(Press-News.org) The COVID-19 pandemic dramatically improved health insurance coverage for millions of Americans who were automatically covered by Medicaid due to the national public health emergency.
With the end of the emergency in April 2023, about 10 million people lost coverage as states began redetermining eligibility. However, an estimated three-quarters of disenrollments occurred not because states decided they were ineligible, but rather due to procedural reasons. These process-related issues could include enrollees not receiving renewal notices, not filling out the correct paperwork, or not completing all the steps needed for Medicaid redetermination.
New research suggests Black and Hispanic people were twice as likely as white people to lose Medicaid coverage due to process-related issues, report findings published today in the journal JAMA Internal Medicine by researchers at Oregon Health & Science University, Northwestern University and Harvard Medical School.
“A lot of people got kicked off Medicaid for administrative reasons,” said senior author Jane Zhu, M.D., associate professor of medicine (general internal medicine and geriatrics) in the OHSU School of Medicine. “Our study found that Black and Hispanic people are twice as likely to lose Medicaid insurance for reasons that can be addressed by systems improvements.”
Researchers noted that state-level information on causes of procedural disenrollments is limited, and that only nine states currently report disenrollments by race and ethnicity.
So they used publicly available data from the U.S. Census Bureau’s Household Pulse Survey between March 29 and Oct. 2, 2023, to estimate adult Medicaid disenrollment by race and ethnicity during the Medicaid unwinding period. They found that individuals who identified as Black and Hispanic were twice as likely as white people to report losing Medicaid coverage due to inability to complete the renewal process.
Researchers called for policymakers to improve Medicaid enrollment processes in order to reduce health disparities.
“Addressing these barriers may include more transparent race and ethnicity data reporting, expedited administrative processes, expanded renewal assistance, and prioritized redeterminations for beneficiaries most likely to be ineligible,” they write.
In addition to Zhu, co-authors include Kranti C. Rumalla of Northwestern University, Daniel B. Nelson, M.D., of Harvard Medical School, and John McConnell, Ph.D., director of the OHSU Center for Health Systems Effectiveness.
END
Study finds people of color disproportionately dropped from Medicaid
OHSU, research team find process issues were twice as likely to impact Black, Hispanic people—highlighting health inequities, system improvement needs
2024-06-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Weight indices, cognition, and mental health from childhood to early adolescence
2024-06-03
About The Study: Lower cognitive performance and greater psychopathology at baseline were associated with increased weight gain as children entered adolescence, and higher baseline body mass index was associated with more depressive symptoms over time. These longitudinal findings highlight the importance of cognitive and mental health to children’s healthy weight development and suggest that clinicians should monitor children with overweight or obesity for increased depression problems.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Tamara Hershey, Ph.D., email tammy@wustl.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
Clinical outcomes after admission of patients with COVID-19 to skilled nursing facilities
2024-06-03
About The Study: The results of this cohort study suggest that admission of COVID-19–positive patients into skilled nursing facilities early in the pandemic was associated with preventable COVID-19 cases and mortality among residents, particularly in facilities with potential staff and personal protective equipment shortages. The findings speak to the importance of equipping skilled nursing facilities to adhere to infection-control best practices as they continue to face COVID-19 strains and other respiratory diseases.
Corresponding Author: To contact ...
Kinship and ancestry of the Celts in Baden-Württemberg, Germany
2024-06-03
The burial mounds of Eberdingen-Hochdorf and Asperg-Grafenbühl, known as Fürstengräber, are among the richest burials of German prehistory, with gold finds and elaborate bronze vessels. A new genetic analysis has now revealed that the two princes, buried about 10 kilometers apart, were biologically closely related. "It has long been suspected that the two princes from the burial mounds in Eberdingen-Hochdorf and Asperg ‘Grafenbühl‘ were related," says Dirk Krausse of the State Office for the ...
How sharks survived a major spike in Earth’s temperature
2024-06-03
The sharks we know today as the open ocean’s top predators evolved from stubby bottom dwellers during a dramatic episode of global warming millions of years ago.
