(Press-News.org) WHAT:
Two clinical trials have launched to examine a novel long-acting form of HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) in cisgender women and people who inject drugs. The mid-stage studies will assess the safety, acceptability, and pharmacokinetic (how a drug moves through the body) of lenacapavir, an antiretroviral drug administered by injection every six months. The studies are sponsored and funded by Gilead Sciences, Inc., and implemented through the HIV Prevention Trails Network (HPTN). The HPTN is supported by grants from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, with scientific collaboration on this study and others from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) as well as co-funding from NIDA and other NIH institutes.
Lenacapavir is already approved by the Food and Drug Administration for HIV treatment, in combination with other antiretroviral therapy, of heavily treatment-experienced individuals, whose HIV infections cannot be successfully treated with other available treatments due to resistance, intolerance, or safety considerations with other drugs and developed multidrug resistance. Lenacapavir is the first of a class of drugs called capsid inhibitors to be FDA-approved for treating HIV infection. It is the first long-acting injectable to be offered with administration just once every six months. Cisgender women—people who self-identify as female and were assigned female sex at birth—and people who inject drugs accounted for 18% and 7% of new HIV diagnoses in the United States in 2021, respectively. Both population groups have been underrepresented in HIV clinical studies, as have transgender people, pregnant people and U.S. communities of color. Both trials complement ongoing large efficacy studies and are intended to provide insights on how these two priority populations experience lenacapavir-based HIV PrEP.
The studies will take place at HPTN sites in the United States and enroll people who might benefit from taking PrEP. The first trial will enroll cisgender women, with a focus on making enrollment accessible to women who self-identify as Black and/or Latina. The second trial will enroll a diverse group of people who inject drugs. In both studies, participants will be randomly assigned to receive either injectable lenacapavir or an FDA-approved PrEP formulation consisting of oral tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and emtricitabine. Participants’ health will be monitored closely throughout the study. Participants will provide laboratory samples and give qualitative feedback on their experience taking each form of PrEP.
The studies will add important clinical data to a global manufacturer-led clinical development program for lenacapavir as HIV PrEP. NIH is supporting the implementation of these two studies through its clinical trials networks to help ensure the meaningful inclusion of diverse and representative populations in clinical research, so that everyone can contribute to scientific progress and benefit from its applications.
For more information about these trials, please visit ClinicalTrials.gov study identifiers NCT06101329 and NCT06101342.
WHO:
Sheryl Zwerski, D.N.P., director of the Prevention Sciences Program in NIAID’s Division of AIDS, is available to discuss these studies.
CONTACT:
To schedule interviews, please contact the NIAID News & Science Writing Branch, (301) 402-1663, NIAIDNews@niaid.nih.gov.
NIAID conducts and supports research—at NIH, throughout the United States, and worldwide—to study the causes of infectious and immune-mediated diseases, and to develop better means of preventing, diagnosing and treating these illnesses. News releases, fact sheets and other NIAID-related materials are available on the NIAID website.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit http://www.nih.gov/.
NIH...Turning Discovery Into Health®
END
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Winters can be tough on managed honey bee colonies, with beekeepers in the United States reporting that one-third of their colonies die each winter. A new study by Penn State researchers has found that using not one but multiple pest treatments may help bees make it to spring.
The researchers found that beekeepers who used a combination of treatments for Varroa mites — tiny parasites that can weaken and spread diseases to honey bees — had higher winter colony survival than those who used only one type of treatment. The findings were published in the Journal of Insect Science.
Additionally, ...
Getting into graduate school to become a doctor or a dentist is difficult. By some estimates, only about 37% to 42% of students who apply to medical or dental school are accepted.
To help pre-medical and -dental students achieve their dreams, UT Arlington created a program called the Health Professions Advisory Committee (HPAC). The odds of graduate school admission for students participating in HPAC is significantly higher than average, with an estimated 85% succeeding.
This is just one of several UT Arlington initiatives helping alleviate ...
CORVALLIS, Ore. – A 15-year period ending in 2020 that included a marine heat wave and a sea star wasting disease epidemic saw major changes in the groups of organisms that live along the rocky shores of the Pacific Northwest.
The study by Oregon State University scientists, involving four capes in Oregon and California, suggests these communities of species may have low resilience to climate change. Findings were published Monday in Nature Ecology & Evolution and.
Researchers learned that ...
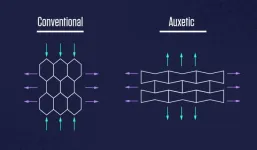
Imagine pulling on the long ends of a rectangular piece of rubber.
It should become narrower and thinner.
But what if, instead, it got wider and fatter?
Now, push in on those same ends. What if the rubber became narrower and thinner?
Such common-sense-defying materials do exist. They’re called auxetics, and they have a raft of unique properties that make them well-suited for sneaker insoles, bomb-resilient buildings, car bumpers and clothing.
Despite this great potential, auxetic products have been slow to market. Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the University of Chicago hope to change this.
In a new study published ...
The Brain & Behavior Research Foundation (BBRF) is hosting a free webinar, “Neurocognitively-Defined Subtypes in Bipolar Disorder: A Path to More Personalized Treatments” on Tuesday, June 11, 2024, at 2:00 pm ET. The presenter, Katherine E. Burdick, PhD, is the Jonathan F. Borus, MD Distinguished Chair in Psychiatry and the Vice Chair for Research in Psychiatry at Brigham and Women’s Hospital. She is the Director of the Mood and Psychosis Research Program at BWH and a Professor at Harvard Medical ...
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Polarized light waves spin clockwise or counterclockwise as they travel, with one direction behaving differently than the other as it interacts with molecules. This directionality, called chirality or handedness, could provide a way to identify and sort specific molecules for use in biomedicine applications, but researchers have had limited control over the direction of the waves — until now.
Using metamaterials, a team of electrical engineering researchers from Penn State and the University of Nebraska-Lincoln ...
PHILADELPHIA — (June 04, 2024) — Advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is a deadly form of kidney cancer with few treatment options; even with new immunotherapies, only around one in 10 patients ultimately survive.
Antibody therapies called bispecific T cell engagers (BTEs) have emerged as effective treatments for some blood cancers but have been more difficult to develop for solid tumors. While clinically successful, first-generation BTEs suffer a short half-life. Now, Wistar scientists have built upon BTE technology to develop new and improved recombinant and synthetic ...
Researchers at the University of São Paulo (USP) in Brazil have shown for the first time that SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, can remain in the sperm of patients for up to 90 days after hospital discharge and up to 110 days after the initial infection, reducing semen quality. The study is reported in an article published in the journal Andrology. The authors suggest that people who plan to have children should observe a period of “quarantine” after recovering ...
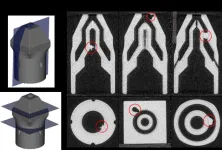
Researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have developed a new method for detecting defects in additively manufactured components.
One of the most important tasks in any factory is to determine whether a manufactured component is free of defects. In additive manufacturing (3D printing), it can be particularly challenging to find defects, because additive manufacturing can make components that have complex three-dimensional shapes and important internal features that are not easily observed.
The novel technology uses deep machine ...
TREX1 is a gene that is supposed to direct the maintenance of the entire body’s DNA, but new research shows that when people are born with mutated TREX1, it causes catastrophic damage to the DNA over time, resulting in a deadly rare disease called retinal vasculopathy with cerebral leukoencephalopathy (RVCL). Published in Nature Communications, the research was led by teams at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and the Brain Research Institute at Niigata University in Japan.
While it was already known that a mutation in TREX1 was behind RVCL, the mechanism by which ...