(Press-News.org) DARIEN, IL – A new study to be presented at the SLEEP 2024 annual meeting found that drowsy driving by teenagers is a common threat to public safety on U.S. roadways.
Results of the National Sleep Foundation study show that approximately one in six adolescent drivers reported having driven drowsy. Based on these responses, the authors project that 1.7 million teenage drivers have driven drowsy, and more than 400,000 teens drive drowsy at least once per week. The majority of teens pointed to work or school schedules as factors preventing them from getting the sleep they need to drive alert, and teen drivers with jobs were more than twice as likely to have driven drowsy than teens without jobs.
“This is a troubling rate, especially given that teens are new drivers with relatively low opportunity to have engaged in drowsy driving when compared to the lifetime of driving opportunities in adults,” said principal investigator Joseph Dzierzewski, who has a doctorate in clinical psychology and is the vice president of research and scientific affairs at the National Sleep Foundation in Washington, D.C.
Additional findings reveal that when asked about the risks associated with drowsy driving, 95% of teens said drowsy driving is extremely or very risky. However, when asked about the likelihood of drunk, drugged, distracted and drowsy driving leading to death or serious injury, drowsy driving was seen as having the lowest risk of death or serious harm.
Formally, the National Sleep Foundation developed and has produced Drowsy Driving Prevention Week® since 2007 and recently published a new drowsy driving position statement. The American Academy of Sleep Medicine identifies drowsy driving as a pervasive threat to public health and recommends that states mandate instruction in drowsy driving education as a requirement for driver’s education programs, provide comprehensive information about drowsy driving in state curricula and driver’s manuals, and include questions related to drowsy driving on driver’s license exams. Additionally, the AASM encourages every driver to take responsibility for staying “Awake at the Wheel” by making it a daily priority to get sufficient sleep, refusing to drive when sleep-deprived, recognizing the signs of drowsiness, and pulling off the road to a safe location when sleepy.
The study involved a nationally-representative, probability-based survey of 1,124 U.S. participants aged 13 to 17 years to assess drowsy driving prevalence, frequency and beliefs. Survey respondents reported whether they have ever driven while so tired they had a hard time keeping their eyes open, how often they did so, what kept them from getting the sleep needed to drive alert, and the perceived risks associated with drowsy driving.
With motor vehicle crashes being a leading cause of death among U.S. teenagers, this research sheds light on the increased attention needed for this preventable public health concern.
“Drowsy driving represents an immediate, and potentially tragic, consequence of poor sleep health, residing at the literal intersection of sleep health and public safety,” Dzierzewski said.
The research abstract was published recently in an online supplement of the journal Sleep and will be presented Wednesday, June 5, during SLEEP 2024 in Houston. SLEEP is the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies, a joint venture of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and the Sleep Research Society.
###
Abstract Title: Population-Based Estimates of Drowsy Driving Among US Teens: A National Sleep Foundation Study
Abstract ID: 0166
Poster Presentation Date: Wednesday, June 5, from 11-11:45 a.m. CDT, Board 20
Presenter: Joseph Dzierzewski, Ph.D.
About the Associated Professional Sleep Societies, LLC
The APSS is a joint venture of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and the Sleep Research Society. The APSS organizes the SLEEP annual meeting each June (sleepmeeting.org).
About the American Academy of Sleep Medicine
Established in 1975, the AASM advances sleep care and enhances sleep health to improve lives. The AASM has a combined membership of 12,000 accredited sleep centers and individuals, including physicians, scientists and other health care professionals who care for patients with sleep disorders. As the leader in the sleep field, the AASM sets standards and promotes excellence in sleep medicine health care, education and research (aasm.org).
About the Sleep Research Society
The SRS is a professional membership society that advances sleep and circadian science. The SRS provides forums for the exchange of information, establishes and maintains standards of reporting and classifies data in the field of sleep research, and collaborates with other organizations to foster scientific investigation on sleep and its disorders. The SRS also publishes the peer-reviewed, scientific journals Sleep and Sleep Advances (sleepresearchsociety.org).
END
DARIEN, IL – A new study to be presented at the SLEEP 2024 annual meeting is the first to find that episodic hypoxemia and hypoxic burden related to obstructive sleep apnea are associated with the risk of accelerated lung cancer reoccurrence.
