(Press-News.org) Rutgers University–New Brunswick researchers conducting a study at a high-traffic intersection in a Jersey Shore town have found that the installation of a bike lane along the road approaching the convergence reduced driving speeds.
As many traffic analyses have identified speeding as a contributing factor in a majority of crashes, inducing such a “traffic calming” effect with a bike lane could enhance road safety and decrease the risk and severity of crashes, the researchers said. The research was published in The Journal of Urban Mobility.
“We are giving you more evidence that bike lanes save lives,” said Hannah Younes, a lead author of the study and a postdoctoral research associate at the Alan M. Voorhees Transportation Center in the Rutgers Bloustein School of Planning and Public Policy. “And it’s not only cyclists’ lives that could be saved. It’s more than that – drivers and pedestrians as well.”
The Rutgers team, which included experts from the Bloustein School, as well as from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering in the Rutgers School of Engineering and the Department of Computer Science in the Rutgers School of Arts and Sciences, focused their efforts on Cookman and Asbury Avenues in Asbury Park, N.J. Cookman, a local two-lane road, intersects with Asbury Avenue, a road that leads directly to the city’s popular Atlantic Ocean beaches.
Drivers heading to the beach often take a legal right-turn-on red at the intersection’s traffic light, gliding along the soft right turn from Cookman onto Asbury. However, Younes said, drivers frequently don’t come to a stop first, as required, but sail through, creating hazardous conditions for pedestrians and cyclists crossing at the corner.
The research team started by creating a temporary bike lane on Cookman and Asbury Avenues on the side of the road heading toward the beach, delineating it with orange road cones.
Bloustein students assisting the study then surveyed random bike and electric scooter riders using the temporary bike lane about their use of bikes and electric scooters, and their attitude toward bike lanes. Most people surveyed like bike lanes, the survey showed.
To analyze the effect of the bike lane on traffic speeds, the researchers employed computer vision techniques to classify the speed and trajectory of more than 9,000 motor vehicles. Computer vision is a subfield of AI that deals with the ability of computers to interpret and analyze visual data from the world. The researchers collected the data before creating the bike lane and after, for comparison purposes.
They found that the presence of the delineated bike lane made a difference: a 28 percent reduction in average maximum speeds and a 21 percent decrease in average speeds for vehicles turning right. For those heading straight and not turning, a smaller speed reduction of 8 percent was observed. In addition, drivers moving at a perpendicular angle to the bike lane did not slow down.
Marking the bike lanes with cones as a clearly delineated space was more effective at reducing speed than a painted-only bike lane. The painted-only bike lane was associated with a smaller speed reduction of between 11 percent and 15 percent, but only for drivers turning right.
Younes hypothesized that drivers slow down when they see a bike lane marked with the cones because the driving lane is narrower and requires more concentration, and it’s easier to notice cones or planters or some other space delineator than it is to spot painted lines on the road surface.
With pedestrian deaths rising nationally, a study such as this could contribute to the development of new traffic policies or the reversal of older ones, Younes said. Cities nationwide are adopting policies that address eliminating all fatalities and serious injuries on public roads, such as the multi-national road traffic safety project, Vision Zero, for example, she said.
A total of 7,388 pedestrian deaths occurred in 2021, representing a 13 percent increase from 2020 and 17 percent of all crash fatalities, according to the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety.
Other researchers on the study were: Clinton Andrews, a professor, Robert Noland, a distinguished professor, Wenwen Zhang, an associate professor and Leigh Ann Von Hagen, a managing director and adjunct professor, all from the Bloustein School; Jie Gong, an associate professor, and Jiahao Xia, a graduate assistant, from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering in the School of Engineering; Dimitris Metaxas, a distinguished professor, and Song Wen, a graduate assistant, in the Department of Computer Science in the School of Arts and Sciences.
END
Traffic speeds decrease when bike lane is present
Rutgers researchers make finding after looking for ways to lower the incidence of vehicle crashes
2024-06-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Proteomics uncover sexual dimorphism and immune changes in aging mice with Werner syndrome
2024-06-03
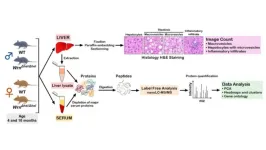
“Proteomics analysis at different ages allows us to follow the progressive biological alterations (including histological fat accumulation) in the liver according to age and/or the Wrn genotype.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 3, 2024 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 10, entitled, “Integrated liver and serum proteomics uncover sexual dimorphism and alteration of several immune response proteins in an aging Werner syndrome mouse model.”
Werner syndrome (WS) is a ...
A technique for more effective multipurpose robots
2024-06-03
CAMBRIDGE, MA – Let’s say you want to train a robot so it understands how to use tools and can then quickly learn to make repairs around your house with a hammer, wrench, and screwdriver. To do that, you would need an enormous amount of data demonstrating tool use.
Existing robotic datasets vary widely in modality — some include color images while others are composed of tactile imprints, for instance. Data could also be collected in different domains, like simulation or human demos. And each dataset ...
Oral nucleoside antiviral is progressing toward future pandemic preparedness
2024-06-03
May 23, 2024
Obeldesivir (GS-5245), a novel investigational small molecule oral antiviral, represents a new tool in the ongoing effort to prepare for future pandemics.
