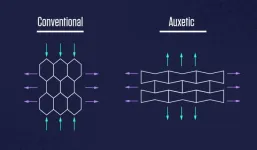
(Press-News.org) Imagine pulling on the long ends of a rectangular piece of rubber.
It should become narrower and thinner.
But what if, instead, it got wider and fatter?
Now, push in on those same ends. What if the rubber became narrower and thinner?
Such common-sense-defying materials do exist. They’re called auxetics, and they have a raft of unique properties that make them well-suited for sneaker insoles, bomb-resilient buildings, car bumpers and clothing.
Despite this great potential, auxetic products have been slow to market. Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the University of Chicago hope to change this.
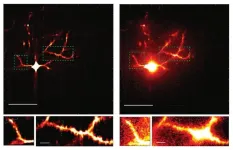
In a new study published in NPJ Computational Materials, they announced they’ve developed a new tool that makes designing materials with auxetic properties easier and faster. An algorithm, the tool enables precise three-dimensional design of auxetics.
“It’s a huge advance for auxetics,” said NIST materials research engineer Edwin Chan, a study co-author. “We can actually optimize the material to have whatever particular mechanical properties and behavior that you want.”
The behavior of elastic materials is partially described by Poisson’s ratio, which explains how the material changes shape when you stretch or squeeze it in one direction.
Most materials have a positive Poisson’s ratio, which means squeezing them in one direction will make them wider and/or thicker in other directions. Stretching them makes them narrower and/or thinner.
Auxetics have a negative value of Poisson’s ratio and do exactly the reverse.
When you punch a nonauxetic material, it gets thinner and expands laterally. When you punch an auxetic, the material bunches up and narrows in width. Under the right circumstances, this provides greater resistance to impact.
For example, if you punch a bag full of water (like you would carry for hiking), the water within it will flow away from the point of impact. If the bag were full of an auxetic foam when you punched it, though, the material would grow denser and stiffen.
This is one of the reasons auxetics are being considered for use in buildings and automobiles. They have the potential to offer greater protection from explosions and collisions. In a sneaker insole, an auxetic gel or rubber foam might better cushion the foot when it strikes the ground.
In clothing, auxetic nylons, fibers and other synthetic materials could prove more comfortable than traditional materials. Since they widen when stretched, they more effectively distribute pressure across the body, potentially relieving strain on the back, joints, neck or shoulders. One study on using auxetic materials in bra straps found that “auxetic polyester and nylon structures exhibited remarkable pressure distribution capabilities.”
The design tool devised by the NIST and University of Chicago scientists is an “inverse design” algorithm, which means users can input their desired value for their auxetic material’s Poisson’s ratio. The algorithm then proposes an optimized structure for the material.
Another way of expressing Poisson’s ratio is that it describes the relationship between shape and volume when one of these changes. The new algorithm allows for fine-tuning this relationship to create auxetic materials that behave in ways you couldn’t find in nature.
“Our research is a beautiful example of theoretical, experimental and computational science working together to realize something new,” said NIST materials research engineer Marcos Reyes-Martinez. “Having a way to make auxetics better will allow them to become more prevalent in our everyday lives.”
The researchers patented the algorithm as well as the underlying methodology and its implementation using 3D printing.
END
A new way of designing auxetic materials
Auxetics defy common sense, widening when stretched and narrowing when compressed. NIST researchers have now made the process of using them much easier.
2024-06-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Neurocognitively-defined subtypes in bipolar disorder: a path to more personalized treatments
2024-06-04
The Brain & Behavior Research Foundation (BBRF) is hosting a free webinar, “Neurocognitively-Defined Subtypes in Bipolar Disorder: A Path to More Personalized Treatments” on Tuesday, June 11, 2024, at 2:00 pm ET. The presenter, Katherine E. Burdick, PhD, is the Jonathan F. Borus, MD Distinguished Chair in Psychiatry and the Vice Chair for Research in Psychiatry at Brigham and Women’s Hospital. She is the Director of the Mood and Psychosis Research Program at BWH and a Professor at Harvard Medical ...
Shining a light on molecules: L-shaped metamaterials can control light direction
2024-06-04
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Polarized light waves spin clockwise or counterclockwise as they travel, with one direction behaving differently than the other as it interacts with molecules. This directionality, called chirality or handedness, could provide a way to identify and sort specific molecules for use in biomedicine applications, but researchers have had limited control over the direction of the waves — until now.
Using metamaterials, a team of electrical engineering researchers from Penn State and the University of Nebraska-Lincoln ...
