Revolutionizing robotics: Integrating actuation and sensing for smarter soft robots
2024-06-02
(Press-News.org)
The world of robotics is witnessing a transformative shift with the rise of soft robotics, which offers unparalleled flexibility and adaptability in various applications, from medical interventions to intricate rescue operations. A groundbreaking review article by Zhou et al. published in Cyborg Bionic Systems in 2024, sheds light on this evolution, highlighting the crucial integration of actuation and sensing technologies that pave the way for truly intelligent soft robots.
Soft robots, unlike their rigid counterparts, are made from materials that mimic the mechanical properties of living tissues, allowing them to move and adapt with a life-like grace. This capability makes them ideal for operating in unstructured and unpredictable environments where traditional robots might falter. The innovative research spearheaded by the team from Southeast University in Nanjing, China, focuses on merging actuation—the ability to move and interact with surroundings—with sensing, which involves collecting data about the environment. This integration is essential for developing soft robots that can react and adapt to their surroundings autonomously.
Actuation technologies enable soft robots to perform diverse tasks, such as navigating rough terrain or delicately handling objects. Sensing technologies, on the other hand, allow these robots to perceive their environment, from detecting obstacles to assessing the properties of the objects they interact with. By integrating these two capabilities, soft robots can perform complex tasks more effectively and with greater autonomy.
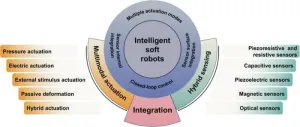
Zhou and colleagues discuss various actuation methods, including pressure-driven, electrically driven, and those utilizing shape memory materials. These methods have allowed soft robots to achieve complex movements such as rotation, crawling, and bending. On the sensing side, the researchers explore advancements in proprioceptive (self-perception) and haptic (touch-based) sensing, which enable robots to understand their body position and react to physical contact.
One of the review's highlights is the detailed examination of three integration methodologies for actuation and sensing:
Sensor Surface Integration: Embedding sensors on the surface of the robot to provide real-time feedback on external interactions.
Sensor Internal Integration: Incorporating sensors within the robot's body to monitor internal states, enhancing the robot's ability to adapt its movements based on dynamic internal and external conditions.
Closed-loop System Integration: Utilizing sensor feedback to create systems where actuation and sensing are continuously informing and optimizing each other's functions.
Despite the promising advancements, the review identifies several challenges facing the field. These include the need for more durable and reliable integration techniques, the development of materials that can withstand diverse operational environments, and the creation of more sophisticated models for predicting and controlling robot behavior.
The future directions suggested by the research team include enhancing the load capacity of these robots, improving their energy efficiency, and refining the technologies that allow them to operate in extreme conditions. These improvements could revolutionize the way robots are used in fields such as deep-sea exploration, disaster recovery, and health-care.
Zhou,Li et al.'s review not only summarizes the current state of soft robotics but also serves as a call to action for researchers. It encourages further exploration into the integration of actuation and sensing to realize the full potential of soft robots. As this field evolves, it promises to bring forth robots that are not only more adaptable and safe for human interaction but also capable of performing tasks that are currently unimaginable.
The paper, "Integrated Actuation and Sensing: Toward Intelligent Soft Robots," was published in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems on Apr 18, 2024, at DOI: https://spj.science.org/doi/10.34133/cbsystems.0105.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-06-02
BOSTON—Almost one out of five breast cancer survivors may experience weight gain of more than 10%, suggests a study presented Monday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass. A number of factors are associated with excessive weight gain, the researchers found.
Factors associated with more than 10% weight gain included a lower weight, younger age, and more advanced cancer stage at cancer diagnosis; hormone-positive breast cancer; mutations of the BRCA2 gene; undergoing more aggressive breast surgery; and the use of chemotherapy and endocrine therapy, the study found.
“Weight ...
2024-06-02
An immunotherapy drug given before surgery instead of chemotherapy meant that over ten times more patients with a certain genetic profile were cancer free after surgery, according to clinical trial results presented by researchers at UCL and UCLH.
