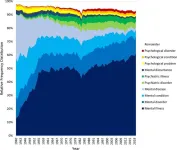
(Press-News.org) A new survey of nearly 340,000 texts spanning 79 years shows that generic terms in mental health have shifted away from words like “disease” and “disturbance” and toward “psychiatric” and “mental health,” with “mental illness” becoming the most-used term. Nick Haslam and Naomi Baes at the University of Melbourne in Australia present these findings in the new open-access journal PLOS Mental Health on June 4.
The authors state that while words such as “crazy” and “lunatic” are clearly stigmatizing to modern ears, mental health professionals and communities continue to wrestle with other words for mental ill health. But while experts and patients debate “depressed person” or “person with depression,” larger umbrella terms, such as “mental illness” itself, have not been studied. To examine how these overarching terms have changed over time, Haslam and Baes analyzed two large collections of texts—Google Books, and a combination of the Corpus of Historical American English, and the Corpus of Contemporary American English. The first collection contained over 1 trillion words drawn from English language books, and the second included over 700 million words from fiction and non-fiction books, magazines, newspapers, spoken language, and TV shows. For the period from 1940-2019, the scientists looked at the popularity of 24 different generic terms for mental ill health. The terms were two- or three-word phrases that combined four adjectives—“mental,” “mental health,” “psychiatric,” and “psychological”—with six nouns “condition,” “disease,” “disorder,” “disturbance,” “illness,” and “problem.”
Generic terms for mental ill health appeared more than twice as often in 2019 as in 1940, as psychiatry, clinical psychology and other mental health professions grew, and the wider public began to recognize the importance of mental health. Phrases which included “disease,” and “disturbance” grew less common over time. Phrases that included words like “mental health,” “psychiatric,” and “illness” we used more commonly. In particular, “mental illness,” after a spike in popularity between the 1940s and 1960s, reigned as the most-used term. It’s important to note that the authors here have specifically looked at numerical frequency of word usage in written culture, rather than community word preferences over time. Based on these results, the scientists suggest further studies should focus on how mental health language is used by scientists and by the general public, and how that language affects people experiencing mental ill health.
The authors add: "Our study shows that the terms people use to refer to mental ill health have evolved over the past 80 years, but "mental illness" has steadily risen to become the most popular expression."
PLOS Mental Health recognizes that terminology can be sensitive, regardless of the choice of words, and interpreted differently between individuals and communities. In this paper, although the frequency of the use of certain terminology is closely assessed, it does not necessarily reflect preferences of all communities. At PLOS Mental Health, we recognize that it is important to strike a balance between not over-medicalizing but also not trivializing mental health conditions and experiences and this balance will be unique to different contexts.
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS Mental Health: https://journals.plos.org/mentalhealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmen.0000032
Citation: Haslam N, Baes N (2024) What should we call mental ill health? Historical shifts in the popularity of generic terms. PLOS Ment Health 1(1): e0000032. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000032
Author Countries: Australia
Funding: This work was supported by Australian Research Council Discovery Project DP210103984 to NH. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
In “mental illness” and “mental health”: how language around psychiatric conditions shifts
A survey of terms over 79 years shows language moving away from “disease” and toward “illness”
2024-06-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Methods to quit smoking effective regardless of mental health history
2024-06-04
Sarah Jackson and colleagues from University College London and King’s College London branches of the SPECTRUM Consortium conducted a survey to study how mental health relates to methods people use to quit smoking, also known as smoking cessation aids. While the number of adults who smoke cigarettes has declined globally, people with mental health conditions are more likely to smoke and to do so more heavily. Because of these differences in tobacco use, the researchers theorized that the effectiveness of smoking cessation aids may be altered in individuals with a mental health condition. However, in their ...
Lived experience should be centered in future mental health research, say people with mental health conditions and their families and carers in nationwide Australian survey
2024-06-04
Lived experience should be centered in future mental health research, say people with mental health conditions and their families and carers in nationwide Australian survey.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/mentalhealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmen.0000010
Article Title: Experience is central and connections matter: A Leximancer analysis of the research priorities of people with lived experience of mental health issues in Australia
Author Countries: Australia
Funding: The ALIVE National Centre for Mental Health Research Translation is supported by a grant from the National Health and Medical Research Council (GNT2002047) ...
