(Press-News.org) About The Study: This study found that comparable levels of sensitivity and specificity as reported for the multitarget stool RNA (mt-sRNA) test in the colorectal cancer (CRC)-PREVENT study could be achieved by lowering the fecal immunochemical test positivity threshold, without additional mt-sRNA testing. The findings are similar to previous observations for multitarget stool DNA testing.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Hermann Brenner, M.D., M.P.H., email h.brenner@dkfz.de.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.9289)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Media advisory: This study is being released to coincide with the 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2024.9289?guestAccessKey=e9d1d41d-b503-4d1c-8d00-6d5666d0c76f&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=060124
END
Lowering fecal immunochemical test positivity threshold vs multitarget stool RNA testing for colorectal cancer screening
JAMA
2024-06-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Revolutionary brain-to-brain technology boosts brain-computer interface performance
2024-06-01
A groundbreaking study from Tsinghua University in collaboration with Imperial College London has unveiled a novel technique that significantly enhances brain-computer interface (BCI) systems by integrating brain-to-brain interactions among users. This innovative approach, detailed in a new study published in the journal Cyborg Bionic Systems, demonstrates the potential for improved BCI performance in applications such as rehabilitation and multitasking devices.
The research, led by Dr. Tianyu Jia and a team of interdisciplinary scientists, explored the effects of social interactions, ...
Insurance often denies GLP-1 medications for teens with type 2 diabetes, obesity
2024-06-01
BOSTON—Health insurance companies often deny coverage for new medications that treat children and teens with obesity and type 2 diabetes, meaning many patients who need treatment are unable to afford it, according to a study presented at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
The medications, called GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP1Ra), are often denied despite being approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, especially if children do not have type 2 diabetes, the researchers found.
GLP1Ra drugs include liraglutide (Victoza, Saxenda). The researchers ...
Childhood stress linked with earlier substance use in male and female teens
2024-06-01
BOSTON—Stress during childhood is associated with earlier substance use in male and female adolescents, according to a study presented Saturday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass. Traumatic events may increase substance use risk for males, while environmental stress and early puberty may increase the risk for females, the researchers found.
Early life stress is children’s experiences of abuse, neglect and conflict. Approximately 20% of adolescents in the United States have experienced early life stress at some point, and these experiences ...
Childhood sedentariness may cause premature liver damage in young adulthood
2024-06-01
BOSTON—Children who are sedentary for more than six waking hours a day have a significantly increased risk of severe fatty liver disease and liver cirrhosis by young adulthood, a new study finds. The research findings will be presented Saturday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass and published in Nature’s npj Gut and Liver.
“We found that this relationship between sedentariness and liver damage is likely causal,” said lead researcher Prof. Andrew Agbaje, M.D., M.P.H., Ph.D., of the University of Eastern Finland ...
Experimental therapy shows promise in pancreatic cancer clinical trial
2024-06-01
WASHINGTON --- Clinicians at Georgetown University’s Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center reported promising preliminary findings based on outcomes in the first six patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer enrolled in a phase 2 clinical trial of the experimental drug BXCL701 in combination with the immunotherapy drug pembrolizumab (Keytruda). Immunotherapy drugs alone have not shown to be responsive to pancreatic cancer.
The findings were presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2024 annual meeting in Chicago on June 1, 2024 (LBA4132).
BXCL701, made by BioXcel Therapeutics, is ...
Clinical trials show promise in treating central nervous system lymphoma, breast cancer, and glioblastoma
2024-06-01
Boston – Dana-Farber Cancer Institute researchers are leading 3 separate studies with encouraging results in treating patients with central nervous system (CNS) lymphoma, breast cancer, and glioblastoma. The studies support future research in these potential breakthroughs where treatment options may be limited. The research teams will present their findings at the 2024 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) in Chicago, May 31-June 4, 2024. ASCO is the world’s largest clinical cancer research meeting, attracting more than 30,000 global oncology professionals.
These findings are among more than 80 studies presented at ASCO that ...
Crisis intervention program leverages social media to reduce suicide risk
2024-06-01
An Oregon-based program that monitors social media use may have helped deter more than 150 youth suicide attempts in the five years it’s operated, reports a new study published online today in the journal Psychiatric Services.
Staff with Lines for Life, a nonprofit that operates mental health crisis support services, and researchers at Oregon Health & Science University collaborated to closely document interventions by the Safe Social Spaces program, launched in 2019 by Lines for Life.
The study’s senior author said it’s an example of meeting people where they are.
“Community engagement is critical,” said Alan Teo, M.D., M.S., associate professor of ...
An unlikely hero in evolution: worms
2024-06-01
One of Earth’s most consequential bursts of biodiversity—a 30-million-year period of explosive evolutionary changes spawning innumerable new species—may have the most modest of creatures to thank for the vital stage in life’s history: worms.
The digging and burrowing of prehistoric worms and other invertebrates along ocean bottoms sparked a chain of events that released oxygen into the ocean and atmosphere and helped kick-start what is known as the Great Ordovician Biodiversification Event, roughly 480 million years ago, according ...
Detecting machine-written content in scientific articles
2024-06-01
The recent surge in popularity of AI tools such as ChatGPT is forcing the science community to reckon with its place in scientific literature. Prestigious journals such as Science and Nature have attempted to restrict or prohibit AI use in submissions, but are finding it difficult to enforce because of how challenging it is becoming to detect machine-generated language.
Because AI is getting more advanced at mimicking human language, researchers at the University of Chicago were interested in learning ...
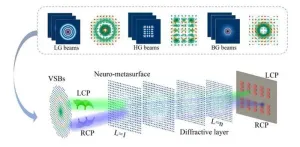
Sorting complex light beams: A breakthrough in optical physics
2024-06-01
In the dynamic realm of optical physics, researchers are continually pushing the boundaries of how light can be manipulated and harnessed for practical applications. As reported in Advanced Photonics Nexus, a groundbreaking study from the Harbin Institute of Technology (HIT) introduces a method for sorting and distinguishing various types of vector structured beams (VSBs), promising significant advancements in optical communication and quantum computing.
Unlike conventional light beams that propagate in simple, straight trajectories, VSBs are engineered to form complex, intricate patterns. These beams transmit ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
[Press-News.org] Lowering fecal immunochemical test positivity threshold vs multitarget stool RNA testing for colorectal cancer screeningJAMA