(Press-News.org) Scientists have discovered genetic clues to the cause of restless leg syndrome, a condition common among older adults. The discovery could help identify those individuals at greatest risk of the condition and point to potential ways to treat it.
Restless leg syndrome can cause an unpleasant crawling sensation in the legs and an overwhelming urge to move them. Some people experience the symptoms only occasionally, while others get symptoms every day. Symptoms are usually worse in the evening or at night-time and can severely impair sleep.
Despite the condition being relatively common – up to one in 10 older adults experience symptoms, while 2-3% are severely affected and seek medical help – little is known about its causes. People with restless leg syndrome often have other conditions, such as depression or anxiety, cardiovascular disorders, hypertension, and diabetes, but the reason why is not known.
Previous studies had identified 22 genetic risk loci – that is, regions of our genome that contain changes associated with increased risk of developing the condition. But there are still no known ‘biomarkers’ – such as genetic signatures – that could be used to objectively diagnose the condition.
To explore the condition further, an international team led by researchers at the Helmholtz Munich Institute of Neurogenomics, Institute of Human Genetics of the Technical University of Munich (TUM) and the University of Cambridge pooled and analysed data from three genome-wide association studies. These studies compared the DNA of patients and healthy controls to look for differences more commonly found in those with restless leg syndrome. By combining the data, the team was able to create a powerful dataset with more than 100,000 patients and over 1.5 million unaffected controls.
The results of the study are published today in Nature Genetics.
Co-author Dr Steven Bell from the University of Cambridge said: “This study is the largest of its kind into this common – but poorly understood – condition. By understanding the genetic basis of restless leg syndrome, we hope to find better ways to manage and treat it, potentially improving the lives of many millions of people affected worldwide.”
The team identified over 140 new genetic risk loci, increasing the number known eight-fold to 164, including three on the X chromosome. The researchers found no strong genetic differences between men and women, despite the condition being twice as common in women as it is men – this suggests that a complex interaction of genetics and the environment (including hormones) may explain the gender differences we observe in real life.
Two of the genetic differences identified by the team involve genes known as glutamate receptors 1 and 4 respectively, which are important for nerve and brain function. These could potentially be targeted by existing drugs, such as anticonvulsants like perampanel and lamotrigine, or used to develop new drugs. Early trials have already shown positive responses to these drugs in patients with restless leg syndrome.
The researchers say it would be possible to use basic information like age, sex, and genetic markers to accurately rank who is more likely to have severe restless leg syndrome in nine cases out of ten.
To understand how restless leg syndrome might affect overall health, the researchers used a technique called Mendelian randomisation. This uses genetic information to examine cause-and-effect relationships. It revealed that the syndrome increases the risk of developing diabetes.
Although low levels of iron in the blood are thought to trigger restless leg syndrome – because they can lead to a fall in the neurotransmitter dopamine – the researchers did not find strong genetic links to iron metabolism. However, they say they cannot completely rule it out as a risk factor.
Professor Juliane Winkelmann from TUM, one of senior authors of the study, said: “For the first time, we have achieved the ability to predict restless leg syndrome risk. It has been a long journey, but now we are empowered to not only treat but even prevent the onset of this condition in our patients.”
A full list of funders can be found in the study paper.
Reference
Schormair et al. Genome-wide meta-analyses of restless legs syndrome yield insights into genetic architecture, disease biology, and risk prediction. Nature Genetics; 5 June 2024; DOI: 10.1038/s41588-024-01763-1
END
Genetics study points to potential treatments for restless leg syndrome
2024-06-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists detect slowest-spinning radio emitting neutron star ever recorded
2024-06-05
Scientists have detected what they believe to be a neutron star spinning at an unprecedentedly slow rate —slower than any of the more than 3,000 radio emitting neutron stars measured to date.
Neutron stars - the ultra-dense remains of a dead star - typically rotate at mind-bendingly fast speeds, taking just seconds or even a fraction of a second to fully spin on their axis.
However, the neutron star, newly discovered by an international team of astronomers, defies this rule, emitting radio signals on a comparatively ...
Tiny tropical puddle frogs show that protecting genetic variation is essential for animals to survive the climate crisis
2024-06-05
Even widespread species could be genomically vulnerable to the climate crisis, scientists warn. By studying the DNA of puddle frogs living in central African rainforests, the scientists found that areas of high environmental variation foster high genetic variation. If these varied habitats and the frogs that live there are lost, genetic variants that could have allowed the species to evolve to survive the climate crisis could be lost too. Meanwhile, populations with low genetic variation could become extinct quickly, unable to adapt.
“Generally, the more genomic variation within ...
