(Press-News.org) BOSTON—A novel male contraceptive gel combining two hormones, segesterone acetate (named Nestorone) and testosterone, suppresses sperm production faster than similar experimental hormone-based methods for male birth control, according to a new study.
Results from an ongoing multicenter phase 2b clinical trial will be presented Sunday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston.
“The development of a safe, highly effective and reliably reversible contraceptive method for men is an unmet need,” said senior researcher Diana Blithe, Ph.D., chief of the Contraceptive Development Program at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in Bethesda, Md. “While studies have shown that some hormonal agents may be effective for male contraception, the slow onset of spermatogenic suppression is a limitation.”
NIH’s Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development is funding the study, which included 222 men who completed at least 3 weeks of daily treatment with the contraceptive gel. The gel contained 8 milligrams (mg) of segesterone acetate and 74 mg of testosterone. Segesterone acetate is an ingredient of the Annovera vaginal birth control ring. Men applied the gel once daily to each shoulder blade.
Early in the study, the researchers measured for suppression of sperm production by obtaining sperm count tests at 4-week intervals. The threshold deemed effective for contraception was 1 million or fewer sperm per milliliter of semen, Blithe noted.
Most study participants (86%) reached this sperm count by week 15, the researchers reported. Among those men, sperm production was suppressed at a median, or midpoint, time of less than 8 weeks of segesterone-testosterone treatment. Blithe said prior studies of male hormonal contraceptives given by injections showed a median time between 9 and 15 weeks for sperm output to become suppressed.
“A more rapid time to suppression may increase the attractiveness and acceptability of this drug to potential users,” Blithe said.
Testosterone treatment alone decreases sperm production, with a median time of 15 weeks but the addition of segesterone acetate speeds the time and lowers the dose of testosterone needed to suppress sperm production over testosterone alone, she said. In the daily segesterone-testosterone gel regimen, blood levels of testosterone are kept in the physiologic range to maintain normal sexual function and other androgen-dependent activities.
The sperm suppression stage of the international phase 2b trial of segesterone-testosterone gel is complete. The study continues to test the contraceptive’s effectiveness, safety, acceptability and reversibility of contraception after treatment stops.
# # #
Endocrinologists are at the core of solving the most pressing health problems of our time, from diabetes and obesity to infertility, bone health, and hormone-related cancers. The Endocrine Society is the world’s oldest and largest organization of scientists devoted to hormone research and physicians who care for people with hormone-related conditions.
The Society has more than 18,000 members, including scientists, physicians, educators, nurses and students in 122 countries. To learn more about the Society and the field of endocrinology, visit our site at www.endocrine.org. Follow us on Twitter at @TheEndoSociety and @EndoMedia.
END
New male birth control gel takes effect sooner than similar contraceptive methods
2024-06-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study finds potentially treatable factors to improve symptoms in men stopping illicit steroids
2024-06-02
BOSTON—Men who illicitly used steroids to boost muscle size and physical performance and have stopped in the past year have impaired sexual function compared with men currently using steroids, according to a study being presented Sunday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
Having a psychiatric diagnosis and stopping steroids was associated with greater impairment in sexual function, the researchers found.
“It is important to recognize the symptoms that men experience within the first year of stopping ...
Hot flashes in menopausal women may signal increased risk for heart and metabolic issues
2024-06-02
BOSTON—Women experiencing moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms face a three times greater risk for metabolic-dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) compared to those with mild symptom severity, according to research being presented Monday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
Vasomotor symptoms include hot flashes or night sweats—symptoms that have become synonymous with menopause.
“This research is significant as it contributes ...
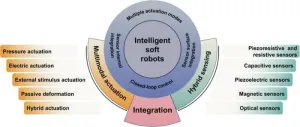
Revolutionizing robotics: Integrating actuation and sensing for smarter soft robots
2024-06-02
The world of robotics is witnessing a transformative shift with the rise of soft robotics, which offers unparalleled flexibility and adaptability in various applications, from medical interventions to intricate rescue operations. A groundbreaking review article by Zhou et al. published in Cyborg Bionic Systems in 2024, sheds light on this evolution, highlighting the crucial integration of actuation and sensing technologies that pave the way for truly intelligent soft robots.