Results show that a 4% oxygen desaturation index of more than 15 and time spent in desaturation events were risk factors for cancer reappearance in less than two years. Measures of hypoxic burden such as time spent below 89% oxygen saturation, average oxygen saturation value below 89%, and single nadir oxygen levels, showed a similar association. After adjustment for potential confounders, average oxygen saturation below 89% and single minimum ...
DARIEN, IL – A new study to be presented at the SLEEP 2024 annual meeting found that healthy sleep has a positive impact on gratitude, resilience and flourishing in adults.
Results show that subjective sleepiness and mood disturbances improved with earlier bedtimes that extended sleep by an average of 46 minutes per night and worsened with later bedtimes that reduced nightly sleep by an average of 37 minutes. Measures of flourishing, resilience and gratitude significantly improved across the week with sleep extension and significantly worsened with sleep restriction. Sleep-extended ...
DARIEN, IL – A new study to be presented at the SLEEP 2024 annual meeting offers a framework for an objective, non-invasive and zero-effort sleep monitoring system utilizing smart thermostats equipped with motion sensors.
Results show that smart thermostats identified three distinct sleep quality clusters, with clear variations in sleep duration, disturbances and efficiency. Comparative analysis underscored the heterogeneity in sleep quality, highlighting the potential of smart devices and NextGen IoT data sources in identifying sleep patterns and contributing to sleep research ...
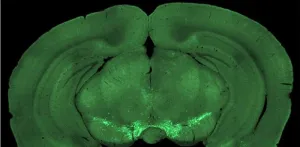
Ever wondered how your brain decides when to act? Initiating actions with a specific goal in mind is a complex process. Previous research has identified certain parts of the brain and chemical signals involved. However, it remains unclear what information these signals convey and how they spark initiative.
Recent research reported in Neurophotonics dives into this mystery by investigating how mice time their actions in pursuit of rewards, exploring the role of a specific brain pathway called the mesocortical pathway, in the context of self-initiated ...
PRESS RELEASE UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL JUNE 4, 2024 at 5 a.m. US EASTERN TIME
CONTACT: Julio Poletti, Public Relations Manager, Julio.poletti@dmns.org, 917.783.6760
DENVER (May 28, 2024) — The Denver Museum of Nature & Science announces the discovery and display of a teenage Tyrannosaurus rex fossil— affectionately named “Teen Rex” — in its temporary experience, "Discovering Teen Rex" opening to the public on June 21, at 1:30 p.m. The fossil was discovered in the badlands of North Dakota by ...
May 30, 2024, Leiden, The Netherlands - A 3D model of imitation blood vessels will make it possible to see exactly how snake venom attacks blood vessels, without having to use laboratory animals. This new research model, called an organ-on-a-chip, was developed by a research team from Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, MIMETAS and Naturalis Biodiversity Center.
Roughly one hundred thousand people die annually from the effects of a snake bite and four times as many sustain chronic injuries. Research into how snake venom ...
Floating solar photovoltaic panels could supply all the electricity needs of some countries, new research has shown.
The study, by researchers from Bangor and Lancaster Universities and the UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology, aimed to calculate the global potential for deploying low-carbon floating solar arrays. The researchers calculated the daily electrical output for floating photovoltaics (FPV) on nearly 68,000 lakes and reservoirs around the world, using available climate data for each location.
The researchers’ ...
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Tuesday, June 4, 2024
DALLAS, June 4, 2024 — Driven by an older, more diverse population, along with a significant increase in risk factors including high blood pressure and obesity, total costs related to cardiovascular disease (CVD) conditions are likely to triple by 2050, according to projections from the American Heart Association, observing 100 years of lifesaving service as the world’s leading nonprofit organization focused on heart and brain ...
June 4, 2024—(BRONX, NY)—The underdiagnosis of dementia, especially among Black and Hispanic patients, is a long-standing challenge in medicine. A new study, published today in Nature Medicine, finds that an easy, five-minute assessment paired with recommendations built into the electronic medical record system led to a three-fold improvement in diagnosis and treatment for patients in a primary care setting compared to a control group. The “5-Cog paradigm,” which was developed by researchers at Albert Einstein College of Medicine and Montefiore Health System, dramatically enhances ...
New research has given the clearest ever picture of young children’s developing brains, using a wearable brain scanner to map electrical brain activity. The work opens up new possibilities for tracking how critical developmental milestones, like walking and talking, are underpinned by changing brain function, and how neurodevelopmental conditions like autism emerge.
The research team, led by scientists from the University of Nottingham’s School of Physics and Astronomy, used a novel design of magnetoencephalography ...