Risk for heart attack and stroke increases in people with obesity for a decade or more
2024-06-01
(Press-News.org) BOSTON—People under age 50 have a greater risk for heart attack or stroke if they’ve lived with obesity for 10 years, according to industry-sponsored research being presented Saturday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
“It is well established that people who have excess weight at any point in time have a greater risk of heart attacks and strokes. What was not known was whether it matters for how long someone has been exposed to excess weight,” said Alexander Turchin, M.D., M.S., Director of Quality at the Division of Endocrinology at Brigham & Women’s Hospital and associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School in Boston.
Turchin and his team, including researchers from Eli Lilly, conducted a comprehensive study using data from the Nurses’ Health Study (NHS) and Health Professionals Follow-Up Study (HPFS). They specifically focused on patients who had a body-mass index (BMI) greater than 25 kg/m2 at least once over a 10-year period (1990-1999) to understand how their weight impacted their risk for heart attack or stroke over the next two decades (2000-2020).
The researchers analyzed data from 109,259 women and 27,239 men who had an average age of 48.6 years and a BMI of 27.2 kg/m2 in 1990. Of those, 6,862 had atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, 3,587 had type 2 diabetes, and 65,101 had a history of smoking. At follow-up in 2020, the data revealed 12,048 cardiovascular events.
“We found that among women younger than 50 and men younger than 65, having obesity over a 10-year period was associated with a 25-60% increase in the risk of heart attack and stroke – and was more important than their weight at a single point in time in 1990,” Turchin said.
However, obesity in women older than 50 and men older than 65 was not associated with an increased risk for heart attack and stroke.
These findings are important for clinicians who see younger people living with obesity, as they show that the sooner someone is treated, the better.
“Viewed as a ‘glass half full,’ these findings mean that obesity at any given point in time does not ‘seal’ one’s fate,” Turchin said. “If obesity is treated in a timely fashion, its complications can be prevented.”
Turchin is scheduled to speak at the Society's obesity news conference at 9 a.m. Eastern June 2. Register to view the livestream at endomediastream.com.
# # #
Endocrinologists are at the core of solving the most pressing health problems of our time, from diabetes and obesity to infertility, bone health, and hormone-related cancers. The Endocrine Society is the world’s oldest and largest organization of scientists devoted to hormone research and physicians who care for people with hormone-related conditions.
The Society has more than 18,000 members, including scientists, physicians, educators, nurses and students in 122 countries. To learn more about the Society and the field of endocrinology, visit our site at www.endocrine.org. Follow us on Twitter at @TheEndoSociety and @EndoMedia.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-06-01
BOSTON—One year after a prediabetes diagnosis, Asians were more likely to develop diabetes mellitus whereas Black patients were more likely to remain in prediabetes range, highlighting racial disparities in diabetes prevention, according to data presented at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
“Every year a small proportion of patients with prediabetes will progress to diabetes mellitus with some proportion of patients reverting to normal glucose levels,” said Ewelina Niedzialkowska, M.D., an internal medicine resident at Corewell Health William Beaumont University Hospital, in Royal Oak, Mich. “While diet, lifestyle ...
2024-06-01
BOSTON—The type of estrogen in hormonal birth control may influence anxiety-like behaviors, according to data presented by Abigail Hegwood, M.S., from the Prakapenka Lab at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
“It is plausible that estrogen type is a key player in mood or cognitive related side effects of hormone-based contraceptive use,” said Alesia Prakapenka, Ph.D., an assistant professor in the Biomedical Sciences program at Midwestern University in Downers Grove, Ill.
According to the CDC, 12.6% of women in the United States between the ages of 15 and 49 reported using oral contraceptives from ...
2024-06-01
In an era where robotics are increasingly becoming a part of everyday life, a significant breakthrough has been made by a team of researchers at Zhe jiang University, China. Their latest creation, a wrist-inspired soft actuator capable of bidirectional torsion, promises to transform the landscape of soft robotics.