Soft robots, unlike their rigid counterparts, are made from materials that mimic the mechanical properties of living tissues, allowing them to move and adapt with a life-like grace. This capability makes ...
Almost 20% of breast cancer survivors may experience excess weight gain
2024-06-02
BOSTON—Almost one out of five breast cancer survivors may experience weight gain of more than 10%, suggests a study presented Monday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass. A number of factors are associated with excessive weight gain, the researchers found.
Factors associated with more than 10% weight gain included a lower weight, younger age, and more advanced cancer stage at cancer diagnosis; hormone-positive breast cancer; mutations of the BRCA2 gene; undergoing more aggressive breast surgery; and the use of chemotherapy and endocrine therapy, the study found.
“Weight ...
Immunotherapy significantly increases the number of patients free from bowel cancer
2024-06-02
An immunotherapy drug given before surgery instead of chemotherapy meant that over ten times more patients with a certain genetic profile were cancer free after surgery, according to clinical trial results presented by researchers at UCL and UCLH.
The findings, presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting 2024, are interim results from the NEOPRISM-CRC phase II clinical trial assessing whether the immunotherapy drug pembrolizumab can improve outcomes for patients with stage two or stage three MMR deficient/MSI-High bowel cancer. The ...
Stepped palliative care for patients with advanced lung cancer
2024-06-02
About The Study: A stepped-care model, with palliative care visits occurring only at key points in patients’ cancer trajectories and using a decrement in quality of life to trigger more intensive palliative care exposure, resulted in fewer palliative care visits without diminishing the benefits for patients’ quality of life. While stepped palliative care was associated with fewer days in hospice, it is a more scalable way to deliver early palliative care to enhance patient-reported outcomes.
Quote from corresponding author Jennifer S. Temel, M.D.:
“This study demonstrates that early palliative ...
Trial reveals benefits of ‘stepped’ palliative care for patients with advanced lung cancer
2024-06-02
BOSTON – A new study led by investigators from Mass General Cancer Center, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, reveals the effectiveness of more scalable ways of delivering palliative care to patients with advanced lung cancer. The findings were highlighted at the American Society of Clinical Oncology’s annual meeting and are published in JAMA.
The study, led by Jennifer S. Temel, MD of the Mass General Cancer Center, assessed the effectiveness of stepped palliative care, in which all patients receive palliative care for their condition, but with a minimum of required contact with a specialty-trained clinician. ...
Socioeconomic status influences genetic risk for many complex diseases
2024-06-02
Berlin, Germany: Differences in socioeconomic status (SES) are known to be linked to differences in the risk of developing disease. While people with lower SES are more likely to develop complex diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease, those with a higher SES are at increased risk of developing certain types of cancer. Using biobank and national register data, researchers from Finland have now found that people with lower SES (educational achievement and occupation) have a greater genetic susceptibility to develop many other complex diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, lung cancer, depression, and alcohol ...
ASCO: New ‘Armored’ CAR produces significant responses in patients whose cancers don't respond to current CAR T cell therapies
2024-06-01
CHICAGO – While CAR T cell therapy has revolutionized treatment for many blood cancers, including non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), many patients who receive CAR T cell therapy do not experience a long-term remission. For those whose cancers return or become resistant after CAR T cell therapy, the prognosis is poor, with few options left.
A new “armored” form of CAR T cell therapy, developed by Carl June, MD, the Richard W. Vague Professor in Immunotherapy in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University ...
People with well-controlled, long-duration type 1 diabetes may still face high risk of heart disease
2024-06-01
BOSTON—People who have had type 1 diabetes for more than 50 years without kidney complications may still be at substantial risk for heart disease, despite excellent control of blood pressure, cholesterol and blood sugar levels, according to a study presented Saturday at ENDO 2024, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Boston, Mass.
Heart disease is a major cause of death in people with type 1 diabetes, especially in those who develop kidney complications from diabetes.
“As people with type 1 diabetes live longer due to improved medical care, a substantial proportion of these patients survive without kidney complications, but are still at high risk for heart ...