(Press-News.org) Recommendations designed to reframe the evaluation of in vitro diagnostic tests have been published today by the Royal Statistical Society in its Series A journal.
The report, which will be submitted to the UK Covid-19 Inquiry, is intended to help prevent future scenarios in which IVDs are marketed widely, but later attract serious concerns about the standards applied to their evaluation.
The research was prompted by concerns about the standards applied to the evaluation of diagnostic tests during the Covid-19 pandemic – particularly lateral flow tests – however the recommendations cover all new tests, especially those designed to detect infectious diseases.
It is published today in the RSS’s Series A journal and also presented at the Evidence Based Early Diagnosis conference at St Andrews.
A working group of statisticians, co-chaired by Professor Jon Deeks, at the University of Birmingham, and former RSS President, Professor Deborah Ashby, at Imperial College London, collaborated on the report with co-authors from the Universities of Oxford, Cambridge, Edinburgh, Birmingham and the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine.
The RSS Working Group on Diagnostic Tests set out 22 recommendations, designed to ensure that in vitro diagnostic (IVD) tests – which typically test samples of fluids such as blood, urine or saliva – are statistically robust and fit for purpose. The RSS Working Group identified Study-Design matters (10 recommendations); Regulation matters (6 recommendations); Transparency matters (6 recommendations).
Jon Deeks, Professor of Biostatistics at the University of Birmingham, said:
“The Covid-19 pandemic provided a microcosmic insight into inadequacies in current processes to evaluate and regulate diagnostic tests. It’s important that we learn from these failures and establish robust processes that can be applied broadly across diagnostic tests.”
The report covers three areas of diagnostic testing: study-design of evaluations; regulation of tests; and transparency of test evaluations.
Key recommendations included:
Evaluation needs to take into account each specific intended use of the test, including the person being tested, the target condition and even the facilities where the testing will be done. Field or clinical evaluation studies should be carried out for each intended use.
Direct comparison of alternative IVDs and testing strategies should be available to inform clinical and public health decision-making.
The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) should collaborate with independent experts to revise the national licensing process for IVDs. This will ensure public safety is protected. Protocols and reports for test evaluations should be publicly available to ensure transparency in all planning and decision-making.
The publication of the report is relevant for the opening of the ‘Test, Trace and Isolate’ module of the UK Covid-19 Inquiry. It also coincides with the MHRA’s recently-launched consultation on improved safety for high-risk diagnostic devices.
Professor Sheila Bird at the MRC Biostatistics Unit at the University of Cambridge, said:
“Past Royal Statistical Society Working Party reports on matters which affect the public health have had enduring impact. Official Statistics – Counting with Confidence led to the UK Statistic Act of 2007; Statistics and Statisticians in Drug Regulation led to the appointment of professional statisticians by the UK, and later, European drug regulator; Statistical Issues in First-in-Man Studies led to safety-enhanced study-designs with open protocols. I hope that this month’s consultation by MHRA is indicative that Diagnostic Tests is making its mark already.”
Dr Andrew Garrett, President of the Royal Statistical Society, said:
“The report provides a thorough evaluation of both diagnostic tests and diagnostic testing. It addresses how to develop, regulate, and use diagnostic tests in the future – a subject that is of increasing importance to individual and public health.”
END
Statisticians call for rigour and transparency in the evaluation of diagnostic tests
2024-05-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Musankwa sanyatiensis, a new dinosaur from Zimbabwe
2024-05-30
Fossils found on the shoreline of Lake Kariba in Zimbabwe represent a completely new dinosaur species. This remarkable find, named Musankwa sanyatiensis, marks only the fourth dinosaur species named from Zimbabwe. The research detailing this significant discovery is set to be published in the prestigious journal Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. The study was conducted by an international team of scientists from the University of the Witwatersrand (Wits) in South Africa, the Natural History Museum of Zimbabwe, Stony Brook University in New York and was led by Prof Paul Barrett from the Natural History Museum ...
Statin therapy may prevent cancer by blocking inflammatory protein
2024-05-30
BOSTON – A new study led by investigators from Mass General Cancer Center, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, reveals that statins—commonly used cholesterol-lowering drugs—may block a particular pathway involved in the development of cancer that results from chronic inflammation. The findings are published in Nature Communications.
“Chronic inflammation is a major cause of cancer worldwide,” said senior author Shawn Demehri, MD, PhD, a principal investigator at the Center for Cancer Immunology and Cutaneous Biology Research Center of Massachusetts General Hospital and an associate professor of Dermatology at ...
A novel ‘senolytic’ strategy for treating aging-related diseases
2024-05-30
The process of aging is accompanied by a decline in physiological functions, which can lead to cardiovascular, neurodegenerative, and metabolic diseases. Aging of cells, also known as ‘cellular senescence’— is a process in which a cell ages and permanently stops dividing but does not die. The accumulation of such ‘senescent’ cells in tissues is then known to contribute to age-associated diseases. Elimination of senescent cells or ‘senolysis’ can, therefore, serve as an effective therapeutic strategy for the improvement of physiological function and prevention ...
