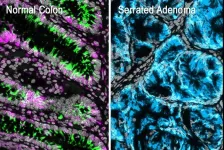
Research led by Weill Cornell Medicine provides new evidence that most colorectal cancers begin with the loss of intestinal stem cells, even before cancer-causing genetic alterations appear. The results, published on May 29 in Developmental Cell, overturn the prevailing theory for colorectal tumor initiation and suggest new ways to diagnose the disease before it has a chance to become established.
“Colorectal cancer is very, very heterogeneous, which has made it difficult for many years to classify these tumors in order to inform therapy,” said senior author Dr. ...
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions have discovered that a protein called hnRNPM helps protect the integrity of the process cells use to make proteins. hnRNPM works by preventing the cell from making mistakes while it is putting together the different components leading to newly produced proteins. In cancer cells, loss of hnRNPM triggers an interferon immune response, suggesting that this protein may hold clinical promise. The findings appeared in Molecular Cell.
“Synthesizing a protein is like putting together the different parts of a machine. If during the assembly process parts that do not belong are incorporated ...
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – When a child peruses YouTube, the content recommended to them is not always age appropriate, a new study suggests.
Researchers mimicked search behaviors of children using popular search terms, such as memes, Minecraft and Fortnite, and captured video thumbnails recommended at the end of each video.
Among the 2,880 thumbnails analyzed, many contained problematic click bait, such as violence or frightening images, according to the Michigan Medicine led research in JAMA Network Open.
“Children spend a significant amount of time on free video sharing platforms that ...
CAMBRIDGE, MA — Quantum computers hold the promise of being able to quickly solve extremely complex problems that might take the world’s most powerful supercomputer decades to crack.
But achieving that performance involves building a system with millions of interconnected building blocks called qubits. Making and controlling so many qubits in a hardware architecture is an enormous challenge that scientists around the world are striving to meet.
Toward this goal, researchers at MIT and MITRE have demonstrated a scalable, modular hardware platform that ...