A massive outpouring of volcanic lava about 93 million years ago sent carbon dioxide levels soaring, creating a greenhouse climate that pushed ocean temperatures to their hottest. UC Riverside researchers discovered that some sharks responded to the heat with elongated pectoral fins.
This discovery is documented in a paper published today in the journal Current Biology. It was made by taking body length and fin measurements from over 500 living and fossilized shark species.
“The ...
Cacao of Excellence announces the launch of the 2025 Edition of the Cacao of Excellence Awards
2024-06-03
[Rome, 3 June 2024] – Cacao of Excellence is delighted to announce the official launch of the 2025 Edition of the Cacao of Excellence Awards. Since its inception in 2009, Cacao of Excellence has been the premier platform for cacao producers to showcase the superior quality of their cacao, celebrating the diversity of flavours of cacao produced worldwide.
Held biennially, the Cacao of Excellence Awards bring together leading sensory evaluation experts and the chocolate industry to recognise and reward cacao producers who demonstrate excellence. The Awards offer the possibility for selected producers and the origins they represent to compete ...
The unexpected connection between brewing coffee and understanding turbulence
2024-06-03
In 1883 Osborne Reynolds injected ink into water in a short, clear pipe to observe its movement. His experiments showed that as the input water velocity increased, the flow went from laminar (smooth and predictable) to turbulent (unsteady and unpredictable) through the development of localized patches of turbulence, known today as “puffs.” His work helped launch the field of fluid mechanics, but, as experiments often do, it raised more questions. For example, why do these transitions between laminar and turbulent flows occur and how can the transitions be characterized quantitatively?
Although ...
Researchers call for return of Sumas Lake following devastating 2021 floods
2024-06-03
A new proposal has emerged in response to the November 2021 floods that swept Sumas Prairie in the Fraser Valley, British Columbia, causing mass evacuations and millions in damages.
Instead of rebuilding the dykes to manage water flows and prevent future floods, scientists at UBC, along with members of the Sumas First Nation and other research partners, suggest an alternative: let Sumas Lake, which was drained in the early 1920s and converted into the farmland known as Sumas Prairie, return to its natural state.
This ...
Transition-metal-free zeolite catalyst for direct conversion of methane to methanol
2024-06-03
In light of the waste-to-wealth movement, technology for converting greenhouse gases into value-added materials has gained significant attention in recent years. One such technology is the catalytic conversion of methane into methanol, a widely used industrial solvent and raw material for chemical synthesis. The industrial process for conversion of methane to methanol is extremely energy and resource-intensive. In the past decade, scientists have developed several catalyst systems that can enable direct oxidation of methane to methanol. However, most of them are based on ...
Retrospective study based on electronic health records finds popular diabetes and weight-loss drugs associated with reduction in incidence and recurrence of alcohol-use disorder by at least half
2024-06-03
CLEVELAND—A new study by researchers at the Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine reveals that the popular diabetes and weight-loss drugs Wegovy and Ozempic are linked to reduced incidence and recurrence of alcohol abuse or dependence.
The team’s findings, recently published in the journal Nature Communications, may suggest a possible new treatment for excessive alcohol use—including alcohol-use disorder (AUD), a health condition that causes about 178,000 deaths in the United States each year, according to the Centers for Disease Control.
To date, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration ...
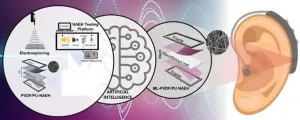
Enhancing nanofibrous acoustic energy harvesters with artificial intelligence
2024-06-03
(LOS ANGELES) June 3, 2024 – Scientists at the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI), have employed artificial intelligence techniques to improve the design and production of nanofibers used in wearable nanofiber acoustic energy harvesters (NAEH). These acoustic devices capture sound energy from the environment and convert it into electrical energy, which can then be applied in useful devices, such as hearing aids.
Many efforts have been made to capture naturally occurring and abundant energy sources ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
[Press-News.org] Study finds people of color disproportionately dropped from MedicaidOHSU, research team find process issues were twice as likely to impact Black, Hispanic people—highlighting health inequities, system improvement needs