Wistar scientists develop novel antibody treatment for kidney cancer
2024-06-04
PHILADELPHIA — (June 04, 2024) — Advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is a deadly form of kidney cancer with few treatment options; even with new immunotherapies, only around one in 10 patients ultimately survive.
Antibody therapies called bispecific T cell engagers (BTEs) have emerged as effective treatments for some blood cancers but have been more difficult to develop for solid tumors. While clinically successful, first-generation BTEs suffer a short half-life. Now, Wistar scientists have built upon BTE technology to develop new and improved recombinant and synthetic ...
Virus that causes COVID-19 can remain in sperm for 110 days after infection
2024-06-04
Researchers at the University of São Paulo (USP) in Brazil have shown for the first time that SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, can remain in the sperm of patients for up to 90 days after hospital discharge and up to 110 days after the initial infection, reducing semen quality. The study is reported in an article published in the journal Andrology. The authors suggest that people who plan to have children should observe a period of “quarantine” after recovering ...
Researchers use machine learning to detect defects in additive manufacturing
2024-06-04
Researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have developed a new method for detecting defects in additively manufactured components.
One of the most important tasks in any factory is to determine whether a manufactured component is free of defects. In additive manufacturing (3D printing), it can be particularly challenging to find defects, because additive manufacturing can make components that have complex three-dimensional shapes and important internal features that are not easily observed.
The novel technology uses deep machine ...
Rare disease’s DNA-damaging mutation could have consequences for more common conditions
2024-06-04
TREX1 is a gene that is supposed to direct the maintenance of the entire body’s DNA, but new research shows that when people are born with mutated TREX1, it causes catastrophic damage to the DNA over time, resulting in a deadly rare disease called retinal vasculopathy with cerebral leukoencephalopathy (RVCL). Published in Nature Communications, the research was led by teams at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and the Brain Research Institute at Niigata University in Japan.
While it was already known that a mutation in TREX1 was behind RVCL, the mechanism by which ...
Exploring three frontiers in marine biomass and blue carbon capture
2024-06-04
A new study offers first-time insights into three emerging climate innovations to safeguard or increase the carbon naturally captured by ocean and coastal ecosystems: rapid interventions to save the Great Barrier Reef, satellite-tracked kelp beds in the deep ocean, and seagrass nurseries in the United Kingdom. The research, published in Environmental Science & Policy and co-authored by leading climate scholars at Boston University, Aarhus University, and the University of Sussex Business School, advances knowledge of understudied interventions in marine ...
Microscope system sharpens scientists’ view of neural circuit connections
2024-06-04
The brain’s ability to learn comes from “plasticity,” in which neurons constantly edit and remodel the tiny connections called synapses that they make with other neurons to form circuits. To study plasticity, neuroscientists seek to track it at high resolution across whole cells, but plasticity doesn’t wait for slow microscopes to keep pace and brain tissue is notorious for scattering light and making images fuzzy. In a paper in Scientific Reports, a collaboration of MIT engineers and neuroscientists describes a new microscopy system designed for fast, clear, and frequent imaging of the living brain.
The system, ...
VHIO researchers demonstrate the utility of high-sensitivity liquid biopsy to predict and monitor response to immunotherapy
2024-06-04
The liquid biopsy technique applied in this work is based on the sequencing of the entire tumor genome from 138 patients and the monitoring of mutations in the blood. This approach achieves high sensitivity in detecting the tumor signal in the blood (1/1,000,000 DNA molecules), and the patterns found reflect how patients respond to immunotherapy.
This study is part of the Comprehensive Program of Cancer Immunotherapy and Immunology (CAIMI) at VHIO, funded by the BBVA Foundation, and is co-led by Dr Rodrigo Toledo, head of the Biomarkers and Clonal Dynamics Group at the Vall d’Hebron Institute of Oncology (VHIO), ...
Muscle disorder caused by key protein mutations uncovered in new study
2024-06-04
A recent study has found that the SMCHD1 protein plays a key role in controlling how genes are processed, which affects the progression of Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy (FSHD). This discovery about SMCHD1's function in gene regulation is important because it opens new possibilities for developing targeted therapeutic strategies to combat the disease. By understanding more about how SMCHD1 works, scientists can explore new ways to fight the disease.
A recent study by MD-PhD student Eden Engal under the guidance of Dr. Yotam Drier and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] A new way of designing auxetic materialsAuxetics defy common sense, widening when stretched and narrowing when compressed. NIST researchers have now made the process of using them much easier.