Is your coffee ‘not hot’ or ‘cold’? Observing how the brain processes negated adjectives
2024-05-30
(Press-News.org) Negating an adjective by placing ‘not’ in front of it affects the way our brains interpret its meaning, mitigating but not entirely inverting our interpretation of its definition. In a study published May 23rd in the open-access journal PLOS Biology, Arianna Zuanazzi at New York University, US, and colleagues offer insight into how the brain represents changes of meaning over time and offer new methods for further linguistic research.
The way the brain processes negated adjectives — ‘not bad’ or ‘not good’ — is not understood. Previous studies suggest that negated phrases are processed more slowly and with more errors than their affirmative counterparts. Cutting-edge artificial neural networks appear to be largely insensitive to the contextual impacts of negation, leading many researchers to wonder how negation operates.
In lab-based experiments, 78 participants were asked to read affirmative or negated adjective phrases, good/bad, not good/not bad, happy/sad, not happy/not sad etc. on a screen and rate their meaning on a scale of one (really really bad/really really sad) to ten (really really good/really really happy). Answers took longer for negated adjectives and interpreted meaning was more varied. Cursor tracking showed that people are slower to interpret them, first understanding them to be affirmative before modifying towards their opposite meaning.
In a second experiment, participants rated affirmative or negated phrases on a scale. Meanwhile, magnetic fields generated by the electrical activity of their brains were captured by magnetoencephalography (MEG). Zuanazzi and colleagues again saw slower reaction times for negated adjectives. The brain activity shows that initial interpretations and early neural representations of negated adjectives are similar to that of affirmative adjectives, but are weakened, backing up the previous suggestion of a mitigated effect.
The analysis contributes to the debate as to how negation operates. The ability to characterize the subtle changes of linguistic meaning through negation in the brain using imaging methods could help to tease apart understanding of other linguistic processes beyond the sum of the processing of individual word meanings.
The authors add, “The study of negation offers a compelling linguistic framework to understand how the human brain builds meaning through combinatoric processes. Our time-resolved behavioral and neurophysiological data show that, in a sentence like ‘your coffee is not hot’, negation (‘not’) mitigates rather than inverts the representations of a scalar adjective (‘hot’). In other words, negation reduces the temperature of your coffee, though it does not make it cold.”
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002622
Citation: Zuanazzi A, Ripollés P, Lin WM, Gwilliams L, King J-R, Poeppel D (2024) Negation mitigates rather than inverts the neural representations of adjectives. PLoS Biol 22(5): e3002622. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3002622
Author Countries: United States, Germany, France
Funding: see manuscript
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-05-30
Researchers have developed a novel version of a key CRISPR gene-editing protein that shows efficient editing activity and is small enough to be packaged within a non-pathogenic virus that can deliver it to target cells. Hongjian Wang and colleagues at Wuhan University, China, present these findings May 23rd in the open-access journal PLOS Biology.
Recent years have seen an explosion of research attempting to harness CRISPR gene-editing systems—which are found naturally in many bacteria as a defense against viruses—so they can be used as potential treatments for human disease. These systems rely on so-called CRISPR-associated (Cas) proteins, with Cas9 and Cas12a being ...
2024-05-30
CAMBRIDGE, Mass., May 30, 2024 – Since the rollout of the COVID-19 vaccine in 2021, fake news on social media has been widely blamed for low vaccine uptake in the United States — but research by MIT Sloan School of Management PhD candidate Jennifer Allen and Professor David Rand finds that the blame lies elsewhere.
In a new paper published in Science and co-authored by Duncan J. Watts of the University of Pennsylvania, the researchers introduce a new methodology for measuring social media content’s causal impact at scale. They show that misleading content from mainstream news sources — rather than outright misinformation or “fake news” ...
2024-05-30
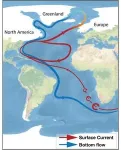
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — A great armada entered the North Atlantic, launched from the cold shores of North America. But rather than ships off to war, this force was a fleet of icebergs. And the havoc it wrought was to the ocean current itself.