Risk of death from COVID-19 lessens, but infection still can cause issues 3 years later
2024-05-30
New findings on long COVID — long-term effects on health experienced by many who have had COVID-19 — present a good-news, bad-news situation, according to a study at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and the Veterans Affairs St. Louis Health Care system.
The bad news: COVID-19 patients who were hospitalized within the first 30 days after infection face a 29% higher risk of death in the third year compared with people who have not had the virus. However, the three-year death risk still marks a significant decline compared with such risk at the one- and two-year marks post-infection. The findings also show that even people with mild COVID-19 were still ...
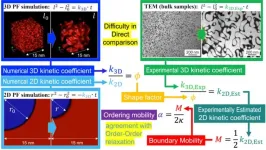
Combining simulations and experiments to get the best out of Fe3Al
2024-05-30
Osaka, Japan – The compound of iron and aluminum with the chemical formula Fe3Al has some very useful mechanical properties. A team from Osaka University has combined simulations with experimental techniques to better understand the kinetics of the formation of microstructures to enhance and utilize these properties and how to harness them for specific applications.
In a study recently published in Acta Materialia, the researchers took an in-depth look at the way the microstructure of Fe3Al develops because the ordered domains that form contribute to one of its key properties: superelasticity.
When high loads are applied to superelastic materials they ...
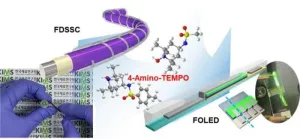
Both high performance and stability were achieved with multifunctional materials!
2024-05-30
Through joint research with Professor Chul-jin Ahn’s team at Changwon National University, the research team of Dr. Jae-Ho Kim and Dr. Myung-kwan Song from the Department of Energy & Electronic Materials in the Surface & Nano Materials Division has developed a 4-Amino-TEMPO derivative with photocatalytic properties and successfully used it to produce high-performance and stable fiber-shaped dye-sensitized solar cells (FDSSCs) and fiber-shaped organic light-emitting diodes (FOLEDs). The developed 4-Amino-TEMPO derivative has the characteristic of simultaneously improving the performance of both fiber-shaped dye-sensitized solar cells (FDSSCs) and fiber-shaped ...
Structural inequities amplify homelessness challenges for pregnant people in Washington DC
2024-05-30
WASHINGTON -- New research conducted with Washington, DC, residents who experienced homelessness during pregnancy sheds light on the intersection of homelessness, pregnancy, and racial inequities. The findings underscore the urgent need for policy and practice changes to support vulnerable populations.
The study, published May 30, 2024 in the journal Health Equity (DOI: 10.1089/heq.2023.0235), is grounded in a reproductive justice framework and delves into the lived experiences of 20 DC residents who faced homelessness while pregnant.
Homelessness ...
University of Maryland study shows N95 masks near-perfect at blocking escape of airborne COVID-19
2024-05-30
COLLEGE PARK, Md. – In a head-to-head comparison of masks worn by people with active
COVID-19, the inexpensive “duckbill” N95 came out on top, stopping 98% of COVID-19 particles
in the breath of infected people from escaping into the air. Led by researchers from the University
of Maryland School of Public Health (SPH), results showed other masks also performed well,
blocking at least 70% of viral particles from escaping from the source – an infected person’s
exhaled breath.
The study, Relative efficacy of masks and respirators as source control for viral aerosol shedding
from people infected with SARS-CoV-2, published May 29 in eBioMedicine, a Lancet ...
The AI paradox: Building creativity to protect against AI
2024-05-30
Cultivating creativity in schools is vital for a future driven by artificial intelligence (AI). But while teachers embrace creativity as an essential 21st century skill, a lack of valid and reliable creativity tests means schools struggle to assess student achievement.
Now, a new machine-learning model developed by the University of South Australia is providing teachers with access to high-quality, fit-for-purpose creativity tests, that can score assessments in a fraction of the time and a fraction of the cost.
Applied to the current ...
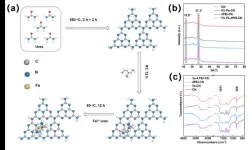
Visible light-induced photocatalysis–self-Fenton degradation of P-Clphoh over graphitic carbon nitride by a polyethylenimine bifunctional catalyst
2024-05-30
The deep degradation of organic pollutants through solar light-coupled photocatalysis and the Fenton reaction (Photo-Fenton) holds significant importance in the field of water purification. In this study, a novel bifunctional catalyst (Fe-PEI-CN) was synthesized by electrostatic self-assembly and hydrothermal methods, doping graphene-like carbon nitride (CN) with polyethyleneimine (PEI) and iron (Fe) species. This catalyst efficiently degraded p-chlorophenol (p-ClPhOH) by generating hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) during the photocatalytic process. The relationship between catalytic efficiency and structure was explored using various characterization techniques.Under ...