Revolutionizing robotics: A breakthrough in soft actuator technology
2024-06-01
(Press-News.org)
In an era where robotics are increasingly becoming a part of everyday life, a significant breakthrough has been made by a team of researchers at Zhe jiang University, China. Their latest creation, a wrist-inspired soft actuator capable of bidirectional torsion, promises to transform the landscape of soft robotics.
The innovative design of this actuator, described in detail in the journal Cyborg Bionic Systems, is inspired by the human wrist's ability to perform complex movements. Unlike traditional robotic mechanisms that rely on rigid components, this soft actuator utilizes a magneto-pneumatic hybrid system combined with a Kresling origami structure. This design allows for an astonishing rotation angle of up to 239.5 degrees, far surpassing the capabilities of existing models.
Yan Xu, Kaiwen Ju, and Chao Zhang, the researchers behind this development, have leveraged the geometric intricacies of origami to create an actuator that can achieve these large rotation angles through a compact and efficient design. The actuator's ability to mimic the human wrist’s bidirectional rotation adds a new layer of functionality to robotic systems, particularly in performing complex, precise tasks that were previously challenging.
The core of the actuator's technology lies in its unique magneto-pneumatic hybrid driving method. This system cleverly combines magnetic and pneumatic forces to control the actuator’s movement, allowing it to maintain three steady states and handle bidirectional torsion deformation effectively. The application of this technology is not just limited to robotics but extends to various fields requiring delicate and precise manipulation, such as biomedical devices and advanced manufacturing processes.
The practical implications of this technology are vast. For instance, in soft robotic applications, such as wearable devices or assistive technology, the actuator’s flexibility and range of motion could significantly enhance user interaction and functionality. Its ability to perform under different conditions without compromising on efficiency makes it a versatile component in both industrial and consumer-oriented applications.
Experimental validations carried out by the team have shown promising results, demonstrating the actuator's efficiency and resilience. The actuator underwent rigorous testing, including kinematic analysis and quasistatic characteristics experiments, to ensure its performance stability and reliability under various operational conditions.
One of the most notable aspects of this development is the potential customization of the actuator. Depending on the specific application, the actuator can be designed with different geometric parameters to suit particular requirements, making it a highly adaptable solution for numerous robotic systems.
Looking ahead, the research team plans to further refine this technology by enhancing its load-bearing capabilities and optimizing its energy efficiency. Such improvements could pave the way for broader applications, potentially leading to more sophisticated and autonomously functioning robotic systems.
This breakthrough marks a significant step forward in the field of robotics, offering a glimpse into the future of how machines could more closely mimic human movements and interactions. As this technology continues to evolve, it may well redefine the boundaries of what is possible in robotics and automation.
The paper, "A Wrist-Inspired Magneto-Pneumatic Hybrid-Driven Soft Actuator with Bidirectional Torsion," was published in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems on Mar 28, 2024, at DOI: https://spj.science.org/doi/10.34133/cbsystems.0111.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-06-01
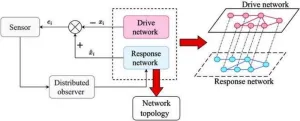
Researchers from Huazhong University of Science and Technology, in collaboration with the Donders Institute for Brain, Cognition and Behavior at Radboud University, have developed a revolutionary method for the rapid identification of network topologies. Their new approach, detailed in a recent publication in Cyborg Bionic Systems, significantly accelerates the process of understanding complex dynamical networks, which are crucial in numerous applications ranging from power grids to transportation systems.
The innovative method, named Finite-Time Topology Identification of Delayed Complex Dynamical Networks (FT-TIDCN), leverages finite-time stability ...
2024-06-01
BOSTON—Prediabetes increases the risk of dying before age 75, particularly due to heart disease, kidney disease and acute diabetic complications, according to a new study presented Saturday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
“Prediabetes is well known to increase the risk of developing diabetes; however, information about other complications of prediabetes in Latin America was limited before this study,” said study researcher Carlos Fermin-Martinez, M.D., of the National Autonomous University of Mexico in Mexico City, Mexico. He is also with the National Institute of Geriatrics in Mexico ...
