Novel virus identified in zebrafish from the pet trade causes disease in laboratory fish
Gene expression analyses revealed many undescribed microbes in apparently healthy pet trade zebrafish
2024-05-30
(Press-News.org) Zebrafish in the pet trade are asymptomatic carriers of previously undescribed microbes, including a novel virus that causes hemorrhaging in infected laboratory fish, Marlen Rice from the University of Utah, US, and colleagues report in the open-access journal PLOS Biology, publishing May 23rd.
Zebrafish (Danio rerio) are a common laboratory research animal, and they are also widely available as pets. In research laboratories, they are kept in specialized aquaculture facilities to prevent infectious disease, but zebrafish are occasionally imported from the pet trade into laboratory colonies.
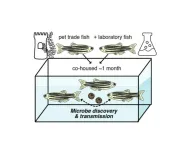
Researchers used metatranscriptomic sequencing of zebrafish from a laboratory population and three pet shops in Salt Lake valley to compare the microbes associated with fish reared in different environments. They identified many microbes in pet trade fish that were not present in laboratory populations, including a novel virus in the Birnaviridae family, which the authors named Rocky Mountain birnavirus (RMBV). To investigate RMBV transmission between fish from different populations, they housed laboratory-reared zebrafish in the same tank as pet trade zebrafish. After around a month, three of the laboratory fish had developed hemorrhaging and tested positive for RMBV. In contrast, RMBV-infected fish from the pet trade showed no symptoms of disease. Transcriptome sequencing of tissues from the fish showed that RMBV infection increased expression of genes involved in the anti-viral immune response and inflammation.
This study shows that the pet trade is a source of viruses and parasites that are not commonly found in laboratory zebrafish. Viruses circulating in apparently healthy zebrafish from the pet trade can transmit to laboratory zebrafish and cause severe disease. Differences in life history, genetics or infection stage may explain why RMBV caused symptoms in laboratory but not pet trade fish. Further sampling of zebrafish in the pet trade is likely to reveal many more novel microbes, the authors say.
The authors add, “Zebrafish are popular research organisms in the laboratory that were originally sourced from the pet trade. We found that the microbes associated with pet trade animals include previously undescribed viruses and other pathogens that can transmit to laboratory animals and potentially be used for investigations of infections with relevance to human health and aquaculture.”
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002606
Citation: Rice MC, Janik AJ, Elde NC, Gagnon JA, Balla KM (2024) Microbe transmission from pet shop to lab-reared zebrafish reveals a pathogenic birnavirus. PLoS Biol 22(5): e3002606. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3002606
Author Countries: United States
Funding: This work was supported by grants awarded by the National Institutes of Health to K.M.B. (5T32AI055434), N.C.E. (R35GM134936), and to J.A.G. (R35GM142950), and by a grant from the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative to N.C.E. and J.A.G. (DAF2020-218441). The funders played no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-05-30
The theory of coevolution says that when closely interacting species drive evolutionary changes in each other this can lead to speciation - the evolution of new species. But until now, real-world evidence for this has been scarce.
Now a team of researchers has found evidence that coevolution is linked to speciation by studying the evolutionary arms race between cuckoos and the host birds they exploit.
Bronze-cuckoos lay their eggs in the nests of small songbirds. Soon after the cuckoo chick hatches, it pushes the host’s eggs out of the nest. The host not only loses all its own eggs, but spends several ...
2024-05-30
A new study from the UC Davis School of Medicine found striking differences at the cellular level between male and female mice with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
The findings could determine how HFpEF is treated in women compared to men.
With HFpEF, the heart muscle contracts normally but the heart is unable to fully relax and refill properly between beats. This condition is known as diastolic dysfunction. It can occur if the heart is too stiff or if the contraction process doesn’t shut off quickly enough between ...
2024-05-30
Amphetamine is a psychostimulant that has been used to treat a variety of brain dysfunctions. However, it is a highly abused drug. In fact, amphetamine and amphetamine-derived compounds such as methamphetamine (Meth) are among the most abused psychostimulants in the world.
The neurological effects caused by acute or chronic use of amphetamine have been broadly investigated and several studies have shown that proteins involved in the synthesis, storage, release and reuptake of dopamine (DA), a neurotransmitter that plays a role as in ...
2024-05-30
ITHACA, N.Y. – Cornell University researchers have found in a public health emergency, most people pick out and click on accurate information during internet searches.
Though higher-ranked results are clicked more often, they are not more trusted. And the presence of misinformation does not damage trust in accurate results that appear on the same page. However, banners at the top of the search results page warning about misinformation decrease trust in accurate information, according to the research published in Scientific Reports.
The relationship between ...
2024-05-30
The Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (UC3M) has become a shareholder of five new companies recently set up and promoted by different researchers: Applied Innovative Methods, Hiili, Persei Space, Seevia Technologies and 60Nd.
UC3M participates in the share capital of its spin-offs in order to contribute to their business development. This minority and temporary shareholding is articulated in accordance with the regulations for the creation of knowledge-based university companies.
AI Methods, S.L., led by Manuel Soler ...
2024-05-30
University of Illinois Chicago engineers have helped design a new method to make hydrogen gas from water using only solar power and agricultural waste, such as manure or husks. The method reduces the energy needed to extract hydrogen from water by 600%, creating new opportunities for sustainable, climate-friendly chemical production.
Hydrogen-based fuels are one of the most promising sources of clean energy. But producing pure hydrogen gas is an energy-intensive process that often requires coal or natural gas and large amounts of electricity.
In a paper for Cell Reports Physical Science, a multi-institutional ...
2024-05-30
“The price on emitting carbon that is harmful to the climate has risen sharply in the past; basically, it roughly increased tenfold over the last five years and two policy reforms. Our analysis implies that besides directly changing the ETS rules, the reforms also increased the long-term credibility of the EU ETS and thereby made firms more farsighted, aligning their market behaviour with long-term climate targets,” explains Joanna Sitarz, PIK scientist and first author of the study published in Nature Energy. “In ...
2024-05-30
FAYETTEVILLE, Ark. — Borrowing a page from the dairy industry, researchers with the Arkansas Agricultural Experiment Station found that a slow-growth diet meant more piglets and healthier and longer-lived momma pigs.
Slowing weight gain for female pigs before breeding showed improvements in performance throughout four breeding cycles, according to Charles Maxwell, professor of animal science for the experiment station, the research arm of the University of Arkansas System Division of Agriculture.
“Scientists have done a wonderful job of increasing litter size and milk production so that our sow lines are essentially ...
2024-05-30
Philadelphia, May 30, 2024 – Researchers from The Possibilities Project and Clinical Futures at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) developed, implemented and successfully tested a nutrition screener to improve access to healthy resources for families eligible for federally funded food benefits. The findings were published this week in the journal Annals of Family Medicine.
Many low-income families rely on the federally funded Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children ...
2024-05-30
SAN ANTONIO — May 30, 2024 —When NASA’s Lucy spacecraft flew past the tiny main belt asteroid Dinkinesh last November, the Southwest Research Institute-led mission discovered a trough and ridge structure on the main asteroid as well as the first-ever-encountered contact binary satellite. The flyby data of this half-mile-wide object revealed a dramatic history of sudden breakups and transformation.
Scientists think a big chunk of Dinkinesh suddenly shifted, excavating the trough and flinging debris into its vicinity. Some materials fell back to the asteroid body, forming the ridge, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Novel virus identified in zebrafish from the pet trade causes disease in laboratory fish
Gene expression analyses revealed many undescribed microbes in apparently healthy pet trade zebrafish