(Press-News.org) BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – RNA transcription is the genomic process in which a cell produces a duplicate of a gene’s DNA sequence.
In a study published in Nucleic Acids Research, University of Alabama at Birmingham Department of Chemistry Professor Jun Zhang, Ph.D., and his team reveal how the protein SRSF1 possesses the novel function of binding and unfolding complex RNA Guanine-quadruplexes.
Present in both DNA and RNA sequences, a G-quadruplex (GQ) is a structure of four guanine bases attached in a planar array. These arrays, known as G-tetrad, are connected via Hoogsteen base pairings. It is commonly seen that three or more layers of G-tetrads are what make up a GQ structure.
In a normally functioning cell, most GQs are eventually unwound, so that the information encoded by the RNA can be used for protein expression. GQs are used commonly to regulate the protein expression level. However, due to the extreme stability of their structures, GQs are relatively difficult to unwind once formed in cells.
For example, if the GQ is not unwound, the ribosome cannot pass through, and the needed protein cannot be produced. This regulating function is important because, if the protein functions to suppress cancer cells, then an inability to unwind a GQ sequence can result in the replication of cancerous and malicious cells.
“This is important because understanding how we can easily open GQ structures could provide another avenue into the future of treatment options for certain illnesses,” Zhang said. “There are previously no other external tools that we can easily use to open these structures in the cell.”
Zhang and his team researched into the Ser/Arg-rich, or SR, protein family.
There are 12 members of the SR protein family. This family of RNA-binding proteins is most known for RNA splicing. SRSF1 oversees the splicing of over 1,500 different messenger RNA transcripts.
“The misfunction of splicing can result in the development of different illnesses such as cancer,” Zhang said. “Around 60 percent of diseases can actually be attributed to the misfunction of splicing.”
Each member of the SR protein family consists of one or two N-terminal RNA recognition motifs, or RRMs, and a phosphorylatable C-terminal protein region rich in repetitive Arg/Ser dipeptides, or RS.
Zhang’s lab is the first to successfully solubilize full-length SRSF1 in its native state. Zhang’s team used this to explore the RNA-binding landscape of SRSF1. In doing so successfully, Zhang’s team found that SRSF1 RS prefers purine over pyrimidine.
In using the fluorescence resonance energy transfer, or FRET, between fluorescent chemicals Cy3 and Cy5, Zhang and his team were able to view the significant Cy5 signal decrease upon the adding of SRSF1. This decrease signifies a cooperative binding of SRSF1 to ARPC2 GQ and unfolding of the ARPC2 GQ.
“Our findings are just a beginning to understanding the broader roles SR proteins play in RNA splicing and translation,” Zhang said. “Understanding these properties is important because it helps us to better understand how protein expression is regulated inside the cell.”
Co-authors and researchers on this study include postdoctoral student Naiduwadura Ivon Upekala De Silva, undergraduate student Nathan Lehman, and graduate students Talia Fargason, Trenton Paul and Zihan Zhang.
This research was supported by the National Institutes of Health grant R35 awarded to Zhang.
END
UAB researchers uncover protein SRSF1’s uncommon ability to bind and unfold RNA G-quadruplexes
2024-05-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
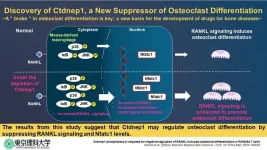
New study reveals key protein that could help prevent excessive bone loss in osteoporosis
2024-05-30
Osteoporosis, a condition characterized by porous and fragile bones, poses a significant threat to skeletal health. As the very framework of the human body, bones provide crucial structural support. When bone mass diminishes, it not only compromises this support but also impairs overall function, leading to a diminished quality of life. With the aging population experiencing a surge in osteoporosis cases, the strain on healthcare resources for long-term care is evident. Hence, there is a need to understand the mechanisms that contribute to osteoporosis and develop effective targeted therapies ...
Testosterone therapy: A safe and effective gender-affirming hormone therapy for trans men
2024-05-30
Transgender individuals often face unique challenges in aligning their physical bodies with their true gender identity. Among the various methods employed, gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT) stands as a vital means for transgender men to achieve physical changes in consonance with their gender identity. Navigating the complexities that come with gender transition, transgender individuals seek medical interventions to alleviate gender dysphoria and align their bodies with their gender identity.
For transgender men, testosterone therapy holds promise in inducing masculinizing effects such as increased muscle mass, cessation of ...
Statisticians call for rigour and transparency in the evaluation of diagnostic tests
2024-05-30
Recommendations designed to reframe the evaluation of in vitro diagnostic tests have been published today by the Royal Statistical Society in its Series A journal.
The report, which will be submitted to the UK Covid-19 Inquiry, is intended to help prevent future scenarios in which IVDs are marketed widely, but later attract serious concerns about the standards applied to their evaluation.
