(Press-News.org)
Since the brittle characteristics of porous ceramics, high mechanical strength is the most important prerequisite among the fundamental requirements especially when used as the supports. Particle grading strategy has been intensively extended in the preparation of porous ceramics to improve the mechanical strength. Unfortunately, this usually accompanies with the notable sacrifice in porosity. The trade-off between the mechanical strength and porosity is well recognized in the field of porous ceramics, and attempts have been increasingly devoted to overcome the issue.
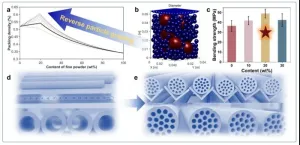
Recently, a research team led by Prof. Weihong Xing from Nanjing Tech University, Jiangsu Province, China proposed a reverse particle grading strategy based on the linear packing model, which enabled the preparation of porous ceramic with both high porosity and mechanical strength. They developed the strategy to prepare single-channel tubular supports and investigated the effect of reverse particle grading strategy on the ceramic paste, macroscopic properties, and microstructure of supports. Also, the strategy was proved to be feasible in the fabrication of 19-channel SiC tubular ceramic supports.
The team published their work in Journal of Advanced Ceramics on May 22, 2024.
“Particle size gradation is a common practice in the fabrication of advanced ceramics, which can regulate the mobility, plasticity and viscosity of the ceramic powder and pastes. While most of them prefers to the addition of fine particles into the coarse powder matrix. This usually results in the simultaneous increase in mechanical strength and density, which is evidently not the target of porous ceramics. In our recent work, a new concept-reverse particle grading strategy was developed based on the linear packing model by unusually introducing coarse particles into fine particles matrix. Tubular porous SiC ceramic supports with improved mechanical strength and maximum porosity were realized.” Said Dr. Qilin Gu, the corresponding author of the paper, a professor in State Key Laboratory of Materials-Oriented Chemical Engineering, National Engineering Research Center for Special Separation Membrane, Nanjing Tech University.
With the increasing content of coarse SiC particles to 30 wt%, the pressure generated in extrusion process decreased from 5.5 ± 0.2 MPa to 1.3 ± 0.1 MPa. Notably, the bending strength of tubular supports increased from 36.6 ± 5.6 MPa to 49.1 ± 4.5 MPa when incorporating 20 wt% of coarse powders. The notable improved mechanical strength was attributed to the distribution of coarse particles that prolonged the route of crack deflection. Also, the optimized tubular supports showed an average pore size of 1.2 ± 0.1 μm and open porosity of 45.1 ± 1.6 % and water permeability of 7163 ± 150 L·m-2·h-1·bar-1 and good alkali and acid corrosion resistances. “We believe that the concept-reverse particle grading strategy will serve as a cost-efficient alternative to prepare porous ceramics with high mechanical strength and porosity.” Qilin Gu said.
In the future, their efforts will be devoted to further optimize the recipe and processing parameters for scalable fabrication of SiC tubular porous ceramic supports. It is believed that the concept of reverse particle grading strategy can benefit the development of other porous ceramics.
Other contributors including Zheng Liang, Han Zhang, Yichuan Li, Wenkang Zhang, Jian Zhou, Zhaoxiang Zhong are all from Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, China.
This work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Project of China (2022YFB3805002), the Natural Science Foundation of China (22308150), the Research Programs of the Science and Technology of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous (GUIKE-AA22117015-1), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20220345), Key Research and Development Program of Jiangsu Province (No. BE2023360), Key Research and Development Project of Nanjing Jiangbei New Area (ZDYF202203) and Youth Science and Technology Talents Lifting Project of Jiangsu Association of Science and Technology (105019ZS_007).
About Journal of Advanced Ceramics
Journal of Advanced Ceramics (JAC) is an international journal that presents the state-of-the-art results of theoretical and experimental studies on the processing, structure, and properties of advanced ceramics and ceramic-based composites. JAC is Fully Open Access, monthly published by Tsinghua University Press on behalf of the State Key Laboratory of New Ceramics and Fine Processing (Tsinghua University) and the Advanced Ceramics Division of the Chinese Ceramic Society, and exclusively available via SciOpen. JAC has been indexed in SCIE (IF = 16.9, top 1/28, Q1), Scopus, and Ei Compendex.
About SciOpen
SciOpen is a professional open access resource for discovery of scientific and technical content published by the Tsinghua University Press and its publishing partners, providing the scholarly publishing community with innovative technology and market-leading capabilities. SciOpen provides end-to-end services across manuscript submission, peer review, content hosting, analytics, and identity management and expert advice to ensure each journal’s development by offering a range of options across all functions as Journal Layout, Production Services, Editorial Services, Marketing and Promotions, Online Functionality, etc. By digitalizing the publishing process, SciOpen widens the reach, deepens the impact, and accelerates the exchange of ideas.
END
Restricting use in bedrooms and at mealtimes have the biggest impact, but modeling good behavior is also important.
For many parents, it can feel like curbing kids’ screen use is a losing battle. But new research from UC San Francisco (UCSF) has found the parenting practices that work best to curb screen time and addictive screen behavior: restricting screens in bedrooms and at mealtimes and modeling healthy practices at home.
