(Press-News.org) New findings on long COVID — long-term effects on health experienced by many who have had COVID-19 — present a good-news, bad-news situation, according to a study at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and the Veterans Affairs St. Louis Health Care system.
The bad news: COVID-19 patients who were hospitalized within the first 30 days after infection face a 29% higher risk of death in the third year compared with people who have not had the virus. However, the three-year death risk still marks a significant decline compared with such risk at the one- and two-year marks post-infection. The findings also show that even people with mild COVID-19 were still experiencing new health problems related to the infection three years later.
The good news: The increased risk of death diminishes significantly one year after a SARS-CoV-2 infection among people who were not hospitalized for the virus. This demographic accounts for most people who have had COVID-19.
The new research, published May 30 in Nature Medicine, tracked the virus’s health effects in people three years after being infected with the original strain of COVID-19 in 2020. That year, about 20 million people tested positive for the virus in the U.S. The new study assessed the risk of death and 80 adverse health conditions in people three years after being diagnosed with COVID-19.
“We aren’t sure why the virus’s effects linger for so long,” said senior author Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, a Washington University clinical epidemiologist and a global leader in long COVID research. “Possibly it has to do with viral persistence, chronic inflammation, immune dysfunction or all the above. We tend to think of infections as mostly short-term illnesses with health effects that manifest around the time of infection. Our data challenges this notion. I feel COVID-19 continues to teach us — and this is an important new lesson — that a brief, seemingly innocuous or benign encounter with the virus can still lead to health problems years later.”
Up to 10% of people infected with the virus experience long COVID, according to federal data.
Al-Aly’s prior research has documented COVID-19’s damage to nearly every human organ, contributing to diseases and conditions affecting the lungs, heart, brain, and the body’s blood, musculoskeletal and gastrointestinal (GI) systems.
Such studies with longer follow-up are limited, said Al-Aly, a nephrologist who treats patients at the Washington University-affiliated John J. Cochran Veterans Hospital in midtown St. Louis. “Addressing this knowledge gap is critical to enhance our understanding of long COVID and will help inform care for people suffering from long COVID.”
Al-Aly and his team analyzed millions of de-identified medical records in a database maintained by the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, the nation’s largest integrated health-care system. The study included more than 114,000 veterans with mild COVID-19 who did not require hospitalization; more than 20,000 hospitalized COVID-19 patients; and 5.2 million veterans with no COVID-19 diagnosis. Patients were enrolled in the study from March 1, 2020, to Dec. 31, 2020, and followed for at least three years, until Dec. 31, 2023. Patients included people of diverse ages, races and sexes; statistical modeling ensured parity in representation.
In the third year after infection, COVID-19 patients who had been hospitalized experienced a 34% elevated health risk across all organ systems compared with people who did not have COVID. That number is down from a 182% increased risk one year after a COVID infection and a 57% risk two years after.
Among nonhospitalized patients, researchers found a 5% increased risk in suffering from long COVID in the third year after infection. This translates into 41 more health problems per 1,000 persons – a small but not trivial burden. The long-term health effects in the third year primarily affected the GI, pulmonary and neurological systems. By comparison, the risk was increased by 23% one year after infection and increased by 16% two years after.
In the analysis, researchers also measured and compared the number of healthy life-years lost due to COVID-19. They found that among the nonhospitalized, at three years after infection, COVID-19 had contributed to 10 lost years of healthy life per 1,000 persons. By comparison, three years post-infection, those hospitalized for COVID-19 had experienced 90 lost years of healthy life per 1,000 persons.
For context, in the U.S., heart disease and cancer each cause about 50 lost years of healthy life per 1,000 persons, while stroke contributes to 10 lost years of healthy life per 1,000 persons.
“That a mild SARS-CoV-2 infection can lead to new health problems three years down the road is a sobering finding,” said Al-Aly, who is also director of the Clinical Epidemiology Center at the VA St. Louis Health Care System, and head of the research and development service. “The problem is even worse for people with severe SARS-CoV-2 infection. It is very concerning that the burden of disease among hospitalized individuals is astronomically higher.”
“COVID-19 is a serious threat to the long-term health and well-being of people and it should not be trivialized,” he said.
The extended trajectory for long COVID may change as researchers incorporate data from years beyond 2020. At that time, vaccines and antivirals had not been developed. Similarly, Al-Aly’s analysis does not consider subsequent variants such as omicron or delta.
“Even three years out, you might have forgotten about COVID-19, but COVID hasn’t forgotten about you,” Al-Aly said. “People might think they’re out of the woods, because they had the virus and did not experience health problems. But three years after infection, the virus could still be wreaking havoc and causing disease or illness in the gut, lungs or brain.”
END
Risk of death from COVID-19 lessens, but infection still can cause issues 3 years later
Study also shows that patients hospitalized within 30 days after infection face 29% higher death risk in 3rd year compared with those not infected
2024-05-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
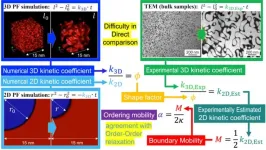
Combining simulations and experiments to get the best out of Fe3Al
2024-05-30
Osaka, Japan – The compound of iron and aluminum with the chemical formula Fe3Al has some very useful mechanical properties. A team from Osaka University has combined simulations with experimental techniques to better understand the kinetics of the formation of microstructures to enhance and utilize these properties and how to harness them for specific applications.
In a study recently published in Acta Materialia, the researchers took an in-depth look at the way the microstructure of Fe3Al develops because the ordered domains that form contribute to one of its key properties: superelasticity.
When high loads are applied to superelastic materials they ...