The research was prompted by concerns about the standards applied to the evaluation of diagnostic tests during the Covid-19 pandemic – particularly lateral flow tests – however the recommendations cover all new tests, especially those ...
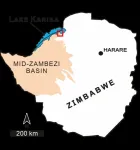
Musankwa sanyatiensis, a new dinosaur from Zimbabwe
2024-05-30
Fossils found on the shoreline of Lake Kariba in Zimbabwe represent a completely new dinosaur species. This remarkable find, named Musankwa sanyatiensis, marks only the fourth dinosaur species named from Zimbabwe. The research detailing this significant discovery is set to be published in the prestigious journal Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. The study was conducted by an international team of scientists from the University of the Witwatersrand (Wits) in South Africa, the Natural History Museum of Zimbabwe, Stony Brook University in New York and was led by Prof Paul Barrett from the Natural History Museum ...
Statin therapy may prevent cancer by blocking inflammatory protein
2024-05-30
BOSTON – A new study led by investigators from Mass General Cancer Center, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, reveals that statins—commonly used cholesterol-lowering drugs—may block a particular pathway involved in the development of cancer that results from chronic inflammation. The findings are published in Nature Communications.
“Chronic inflammation is a major cause of cancer worldwide,” said senior author Shawn Demehri, MD, PhD, a principal investigator at the Center for Cancer Immunology and Cutaneous Biology Research Center of Massachusetts General Hospital and an associate professor of Dermatology at ...
A novel ‘senolytic’ strategy for treating aging-related diseases
2024-05-30
The process of aging is accompanied by a decline in physiological functions, which can lead to cardiovascular, neurodegenerative, and metabolic diseases. Aging of cells, also known as ‘cellular senescence’— is a process in which a cell ages and permanently stops dividing but does not die. The accumulation of such ‘senescent’ cells in tissues is then known to contribute to age-associated diseases. Elimination of senescent cells or ‘senolysis’ can, therefore, serve as an effective therapeutic strategy for the improvement of physiological function and prevention ...
Risk of death from COVID-19 lessens, but infection still can cause issues 3 years later
2024-05-30
New findings on long COVID — long-term effects on health experienced by many who have had COVID-19 — present a good-news, bad-news situation, according to a study at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and the Veterans Affairs St. Louis Health Care system.
The bad news: COVID-19 patients who were hospitalized within the first 30 days after infection face a 29% higher risk of death in the third year compared with people who have not had the virus. However, the three-year death risk still marks a significant decline compared with such risk at the one- and two-year marks post-infection. The findings also show that even people with mild COVID-19 were still ...
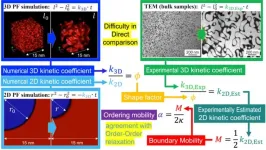
Combining simulations and experiments to get the best out of Fe3Al
2024-05-30
Osaka, Japan – The compound of iron and aluminum with the chemical formula Fe3Al has some very useful mechanical properties. A team from Osaka University has combined simulations with experimental techniques to better understand the kinetics of the formation of microstructures to enhance and utilize these properties and how to harness them for specific applications.
In a study recently published in Acta Materialia, the researchers took an in-depth look at the way the microstructure of Fe3Al develops because the ordered domains that form contribute to one of its key properties: superelasticity.
When high loads are applied to superelastic materials they ...
Both high performance and stability were achieved with multifunctional materials!
2024-05-30
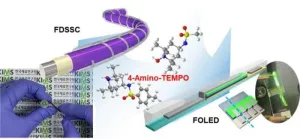
Through joint research with Professor Chul-jin Ahn’s team at Changwon National University, the research team of Dr. Jae-Ho Kim and Dr. Myung-kwan Song from the Department of Energy & Electronic Materials in the Surface & Nano Materials Division has developed a 4-Amino-TEMPO derivative with photocatalytic properties and successfully used it to produce high-performance and stable fiber-shaped dye-sensitized solar cells (FDSSCs) and fiber-shaped organic light-emitting diodes (FOLEDs). The developed 4-Amino-TEMPO derivative has the characteristic of simultaneously improving the performance of both fiber-shaped dye-sensitized solar cells (FDSSCs) and fiber-shaped ...
Structural inequities amplify homelessness challenges for pregnant people in Washington DC
2024-05-30
WASHINGTON -- New research conducted with Washington, DC, residents who experienced homelessness during pregnancy sheds light on the intersection of homelessness, pregnancy, and racial inequities. The findings underscore the urgent need for policy and practice changes to support vulnerable populations.
The study, published May 30, 2024 in the journal Health Equity (DOI: 10.1089/heq.2023.0235), is grounded in a reproductive justice framework and delves into the lived experiences of 20 DC residents who faced homelessness while pregnant.
Homelessness ...