This scene describes a Heinrich Event, or a period of rapid iceberg discharge from the Laurentide Ice Sheet during the last glacial maximum. These episodes greatly weakened the system of ocean currents that circulates water within the Atlantic Ocean. The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation, or AMOC for short, brings warm surface water ...
2024-05-30
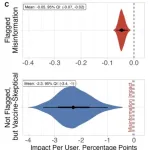
What threatens public health more, a deliberately false Facebook post about tracking microchips in the COVID-19 vaccine that is flagged as misinformation, or an unflagged, factual article about the rare case of a young, healthy person who died after receiving the vaccine?
According to Duncan J. Watts, Stevens University Professor in Computer and Information Science at Penn Engineering and Director of the Computational Social Science (CSS) Lab, along with David G. Rand, Erwin H. Schell Professor at MIT Sloan School of Management, and Jennifer Allen, 2024 MIT Sloan School of Management Ph.D. graduate ...
2024-05-30
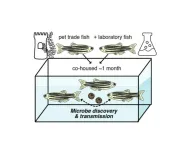
Zebrafish in the pet trade are asymptomatic carriers of previously undescribed microbes, including a novel virus that causes hemorrhaging in infected laboratory fish, Marlen Rice from the University of Utah, US, and colleagues report in the open-access journal PLOS Biology, publishing May 23rd.
Zebrafish (Danio rerio) are a common laboratory research animal, and they are also widely available as pets. In research laboratories, they are kept in specialized aquaculture facilities to prevent infectious disease, but zebrafish are occasionally ...
2024-05-30
The theory of coevolution says that when closely interacting species drive evolutionary changes in each other this can lead to speciation - the evolution of new species. But until now, real-world evidence for this has been scarce.
Now a team of researchers has found evidence that coevolution is linked to speciation by studying the evolutionary arms race between cuckoos and the host birds they exploit.
Bronze-cuckoos lay their eggs in the nests of small songbirds. Soon after the cuckoo chick hatches, it pushes the host’s eggs out of the nest. The host not only loses all its own eggs, but spends several ...
2024-05-30
A new study from the UC Davis School of Medicine found striking differences at the cellular level between male and female mice with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
The findings could determine how HFpEF is treated in women compared to men.
With HFpEF, the heart muscle contracts normally but the heart is unable to fully relax and refill properly between beats. This condition is known as diastolic dysfunction. It can occur if the heart is too stiff or if the contraction process doesn’t shut off quickly enough between ...
2024-05-30
Amphetamine is a psychostimulant that has been used to treat a variety of brain dysfunctions. However, it is a highly abused drug. In fact, amphetamine and amphetamine-derived compounds such as methamphetamine (Meth) are among the most abused psychostimulants in the world.
The neurological effects caused by acute or chronic use of amphetamine have been broadly investigated and several studies have shown that proteins involved in the synthesis, storage, release and reuptake of dopamine (DA), a neurotransmitter that plays a role as in ...
2024-05-30
ITHACA, N.Y. – Cornell University researchers have found in a public health emergency, most people pick out and click on accurate information during internet searches.
Though higher-ranked results are clicked more often, they are not more trusted. And the presence of misinformation does not damage trust in accurate results that appear on the same page. However, banners at the top of the search results page warning about misinformation decrease trust in accurate information, according to the research published in Scientific Reports.
The relationship between ...
2024-05-30
The Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (UC3M) has become a shareholder of five new companies recently set up and promoted by different researchers: Applied Innovative Methods, Hiili, Persei Space, Seevia Technologies and 60Nd.
UC3M participates in the share capital of its spin-offs in order to contribute to their business development. This minority and temporary shareholding is articulated in accordance with the regulations for the creation of knowledge-based university companies.
AI Methods, S.L., led by Manuel Soler ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Is your coffee ‘not hot’ or ‘cold’? Observing how the brain processes negated adjectives