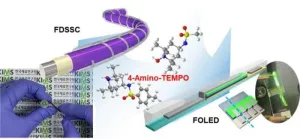
Both high performance and stability were achieved with multifunctional materials!
2024-05-30
Through joint research with Professor Chul-jin Ahn’s team at Changwon National University, the research team of Dr. Jae-Ho Kim and Dr. Myung-kwan Song from the Department of Energy & Electronic Materials in the Surface & Nano Materials Division has developed a 4-Amino-TEMPO derivative with photocatalytic properties and successfully used it to produce high-performance and stable fiber-shaped dye-sensitized solar cells (FDSSCs) and fiber-shaped organic light-emitting diodes (FOLEDs). The developed 4-Amino-TEMPO derivative has the characteristic of simultaneously improving the performance of both fiber-shaped dye-sensitized solar cells (FDSSCs) and fiber-shaped ...
Structural inequities amplify homelessness challenges for pregnant people in Washington DC
2024-05-30
WASHINGTON -- New research conducted with Washington, DC, residents who experienced homelessness during pregnancy sheds light on the intersection of homelessness, pregnancy, and racial inequities. The findings underscore the urgent need for policy and practice changes to support vulnerable populations.
The study, published May 30, 2024 in the journal Health Equity (DOI: 10.1089/heq.2023.0235), is grounded in a reproductive justice framework and delves into the lived experiences of 20 DC residents who faced homelessness while pregnant.
Homelessness ...
University of Maryland study shows N95 masks near-perfect at blocking escape of airborne COVID-19
2024-05-30
COLLEGE PARK, Md. – In a head-to-head comparison of masks worn by people with active
COVID-19, the inexpensive “duckbill” N95 came out on top, stopping 98% of COVID-19 particles
in the breath of infected people from escaping into the air. Led by researchers from the University
of Maryland School of Public Health (SPH), results showed other masks also performed well,
blocking at least 70% of viral particles from escaping from the source – an infected person’s
exhaled breath.
The study, Relative efficacy of masks and respirators as source control for viral aerosol shedding
from people infected with SARS-CoV-2, published May 29 in eBioMedicine, a Lancet ...
The AI paradox: Building creativity to protect against AI
2024-05-30
Cultivating creativity in schools is vital for a future driven by artificial intelligence (AI). But while teachers embrace creativity as an essential 21st century skill, a lack of valid and reliable creativity tests means schools struggle to assess student achievement.
Now, a new machine-learning model developed by the University of South Australia is providing teachers with access to high-quality, fit-for-purpose creativity tests, that can score assessments in a fraction of the time and a fraction of the cost.
Applied to the current ...
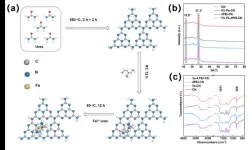
Visible light-induced photocatalysis–self-Fenton degradation of P-Clphoh over graphitic carbon nitride by a polyethylenimine bifunctional catalyst
2024-05-30
The deep degradation of organic pollutants through solar light-coupled photocatalysis and the Fenton reaction (Photo-Fenton) holds significant importance in the field of water purification. In this study, a novel bifunctional catalyst (Fe-PEI-CN) was synthesized by electrostatic self-assembly and hydrothermal methods, doping graphene-like carbon nitride (CN) with polyethyleneimine (PEI) and iron (Fe) species. This catalyst efficiently degraded p-chlorophenol (p-ClPhOH) by generating hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) during the photocatalytic process. The relationship between catalytic efficiency and structure was explored using various characterization techniques.Under ...
Engineered DNA 'warhead' targets a common cancer mutation
2024-05-30
Tumour protein P53 (TP53) plays an important role in suppressing the growth of tumours. Mutations in the gene for TP53 can have a disastrous effect, hampering the body's ability to fight tumours and even encouraging their growth. Because these are the most common mutations in cancers, TP53 has long been an interesting therapeutic target. However, efforts to destroy the mutant protein have been hampered by the difficulty of finding a way to bind to it.
Now, a team of researchers from Xi'an ...
Picture this: Snapping photos of our food could be good for us
2024-05-30
New Curtin University research reveals taking pictures of food isn’t just content for our social media feeds, but could be the key to improving people’s diets.
Published in the prestigious American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, the feeding study saw researchers measure the weight of meals, which were then provided to participants over a day for breakfast, lunch and dinner.
Participants compared different technology-assisted methods to recall what they had eaten over the past 24 hours.
One method asked participants to take photos of their meals using the mobile Food Record app.
These ...
Portable pathology passes the test
2024-05-30
On-site pathology tests for infectious diseases in rural and remote locations can be just as reliable and accurate as tests carried out in a hospital laboratory, a new report from Flinders University shows.
Flinders University researchers tested the quality of on-site pathology testing, or Point-of-Care-Testing (POCT), for molecular-based, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) detection in over 100 remote Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities across Australia.
“Our study demonstrates that when point-of-care testing models are effectively established and managed, the quality of pathology results can be equivalent to ...
USC medical school dean appointed to CIRM board
2024-05-30
Carolyn C. Meltzer, MD, dean of the Keck School of Medicine of USC, has been appointed to the board overseeing the California Institute of Regenerative Medicine (CIRM). CIRM is the voter-created agency that funds stem cell research throughout the state.
“Stem cell research holds the tremendous promise to unlock health solutions that patients need,” said Steven D. Shapiro, MD, USC’s senior vice president for health affairs. “The CIRM board—and the people of our state—will benefit greatly from Meltzer’s wide-ranging leadership experience and place at the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
[Press-News.org] Risk of death from COVID-19 lessens, but infection still can cause issues 3 years laterStudy also shows that patients hospitalized within 30 days after infection face 29% higher death risk in 3rd year compared with those not infected