Internet addiction affects the behavior and development of adolescents
2024-06-04
Adolescents with an internet addiction undergo changes in the brain that could lead to additional addictive behaviour and tendencies, finds a new study by UCL researchers.
The findings, published in PLOS Mental Health, reviewed 12 articles involving 237 young people aged 10-19 with a formal diagnosis of internet addiction between 2013 and 2023.
Internet addiction has been defined as a person’s inability to resist the urge to use the internet, negatively impacting their psychological wellbeing, as well as their social, academic and professional lives.
The studies used functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to inspect the functional connectivity (how regions of ...
Giant viruses found on Greenland ice sheet
2024-06-04
Every spring when the sun rises in the Arctic after months of darkness, life returns. The polar bears pop up from their winter lairs, the arctic tern soar back from their long journey south and the musk oxen wade north.
But the animals are not the only life being reawakened by the spring sun. Algae lying dormant on the ice starts blooming in spring blackening large areas of the ice.
When the ice blackens it’s ability to reflect the sun diminishes and this accelerates the melting of the ice. Increased melting exacerbates global ...
SNMMI Annual Meeting to take place June 8-11, 2024
2024-06-04
WHAT: The Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2024 Annual Meeting
The field of nuclear medicine is undergoing rapid and widespread growth—offering patients increasingly precise, tailored, painless diagnosis and treatment with minimal side effects and exceptional results.
This year’s program will focus on new radiopharmaceuticals, instrumentation, and techniques for managing a wide range of diseases, from cancer, brain, and heart disease to infection and inflammation.
The meeting will convene more than 6,500 attendees from around the globe. With more than 100 ...
Flying saucers and alien abductions: New book explores history of UFOs
2024-06-04
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — The end of the Second World War ushered in a new age, one dominated by novel technologies, the Cold War, the threat of nuclear destruction — and the first reported UFO sightings.
Humans have witnessed strange aerial events since ancient times, but what makes UFOs unique is that the term “unidentified flying object” represents both a concept and a theory, according to Greg Eghigian, professor of history and bioethics at Penn State. In his new book, “After the Flying Saucers Came: A Global History of the UFO Phenomenon,” Eghigian explores how individuals, scientists, governments ...
Lost in lockdown: Study reveals feeling isolated from others can warp our perception of time
2024-06-04
Feelings of loneliness and social isolation during the pandemic left many people confused about the order of events and struggling to remember what day of the week it was, a new study reveals.
The research, from the University of York, looked at the psychological impact of the pandemic, which spread to the UK in March 2020, through the lens of disorientation.
The researchers asked more than 3,300 French participants nearly 60 questions analysing the psychological effects of lockdowns. The survey took place during an acute phase of restrictions when there was a lockdown followed by a strict curfew.
The findings ...
U.S. clinical trials begin for twice-yearly HIV prevention injection
2024-06-04
WHAT:
Two clinical trials have launched to examine a novel long-acting form of HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) in cisgender women and people who inject drugs. The mid-stage studies will assess the safety, acceptability, and pharmacokinetic (how a drug moves through the body) of lenacapavir, an antiretroviral drug administered by injection every six months. The studies are sponsored and funded by Gilead Sciences, Inc., and implemented through the HIV Prevention Trails Network (HPTN). The HPTN is supported by grants from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of ...
Combining pest treatments may be key to helping honey bees survive the winter
2024-06-04
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Winters can be tough on managed honey bee colonies, with beekeepers in the United States reporting that one-third of their colonies die each winter. A new study by Penn State researchers has found that using not one but multiple pest treatments may help bees make it to spring.
The researchers found that beekeepers who used a combination of treatments for Varroa mites — tiny parasites that can weaken and spread diseases to honey bees — had higher winter colony survival than those who used only one type of treatment. The findings were published in the Journal of Insect Science.
Additionally, ...
UTA program helps students achieve medical school dreams
2024-06-04
Getting into graduate school to become a doctor or a dentist is difficult. By some estimates, only about 37% to 42% of students who apply to medical or dental school are accepted.
To help pre-medical and -dental students achieve their dreams, UT Arlington created a program called the Health Professions Advisory Committee (HPAC). The odds of graduate school admission for students participating in HPAC is significantly higher than average, with an estimated 85% succeeding.
This is just one of several UT Arlington initiatives helping alleviate ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] In “mental illness” and “mental health”: how language around psychiatric conditions shiftsA survey of terms over 79 years shows language moving away from “disease” and toward “illness”