3 in 4 Americans under 65 are worried about future of Medicare
2024-06-05
WASHINGTON, D.C. — June 5, 2024 — Concerns over the potential insolvency of Medicare among those under 65 have risen, with 73% now expressing worry that it won’t be available when they need it, up from 67% in 2022, according to the new West Health-Gallup 2024 Survey on Aging in America. Worry rose most amongst those aged 50 to 64, up 13 percentage points to 74%. Higher percentages of adult’s express concern about the future of Social Security, with 80% of people under 62 and 86% of people aged 40 to 49 fearing it will not be around once they are eligible.
According ...
Gold nanoparticles that selectively emit left-/right-handed light
2024-06-05
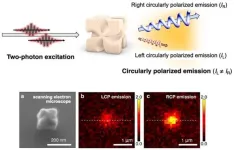
doi.org/10.1002/adom.202400699When chiral(1) gold nanoparticles(2) are irradiated with near-infrared(3) femtosecond pulses(4), visible emission of luminescence is observed. In this study, this luminescence was found to yield high selectivity for left- or right-handed circularly polarized(5) light, depending on the chirality of the nanoparticles, with a dissymmetry factor(6) of approximately 0.7. This finding suggests the potential to elevate various applications using circularly polarized light to practical levels.
Abstruct
The research group led by Project Assistant Professor Dr. Hyo-Yong AHN, ...
New AI algorithm detects rare epileptic seizures
2024-06-05
More than 3.4 million people in the US and 65 million people worldwide have epilepsy, a neurological disorder that affects the nervous system and causes seizures. One in 26 people will develop epilepsy at some point in their lives, and 1 out of 1000 people with epilepsy die from unexpected deaths each year.
Like many conditions, epilepsy treatment starts with early detection. The World Health Organization estimates that 70% of people with epilepsy could live seizure-free if adequately diagnosed and treated.
Over the years, ...
People underestimate the probability of including at least one minority member in a group
2024-06-05
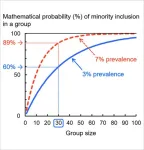
Niigata, Japan - Human society includes various minority groups. However, it is often difficult to know whether someone is a minority member simply by looking at the person, as minority traits may not be visually apparent (e.g., sexual orientation, color vision deficiency). In addition, minorities may hide their minority traits or identities. Consequently, we may have been unaware of the presence of minorities in daily life. Probabilistic thinking is critical in such uncertain situations. The people with whom we interact in our daily lives are typically a group of several dozen individuals (e.g., a school class). How do we judge the probability of including at least one minority ...
Celebrate Pride Month by learning CPR. The life you save may be someone you love
2024-06-05
DALLAS, June 4, 2024 — According to the American Heart Association, when someone suffers a cardiac arrest, immediate cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is critical and can double or triple a person’s chance of survival. More than 350,000 out-of-hospital cardiac arrests occur in the United States each year. Of those, 90% will not survive, according to the Association, which is working to turn more bystanders into lifesavers who can use CPR in an emergency. The American Heart Association, celebrating one hundred years of lifesaving service as a global ...
Dr. Erin Belval honored for exemplary fire science research
2024-06-05
FORT COLLINS, Colo., June 4, 2024 — Dr. Erin Belval, a research forester at the USDA Forest Service Rocky Mountain Research Station, was awarded the Early Career Scientist Award in Fire Science from the International Association of Wildland Fire (IAWF). She received the honor last month at the 2024 International Wildland Fire Conference in Boise, Idaho.
The award recognizes promising early-career professionals who demonstrate outstanding ability in any field of wildland fire science. Belval was nominated by colleagues and peers for her outstanding contributions.
“The award is particularly meaningful because ...
A novel approach to tracking conservation reveals more areas may be conserved than currently accounted for
2024-06-05
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Thirty by thirty. It’s an ambitious answer to growing calls for protecting more of our planet’s surface. The goal is to conserve 30% of the Earth’s oceans, lands and freshwaters by 2030. While this may seem a lofty aim, the diversity and coverage of conservation areas today might be greater than what’s currently recognized by global tracking systems.
An international team of conservation researchers and practitioners, led by scientists at UC Santa Barbara and The Nature Conservancy, has developed an inclusive inventory approach for tracking ...
Commonly used alcohol-based mouthwash brand disrupts the balance of your oral microbiome, scientists say
2024-06-05
SUMMARY
Researchers have identified a significant change in composition and abundance of bacteria in study participants’ oral microbiomes after using a popular brand of alcohol-based mouthwash.
The oral microbiome is the community of bacteria that live in the mouth, they help us digest our food and keep our mouth healthy.
Researchers found that two species of opportunistic bacteria were significantly more abundant in the mouth after daily use of the alcohol-based mouthwash, Fusobacterium nucleatum and Streptococcus anginosus. ...