Researchers asked 12- to 13-year-olds how often they used screens for everything but school, including gaming, texting, social media, video chatting, watching videos and browsing the internet; and whether their ...
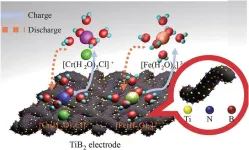
Researchers at the State Key Laboratory of Heavy Oil Processing, China University of Petroleum Beijing, have achieved a significant advancement in battery technology that could revolutionize how energy is stored and utilized, particularly for large-scale applications. In a recently published article in the journal Green Energy and Intelligent Transportation, the team, led by Yingchun Niu and Senwei Zeng, introduced a novel N-B doped composite electrode for iron-chromium redox flow batteries (ICRFB), demonstrating outstanding improvements in performance and efficiency.
Iron-chromium redox flow batteries are pivotal in addressing the ...
Achieving a sustained fusion reaction is a delicate balancing act, requiring a sea of moving parts to come together to maintain a high-performing plasma: one that is dense enough, hot enough, and confined for long enough for fusion to take place.
Yet as researchers push the limits of plasma performance, they have encountered new challenges for keeping plasmas under control, including one that involves bursts of energy escaping from the edge of a super-hot plasma. These edge bursts negatively impact overall performance and even damage the plasma-facing ...
A compact, lightweight sensor system with infrared imaging capabilities developed by an international team of engineers could be easily fitted to a drone for remote crop monitoring.
This flat-optics technology has the potential to replace traditional optical lens applications for environmental sensing in a range of industries.
This innovation could result in cheaper groceries as farmers would be able to pinpoint which crops require irrigation, fertilisation and pest control, instead of taking a one-size-fits-all approach, thereby potentially boosting their harvests.
The sensor system can rapidly switch between edge ...
Car tires contain hundreds of chemical additives that can leach out of them. This is how they end up in crops and subsequently in the food chain. Researchers at the Center for Microbiology and Environmental Systems Science at the University of Vienna and the Hebrew University of Jerusalem have now detected these chemical residues in leafy vegetables for the first time. Although the concentrations were low, the evidence was clear, a finding that is also known for drug residues in plant-based foods. The study was published in the internationally renowned journal Frontiers in Environmental Science.
The presence of drug residues in commercially sold fruit ...
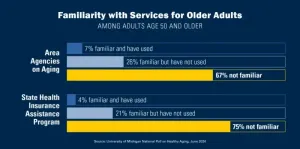
Older Americans may be missing out on a wide range of programs and services that could help them meet their needs or assist their aging loved ones, a new poll suggests.
The new findings from the National Poll on Healthy Aging, based at the University of Michigan, show most older adults don’t know about important public resources for older adults and their caregivers, either by name or general description.
The poll asked more than 4,000 adults over age 50 about their awareness and use of Area Agencies on Aging (AAAs), State Health Insurance Assistance ...
Highlights:
Dermatophytes are fungi that cause skin, hair and nail fungal infections.
These infections often develop resistance to azoles, a common anti-fungal treatment.
A new study suggests that adding common bone loss drugs to azoles can improve efficacy.
In lab tests, combinations of these drugs worked against dermatophyte species and prevented resistance.
Washington, D.C.—Human skin, hair and nails are all vulnerable to fungal infections. While these infections are usually not serious, they’re difficult to fully resolve and often recur after treatment—sometimes for years. They’re also often resistant to treatments, including a common class of antifungals ...
Benefits of emerging near-field communications:
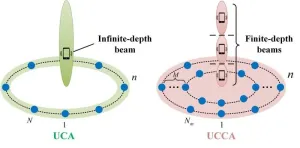
The progression of 5G mobile communication commercialization has spurred anticipation for 6G communication. To support emerging applications like digital twins, holographic video, and augmented reality (AR), extremely large-scale antenna array (ELAA) is regarded as key candidates for future 6G mobile communication due to its potential to enhance spectrum efficiency.
“Compared with 5G massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems, 6G ELAA not only entails an increase in the number of antennas, but also signifies a fundamental shift in electromagnetic ...
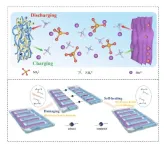
Researchers have developed a safer, cheaper, better performing and more flexible battery option for wearable devices.
A paper describing the ‘recipe’ for their new battery type was published in the journal Nano Research Energy on June 3.
Fitness trackers. Smart watches. Virtual-reality headsets. Even smart clothing and implants. Wearable smart devices are everywhere these days. But for greater comfort, reliability and longevity, these devices will require greater levels of flexibility and miniaturization of their energy storage mechanisms, which are often frustratingly bulky, heavy and fragile. On top of this, any improvements cannot come at the expense of ...
CLEVELAND—A team of researchers from the Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine has developed a new method for target DNA sequence amplification, testing and analysis.
This new technique, or reaction, known as AMPLON (Amplifying DNA with Multiarm Priming and Looping Optimization of Nucleic Acid), offers an alternative to the previously accepted “gold-standard” Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) method, opening the opportunity for more applications in medical diagnosis.
The team’s findings were recently published in the journal Advanced Materials.
“AMPLON ...