The findings, presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting 2024, are interim results from the NEOPRISM-CRC phase II clinical trial assessing whether the immunotherapy drug pembrolizumab can improve outcomes for patients with stage two or stage three MMR deficient/MSI-High bowel cancer. The ...
2024-06-02
About The Study: A stepped-care model, with palliative care visits occurring only at key points in patients’ cancer trajectories and using a decrement in quality of life to trigger more intensive palliative care exposure, resulted in fewer palliative care visits without diminishing the benefits for patients’ quality of life. While stepped palliative care was associated with fewer days in hospice, it is a more scalable way to deliver early palliative care to enhance patient-reported outcomes.
Quote from corresponding author Jennifer S. Temel, M.D.:
“This study demonstrates that early palliative ...
2024-06-02
BOSTON – A new study led by investigators from Mass General Cancer Center, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, reveals the effectiveness of more scalable ways of delivering palliative care to patients with advanced lung cancer. The findings were highlighted at the American Society of Clinical Oncology’s annual meeting and are published in JAMA.
The study, led by Jennifer S. Temel, MD of the Mass General Cancer Center, assessed the effectiveness of stepped palliative care, in which all patients receive palliative care for their condition, but with a minimum of required contact with a specialty-trained clinician. ...
2024-06-02
Berlin, Germany: Differences in socioeconomic status (SES) are known to be linked to differences in the risk of developing disease. While people with lower SES are more likely to develop complex diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease, those with a higher SES are at increased risk of developing certain types of cancer. Using biobank and national register data, researchers from Finland have now found that people with lower SES (educational achievement and occupation) have a greater genetic susceptibility to develop many other complex diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, lung cancer, depression, and alcohol ...
2024-06-01
CHICAGO – While CAR T cell therapy has revolutionized treatment for many blood cancers, including non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), many patients who receive CAR T cell therapy do not experience a long-term remission. For those whose cancers return or become resistant after CAR T cell therapy, the prognosis is poor, with few options left.
A new “armored” form of CAR T cell therapy, developed by Carl June, MD, the Richard W. Vague Professor in Immunotherapy in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University ...
2024-06-01
BOSTON—People who have had type 1 diabetes for more than 50 years without kidney complications may still be at substantial risk for heart disease, despite excellent control of blood pressure, cholesterol and blood sugar levels, according to a study presented Saturday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
Heart disease is a major cause of death in people with type 1 diabetes, especially in those who develop kidney complications from diabetes.
“As people with type 1 diabetes live longer due to improved medical care, a substantial proportion of these patients survive without kidney complications, but are still at high risk for heart ...
2024-06-01
BOSTON—Medications for type 2 diabetes and obesity known as GLP-1 receptor agonists may lower the risk of acute pancreatitis recurrence in people with obesity and those with type 2 diabetes, according to a study presented Saturday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
Doctors have been cautious about prescribing these medications in patients with a history of pancreatitis due to the potential risk of worsening the condition – a warning that is included in prescribing information, said lead researcher Mahmoud Nassar, M.D., Ph.D., Department of Medicine ...
2024-06-01
BOSTON—Having medical conditions linked to obesity does not impact the total weight loss achieved with the anti-obesity medication tirzepatide, according to an industry-supported study being presented Saturday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
Obesity causes or worsens over 200 diseases. It has been widely believed that when patients suffer multiple medical problems, they are not able to lose as much weight as those without medical issues. The new study, funded by tirzepatide maker Eli Lilly Inc., was designed to see if having more obesity-associated ...
2024-06-01
BOSTON—People under age 50 have a greater risk for heart attack or stroke if they’ve lived with obesity for 10 years, according to industry-sponsored research being presented Saturday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
“It is well established that people who have excess weight at any point in time have a greater risk of heart attacks and strokes. What was not known was whether it matters for how long someone has been exposed to excess weight,” said Alexander Turchin, M.D., M.S., Director of Quality at the Division of Endocrinology at Brigham & Women’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Revolutionizing robotics: Integrating actuation and sensing for smarter soft robots