Several researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill’s Gillings School of Global Public Health are co-authors of a new study published online May 22 by the journal Science Translational Medicine.
The study shares findings from an academic-corporate partnership between biopharmaceutical company Gilead Sciences and the Sheahan ...
Shape and depth of ocean floor profoundly influence how carbon is stored there
2024-06-03
Key takeaways
The movement of carbon between the atmosphere, oceans and continents — or carbon cycle — regulates Earth’s climate, with the ocean playing a major role in carbon sequestration.
A new study finds that the shape and depth of the ocean floor explain up to 50% of the changes in depth at which carbon has been sequestered there over the past 80 million years.
While these changes have been previously attributed to other causes, the new finding could inform ongoing efforts to combat climate change through marine carbon sequestration.
The movement of carbon between the atmosphere, oceans and continents — the carbon ...
Airplane noise exposure may increase risk of chronic disease
2024-06-03
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Monday, June 3, 2024
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
##
Airplane Noise Exposure May Increase Risk of Chronic Disease
A new study found that people who were exposed to higher levels of noise from aircraft were more likely to have a higher body mass index, an indicator for obesity that can lead to stroke or hypertension. The findings highlight how the environment—and environmental injustices—can shape health outcomes.
Research has shown that noise from airplanes and helicopters flying overhead are far more bothersome to people than noise from other modes of transportation, ...
Mental health, lack of workplace support are leading factors driving nurses from jobs
2024-06-03
Coworker and employer support are strong predictors of nurses planning to stay in their jobs, while symptoms of depression are linked to nurses planning to leave, according to a study conducted at the height of the COVID-19 pandemic by researchers at NYU Rory Meyers College of Nursing.
The research—published in the Online Journal of Issues in Nursing, a journal of the American Nurses Association—examines both pandemic-related factors and the overall work environment for nurses and can help organizational ...
U.S. health departments experience workforce shortages and struggle to reach adequate staffing levels in public health
2024-06-03
Gaps persist in hiring enough U.S. public health workers and health departments continue to face challenges in recruiting new employees, according to a new study by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health and Indiana University. Insufficient funding, a shortage of people with public health training, and a lack of visibility for public careers, in addition to lengthy hiring processes, are cited as barriers contributing to an absence of progress for achieving a satisfactory level of workers. The results ...
Redox Science Meets Medicine at the 26th International Conference on Redox Medicine 2024 this June in Paris
2024-06-03
Redox Science Meets Medicine at the 26th International Conference on Redox Medicine 2024 this June in Paris
The 26th International Conference on Redox Medicine 2024 will take place this month, on June 27-28 at Fondation Biermans-Lapôtre in Paris, France.
With 41+ communications and participants from 20 different countries, the conference promises a diverse exchange of knowledge and ideas.
The sessions of the conference are organized around key topics, with each speaker addressing a specific ...
Albert Einstein College of Medicine names Marla Keller, MD, Executive Dean
2024-06-03
June 3, 2024—(BRONX, NY)—Marla Keller, M.D., a national leader in academic medicine and in clinical and translational research and training, has been appointed executive dean at Albert Einstein College of Medicine. In this role, Dr. Keller will work closely with Yaron Tomer, M.D., the Marilyn and Stanley M. Katz Dean at Einstein, other executive leaders at the College of Medicine and Montefiore, and the Board of Trustees to achieve the vision for the institution. As Einstein’s second most senior officer, she will drive strategic planning for the College of Medicine and provide guidance across all academic and research programs.
Dr. ...
Two-pronged attack strategy boosts immunotherapy in preclinical studies
2024-06-03
JUNE 3, 2024, NEW YORK – A novel immunotherapy approach developed by Ludwig Cancer Research scientists employs a two-pronged attack against solid tumors to boost the immune system’s ability to target and eliminate cancer cells.
The research focuses on an immunotherapy called adoptive cell transfer (ACT), which involves extracting T cells from a patient, enhancing their ability to fight cancer, expanding them in culture and reinfusing them into the patient’s body.
“While T cell therapies have shown tremendous ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
UCSB researcher bridges the worlds of general relativity and supernova astrophysics
Global exchange of knowledge and technology to significantly advance reef restoration efforts
Vision sensing for intelligent driving: technical challenges and innovative solutions
To attempt world record, researchers will use their finding that prep phase is most vital to accurate three-point shooting
AI is homogenizing human expression and thought, computer scientists and psychologists say
Severe COVID-19, flu facilitate lung cancer months or years later, new research shows
Housing displacement, employment disruption, and mental health after the 2023 Maui wildfires
GLP-1 receptor agonist use and survival among patients with type 2 diabetes and brain metastases
Solid but fluid: New materials reconfigure their entire crystal structure in response to humidity
New research reveals how development and sex shape the brain
New discovery may improve kidney disease diagnosis in black patients
What changes happen in the aging brain?
Pew awards fellowships to seven scientists advancing marine conservation
Turning cancer’s protein machinery against itself to boost immunity
Current Pharmaceutical Analysis releases Volume 22, Issue 2 with open access research
Researchers capture thermal fluctuations in polymer segments for the first time
16-year study finds major health burden in single‑ventricle heart
Disposable vapes ban could lead young adults to switch to cigarettes, study finds
[Press-News.org] Traffic speeds decrease when bike lane is presentRutgers researchers make finding after looking for ways to lower the incidence of vehicle crashes