SNMMI Annual Meeting to take place June 8-11, 2024
In-depth research highlights how nuclear medicine provides more effective and less costly diagnosis and treatment
2024-06-04
(Press-News.org) WHAT: The Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2024 Annual Meeting
The field of nuclear medicine is undergoing rapid and widespread growth—offering patients increasingly precise, tailored, painless diagnosis and treatment with minimal side effects and exceptional results.
This year’s program will focus on new radiopharmaceuticals, instrumentation, and techniques for managing a wide range of diseases, from cancer, brain, and heart disease to infection and inflammation.
The meeting will convene more than 6,500 attendees from around the globe. With more than 100 scientific and CE sessions offered, as well as a completely reimagined Science Pavilion, there will be no shortage of high-quality education and cutting-edge research.
WHEN: June 8-11, 2024
WHERE: Metro Toronto Convention Centre, Toronto, Ontario OR Virtual
The SNMMI 2024 Annual Meeting is a hybrid event, allowing attendance both in person and virtually. The virtual meeting will utilize an innovative, interactive platform to offer live continuing education sessions, on-demand access to hundreds of scientific abstracts, a cutting-edge exhibit hall, and networking events—all in a flexible format designed to accommodate any schedule.
HOW: **Media must register in order to gain access to the meeting.**
To register, please contact Rebecca Maxey, SNMMI Director of Communications, at: rmaxey@snmmi.org or (703) 652-6772.
###
About the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging
The Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) is an international scientific and medical organization dedicated to advancing nuclear medicine and molecular imaging, vital elements of precision medicine that allow diagnosis and treatment to be tailored to individual patients in order to achieve the best possible outcomes. For more information, visit www.snmmi.org.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-06-04
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — The end of the Second World War ushered in a new age, one dominated by novel technologies, the Cold War, the threat of nuclear destruction — and the first reported UFO sightings.
Humans have witnessed strange aerial events since ancient times, but what makes UFOs unique is that the term “unidentified flying object” represents both a concept and a theory, according to Greg Eghigian, professor of history and bioethics at Penn State. In his new book, “After the Flying Saucers Came: A Global History of the UFO Phenomenon,” Eghigian explores how individuals, scientists, governments ...
2024-06-04
Feelings of loneliness and social isolation during the pandemic left many people confused about the order of events and struggling to remember what day of the week it was, a new study reveals.
The research, from the University of York, looked at the psychological impact of the pandemic, which spread to the UK in March 2020, through the lens of disorientation.
The researchers asked more than 3,300 French participants nearly 60 questions analysing the psychological effects of lockdowns. The survey took place during an acute phase of restrictions when there was a lockdown followed by a strict curfew.
The findings ...
2024-06-04
WHAT:
Two clinical trials have launched to examine a novel long-acting form of HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) in cisgender women and people who inject drugs. The mid-stage studies will assess the safety, acceptability, and pharmacokinetic (how a drug moves through the body) of lenacapavir, an antiretroviral drug administered by injection every six months. The studies are sponsored and funded by Gilead Sciences, Inc., and implemented through the HIV Prevention Trails Network (HPTN). The HPTN is supported by grants from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of ...
2024-06-04
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Winters can be tough on managed honey bee colonies, with beekeepers in the United States reporting that one-third of their colonies die each winter. A new study by Penn State researchers has found that using not one but multiple pest treatments may help bees make it to spring.
The researchers found that beekeepers who used a combination of treatments for Varroa mites — tiny parasites that can weaken and spread diseases to honey bees — had higher winter colony survival than those who used only one type of treatment. The findings were published in the Journal of Insect Science.
Additionally, ...
2024-06-04
Getting into graduate school to become a doctor or a dentist is difficult. By some estimates, only about 37% to 42% of students who apply to medical or dental school are accepted.
To help pre-medical and -dental students achieve their dreams, UT Arlington created a program called the Health Professions Advisory Committee (HPAC). The odds of graduate school admission for students participating in HPAC is significantly higher than average, with an estimated 85% succeeding.
This is just one of several UT Arlington initiatives helping alleviate ...
2024-06-04
CORVALLIS, Ore. – A 15-year period ending in 2020 that included a marine heat wave and a sea star wasting disease epidemic saw major changes in the groups of organisms that live along the rocky shores of the Pacific Northwest.
The study by Oregon State University scientists, involving four capes in Oregon and California, suggests these communities of species may have low resilience to climate change. Findings were published Monday in Nature Ecology & Evolution and.
Researchers learned that ...
2024-06-04
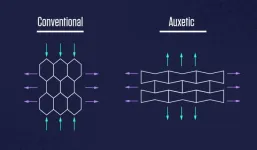
Imagine pulling on the long ends of a rectangular piece of rubber.
It should become narrower and thinner.
But what if, instead, it got wider and fatter?
Now, push in on those same ends. What if the rubber became narrower and thinner?
Such common-sense-defying materials do exist. They’re called auxetics, and they have a raft of unique properties that make them well-suited for sneaker insoles, bomb-resilient buildings, car bumpers and clothing.
Despite this great potential, auxetic products have been slow to market. Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the University of Chicago hope to change this.
In a new study published ...
2024-06-04
The Brain & Behavior Research Foundation (BBRF) is hosting a free webinar, “Neurocognitively-Defined Subtypes in Bipolar Disorder: A Path to More Personalized Treatments” on Tuesday, June 11, 2024, at 2:00 pm ET. The presenter, Katherine E. Burdick, PhD, is the Jonathan F. Borus, MD Distinguished Chair in Psychiatry and the Vice Chair for Research in Psychiatry at Brigham and Women’s Hospital. She is the Director of the Mood and Psychosis Research Program at BWH and a Professor at Harvard Medical ...
2024-06-04
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Polarized light waves spin clockwise or counterclockwise as they travel, with one direction behaving differently than the other as it interacts with molecules. This directionality, called chirality or handedness, could provide a way to identify and sort specific molecules for use in biomedicine applications, but researchers have had limited control over the direction of the waves — until now.
Using metamaterials, a team of electrical engineering researchers from Penn State and the University of Nebraska-Lincoln ...
2024-06-04
PHILADELPHIA — (June 04, 2024) — Advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is a deadly form of kidney cancer with few treatment options; even with new immunotherapies, only around one in 10 patients ultimately survive.
Antibody therapies called bispecific T cell engagers (BTEs) have emerged as effective treatments for some blood cancers but have been more difficult to develop for solid tumors. While clinically successful, first-generation BTEs suffer a short half-life. Now, Wistar scientists have built upon BTE technology to develop new and improved recombinant and synthetic ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] SNMMI Annual Meeting to take place June 8-11, 2024
In-depth research highlights how nuclear medicine provides more effective and less costly diagnosis and treatment