2024-06-01
BOSTON—Semaglutide improved taste sensitivity, changed gene expression in the tongue that’s responsible for taste perception, and changed the brain’s response to sweet tastes, according to research presented Saturday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
“People with obesity often perceive tastes less ‘intensely,’ and they have an inherently elevated desire for sweet and energy-dense food,” said Mojca Jensterle Sever, Ph.D., of the University Medical Centre in Ljubljana, Slovenia.
Jensterle Sever and colleagues designed a proof-of-concept study on the impact of GLP-1 ...
2024-06-01
BOSTON—People of color and those who experience social vulnerability are more likely to experience worse glycemic control than their white counterparts, according to research presented Sunday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
“As of 2021, 29.7 million people were living with diabetes, contributing to significant morbidity across the population. Despite advances in diabetic care, marginalized populations bear an increased burden of diabetic complications,” said study author Jennifer Tich, M.D., from Internal Medicine-Pediatrics R3 at the University of Rochester in Rochester, N.Y.
Tich and colleagues identified ...
2024-06-01
BOSTON—Testosterone appears protective against developing type 2 diabetes in men who are overweight or obese and under age 65, but not in men over that age, according to a study presented Saturday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
“A low blood testosterone concentration is an independent risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes, and high levels of testosterone appear protective against the development of type 2 diabetes,” said lead researcher ...
2024-06-01
About The Study: This study found that comparable levels of sensitivity and specificity as reported for the multitarget stool RNA (mt-sRNA) test in the colorectal cancer (CRC)-PREVENT study could be achieved by lowering the fecal immunochemical test positivity threshold, without additional mt-sRNA testing. The findings are similar to previous observations for multitarget stool DNA testing.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Hermann Brenner, M.D., M.P.H., email h.brenner@dkfz.de.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
2024-06-01
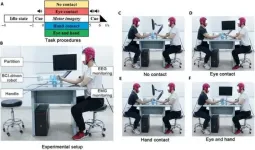
A groundbreaking study from Tsinghua University in collaboration with Imperial College London has unveiled a novel technique that significantly enhances brain-computer interface (BCI) systems by integrating brain-to-brain interactions among users. This innovative approach, detailed in a new study published in the journal Cyborg Bionic Systems, demonstrates the potential for improved BCI performance in applications such as rehabilitation and multitasking devices.
The research, led by Dr. Tianyu Jia and a team of interdisciplinary scientists, explored the effects of social interactions, ...
2024-06-01
BOSTON—Health insurance companies often deny coverage for new medications that treat children and teens with obesity and type 2 diabetes, meaning many patients who need treatment are unable to afford it, according to a study presented at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
The medications, called GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP1Ra), are often denied despite being approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, especially if children do not have type 2 diabetes, the researchers found.
GLP1Ra drugs include liraglutide (Victoza, Saxenda). The researchers ...
2024-06-01
BOSTON—Stress during childhood is associated with earlier substance use in male and female adolescents, according to a study presented Saturday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass. Traumatic events may increase substance use risk for males, while environmental stress and early puberty may increase the risk for females, the researchers found.
Early life stress is children’s experiences of abuse, neglect and conflict. Approximately 20% of adolescents in the United States have experienced early life stress at some point, and these experiences ...
2024-06-01
BOSTON—Children who are sedentary for more than six waking hours a day have a significantly increased risk of severe fatty liver disease and liver cirrhosis by young adulthood, a new study finds. The research findings will be presented Saturday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass and published in Nature’s npj Gut and Liver.
“We found that this relationship between sedentariness and liver damage is likely causal,” said lead researcher Prof. Andrew Agbaje, M.D., M.P.H., Ph.D., of the University of Eastern Finland ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Revolutionizing robotics: A breakthrough in soft actuator technology