Visible light-induced photocatalysis–self-Fenton degradation of P-Clphoh over graphitic carbon nitride by a polyethylenimine bifunctional catalyst
2024-05-30
(Press-News.org)
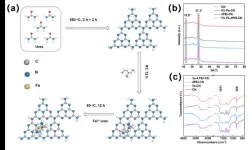
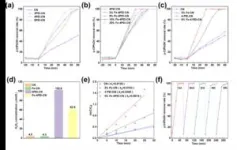
The deep degradation of organic pollutants through solar light-coupled photocatalysis and the Fenton reaction (Photo-Fenton) holds significant importance in the field of water purification. In this study, a novel bifunctional catalyst (Fe-PEI-CN) was synthesized by electrostatic self-assembly and hydrothermal methods, doping graphene-like carbon nitride (CN) with polyethyleneimine (PEI) and iron (Fe) species. This catalyst efficiently degraded p-chlorophenol (p-ClPhOH) by generating hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) during the photocatalytic process. The relationship between catalytic efficiency and structure was explored using various characterization techniques.Under visible light irradiation, the prepared Fe-PEI-CN firstly generated H2O2 via photocatalysis and subsequently degraded the produced p-ClPhOH through the Fenton reaction, wherein Fe ions activated H2O2 to generate ·OH radicals. Due to the modification by PEI and Fe, the light absorption and excitation capabilities of CN were significantly enhanced, while the rate of photogenerated electron-hole recombination was suppressed, thereby greatly improving the photocatalytic activity. Moreover, the photocatalytic reaction also facilitated the in-situ generation of H2O2 and promoted the reduction of Fe3+ to Fe2+, further enhancing the efficiency of the Fenton reaction. The research results demonstrate that this photo-Fenton reaction exhibits highly efficient degradation of p-ClPhOH, with a maximum H2O2 production rate of 102.6 µmol/L, which is 22 times higher than that of pristine CN. The combined two-step oxidation process of photocatalytic oxidation and Fenton oxidation shows remarkable effectiveness in degrading p-ClPhOH, indicating broad application prospects in the treatment of recalcitrant organic wastewater.This study not only reveals the superior performance of Fe-PEI-CN but also provides new insights and methods for exploring the application of novel photocatalysts in environmental governance. In the future, further optimization of catalyst synthesis methods and reaction conditions may further enhance their application effectiveness in actual water treatment processes, making a greater contribution to solving water pollution problems.
See the article:
Visible Light-Induced Photocatalysis–Self-Fenton Degradation of P-Clphoh over Graphitic Carbon Nitride by a Polyethylenimine Bifunctional Catalyst
https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-024-00386-1
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-05-30
Tumour protein P53 (TP53) plays an important role in suppressing the growth of tumours. Mutations in the gene for TP53 can have a disastrous effect, hampering the body's ability to fight tumours and even encouraging their growth. Because these are the most common mutations in cancers, TP53 has long been an interesting therapeutic target. However, efforts to destroy the mutant protein have been hampered by the difficulty of finding a way to bind to it.
Now, a team of researchers from Xi'an ...
2024-05-30
New Curtin University research reveals taking pictures of food isn’t just content for our social media feeds, but could be the key to improving people’s diets.
Published in the prestigious American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, the feeding study saw researchers measure the weight of meals, which were then provided to participants over a day for breakfast, lunch and dinner.
Participants compared different technology-assisted methods to recall what they had eaten over the past 24 hours.
One method asked participants to take photos of their meals using the mobile Food Record app.
These ...
2024-05-30
On-site pathology tests for infectious diseases in rural and remote locations can be just as reliable and accurate as tests carried out in a hospital laboratory, a new report from Flinders University shows.
Flinders University researchers tested the quality of on-site pathology testing, or Point-of-Care-Testing (POCT), for molecular-based, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) detection in over 100 remote Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities across Australia.
“Our study demonstrates that when point-of-care testing models are effectively established and managed, the quality of pathology results can be equivalent to ...
2024-05-30
Carolyn C. Meltzer, MD, dean of the Keck School of Medicine of USC, has been appointed to the board overseeing the California Institute of Regenerative Medicine (CIRM). CIRM is the voter-created agency that funds stem cell research throughout the state.
“Stem cell research holds the tremendous promise to unlock health solutions that patients need,” said Steven D. Shapiro, MD, USC’s senior vice president for health affairs. “The CIRM board—and the people of our state—will benefit greatly from Meltzer’s wide-ranging leadership experience and place at the ...
2024-05-30
Antibiotics prevent snails from forming new memories by disrupting their gut microbiome - the community of beneficial bacteria found in their guts.
The new research, led by the University of East Anglia (UEA) in collaboration with Aberystwyth University, highlights the damaging effects that human pollution could be having on aquatic wildlife.
In the study, pond snails were given a favourite food – carrot juice – but had to quickly learn and remember that it was no longer safe to eat.
Snails ...
2024-05-30
STARKVILLE, Miss.— A Mississippi State faculty member’s work on symbiosis—a mutually beneficial relationship between living organisms—is pushing back against the newer theory of a “single-origin” of root nodule symbiosis (RNS)—that all symbiosis between plant root nodules and nitrogen-fixing bacteria stems from one point—instead suggesting a “multiple-origin” theory of symbiosis which opens a better understanding for genetically engineering crops.
Ryan A. Folk, an assistant professor in the MSU Department of Biological Sciences and herbarium curator, is an author on a paper published this month in Nature ...
2024-05-30
Shortly after artificial intelligence models including Midjourney and OpenAI’s Dall-E went public, AI-generated art started winning competitions: one in digital art, another in photography. Concern rumbled that AI could replace artists — and even, by some metrics, be more creative than humans. But simultaneously, people were exploring these tools as ways to augment their creative processes, not replace them.
University of Washington researchers grew curious about how AI might affect creativity in children, specifically, so they worked with a group of 12 Seattle-area kids ages seven to 13 to explore how the kids’ creative processes interacted ...
2024-05-30
Moisés A. Bernal, assistant professor in the Department of Biological Sciences at Auburn University, is collaborating with researchers Kathleen Lotterhos (Northeast University), Megan Phifer-Rixey (Drexel University), and Torrance Hanley, (Sacred Heart University) to evaluate the effectiveness of virtual lab meetings in demystifying the hidden curriculum in academia, incentivize primary research among students without previous experience, and foster participation of underrepresented groups in STEM.
The “Biological Practices” article entitled A virtual lab meeting training program mutually benefits mentees and host labs was recently published ...
2024-05-30
May 29, 2024
Boosters that target the omicron subvariants of SARS-CoV-2 are still providing reasonably durable protection against infection, hospitalization and death from COVID-19, according to new data from a study led by researchers at the UNC Gillings School of Global Public Health.
Published today in the New England Journal of Medicine, the study found that COVID-19 boosters targeting the XBB.1.5 subvariants were most effective one month after receiving one. After four weeks, the vaccines were 52.2% effective at preventing infection and 66.8% effective at preventing hospitalization.
The vaccines were also highly effective ...
2024-05-29
STARKVILLE, Miss.—A Mississippi State faculty member’s work on plant life symbiosis—a mutually beneficial relationship between living organisms—is pushing back against the newer theory of “single-origin”—that all life stems from one point—instead suggesting “multiple-origin” theory which opens a better understanding for genetically engineering crops.
Ryan A. Folk, an assistant professor in the MSU Department of Biological Sciences and herbarium curator, is an author on a paper published this month in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Visible light-induced photocatalysis–self-Fenton degradation of P-Clphoh over graphitic carbon nitride by a polyethylenimine bifunctional catalyst