The innovative design of this actuator, described in detail in the journal Cyborg Bionic Systems, is inspired by the human wrist's ability to perform complex movements. Unlike traditional robotic mechanisms that rely on rigid components, this soft actuator utilizes a magneto-pneumatic hybrid system combined with a Kresling origami structure. This design allows for an astonishing ...
2024-06-01
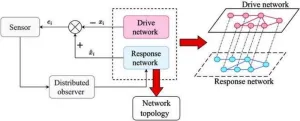
Researchers from Huazhong University of Science and Technology, in collaboration with the Donders Institute for Brain, Cognition and Behavior at Radboud University, have developed a revolutionary method for the rapid identification of network topologies. Their new approach, detailed in a recent publication in Cyborg Bionic Systems, significantly accelerates the process of understanding complex dynamical networks, which are crucial in numerous applications ranging from power grids to transportation systems.
The innovative method, named Finite-Time Topology Identification of Delayed Complex Dynamical Networks (FT-TIDCN), leverages finite-time stability ...
2024-06-01
BOSTON—Prediabetes increases the risk of dying before age 75, particularly due to heart disease, kidney disease and acute diabetic complications, according to a new study presented Saturday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
“Prediabetes is well known to increase the risk of developing diabetes; however, information about other complications of prediabetes in Latin America was limited before this study,” said study researcher Carlos Fermin-Martinez, M.D., of the National Autonomous University of Mexico in Mexico City, Mexico. He is also with the National Institute of Geriatrics in Mexico ...
2024-06-01
BOSTON—Semaglutide improved taste sensitivity, changed gene expression in the tongue that’s responsible for taste perception, and changed the brain’s response to sweet tastes, according to research presented Saturday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
“People with obesity often perceive tastes less ‘intensely,’ and they have an inherently elevated desire for sweet and energy-dense food,” said Mojca Jensterle Sever, Ph.D., of the University Medical Centre in Ljubljana, Slovenia.
Jensterle Sever and colleagues designed a proof-of-concept study on the impact of GLP-1 ...
2024-06-01
BOSTON—People of color and those who experience social vulnerability are more likely to experience worse glycemic control than their white counterparts, according to research presented Sunday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
“As of 2021, 29.7 million people were living with diabetes, contributing to significant morbidity across the population. Despite advances in diabetic care, marginalized populations bear an increased burden of diabetic complications,” said study author Jennifer Tich, M.D., from Internal Medicine-Pediatrics R3 at the University of Rochester in Rochester, N.Y.
Tich and colleagues identified ...
2024-06-01
BOSTON—Testosterone appears protective against developing type 2 diabetes in men who are overweight or obese and under age 65, but not in men over that age, according to a study presented Saturday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
“A low blood testosterone concentration is an independent risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes, and high levels of testosterone appear protective against the development of type 2 diabetes,” said lead researcher ...
2024-06-01
About The Study: This study found that comparable levels of sensitivity and specificity as reported for the multitarget stool RNA (mt-sRNA) test in the colorectal cancer (CRC)-PREVENT study could be achieved by lowering the fecal immunochemical test positivity threshold, without additional mt-sRNA testing. The findings are similar to previous observations for multitarget stool DNA testing.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Hermann Brenner, M.D., M.P.H., email h.brenner@dkfz.de.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
2024-06-01
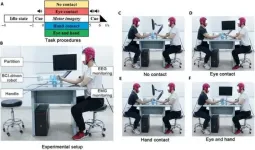
A groundbreaking study from Tsinghua University in collaboration with Imperial College London has unveiled a novel technique that significantly enhances brain-computer interface (BCI) systems by integrating brain-to-brain interactions among users. This innovative approach, detailed in a new study published in the journal Cyborg Bionic Systems, demonstrates the potential for improved BCI performance in applications such as rehabilitation and multitasking devices.
The research, led by Dr. Tianyu Jia and a team of interdisciplinary scientists, explored the effects of social interactions, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Risk for heart attack and stroke increases in people with obesity for a decade or more