(Press-News.org)
In a study published in Cell, a research team led by ZHANG Yong'e and WANG Haoyi from the Institute of Zoology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has characterized the diversity of DNA transposons and expanded the genome engineering toolbox.
"Our systematic and comparative framework complements conventional case studies in elucidating basic biology and strengthening applied biology," said Prof. ZHANG, corresponding author of the study.
Since the first discovery of transposons by Barbara McClintock in the 1940s, scientists have been fascinated by these "jumping genes" and their role in evolution. As one of the major transposon types, DNA transposons have received considerable attention. However, due to the limited scale of previous case studies, the factors associated with transposition activity and evolutionary patterns have remained unclear.
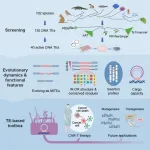
In this study, the researchers predicted 130 potentially active DNA transposons from 102 animal genomes. Through experimental screening and validation, they identified 40 novel transposons with activity in human cells, increasing the number of active transposon vectors in mammals from 20 to 60 and significantly expanding their evolutionary diversity.
Taking advantage of the largest dataset of active DNA transposons ever obtained through systematic experimental screening, they performed further in-depth analyses, deciphering factors underlying transposition activity, exploring evolutionary dynamics, and identifying diverse functional properties.
One notable finding is that the Tc1/mariner superfamily exhibits enhanced activity, which underlies their ubiquitous horizontal transfers.
In addition, although DNA transposons could be used as genetic engineering tools for insertional mutagenesis or transgenic vectors in previous applications, only a few of them have been widely used, such as Sleeping Beauty (SB).
The researchers explored new transposons with different functional properties. Among them, the most active transposon, Mariner2_AG (MAG), largely outperformed widely used vectors in CAR-T cell therapy, including lentivirus and SB, indicating its potential for clinical application.
The newly identified transposons with diverse functional characteristics described in the current study significantly expand the genetic engineering toolbox based on DNA transposons, supporting various application scenarios.
Overall, by utilizing the abundant genetic resources of the animal kingdom, the researchers conducted the largest-scale DNA transposon activity screening ever undertaken, resulting in the largest active DNA transposon dataset to date.
This study not only highlights the diverse functional and evolutionary characteristics of DNA transposons, but also expands the genomic engineering toolbox.
END
Antibiotic treatment prior to surgical repair of a pediatric elbow fracture does not reduce the risk for post-operative infection, according to new findings from a team of researchers and surgeons from the University of Missouri School of Medicine.
A humerus bone fracture near the elbow is a common injury among children who fall. The typical surgical approach for repairing pediatric elbow fractures is a procedure called closed reduction percutaneous pinning (CRPP). It involves inserting pins or wires through the skin to promote stability and healing of the bone. CRPP is a minimally invasive, safe and effective ...
Healthcare providers should watch out for new and highly contagious forms of ringworm or jock itch, which are emerging as a potential public health threat, according to a pair of reports.
In the first of the studies, experts at NYU Langone Health who focus on the spread of contagious rashes document the first reported U.S. case of a sexually transmitted fungal infection that can take months to clear up even with treatment. In the second report, NYU Langone physicians partnered with authorities at the New York State ...
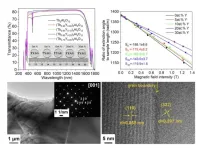
A team of material scientists led by Jiang Li from Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, in Shanghai, China recently reported (Tb1-xYx)3Al5O12 magneto-optical ceramics with high optical quality. The optical transmittance, microstructure, Verdet constant, and thermal conductivity of (Tb1-xYx)3Al5O12 with different Y content were investigated in detail. It was found that Y2O3 can suppress the secondary phase and improve the optical quality of TAG ceramics. As optical quality occupies one ...
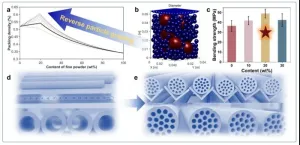
Since the brittle characteristics of porous ceramics, high mechanical strength is the most important prerequisite among the fundamental requirements especially when used as the supports. Particle grading strategy has been intensively extended in the preparation of porous ceramics to improve the mechanical strength. Unfortunately, this usually accompanies with the notable sacrifice in porosity. The trade-off between the mechanical strength and porosity is well recognized in the field of porous ceramics, and attempts have been increasingly devoted to overcome the issue.
Recently, a research team ...
Restricting use in bedrooms and at mealtimes have the biggest impact, but modeling good behavior is also important.
For many parents, it can feel like curbing kids’ screen use is a losing battle. But new research from UC San Francisco (UCSF) has found the parenting practices that work best to curb screen time and addictive screen behavior: restricting screens in bedrooms and at mealtimes and modeling healthy practices at home.
Researchers asked 12- to 13-year-olds how often they used screens for everything but school, including gaming, texting, social media, video chatting, watching videos and browsing the internet; and whether their ...
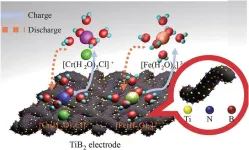
Researchers at the State Key Laboratory of Heavy Oil Processing, China University of Petroleum Beijing, have achieved a significant advancement in battery technology that could revolutionize how energy is stored and utilized, particularly for large-scale applications. In a recently published article in the journal Green Energy and Intelligent Transportation, the team, led by Yingchun Niu and Senwei Zeng, introduced a novel N-B doped composite electrode for iron-chromium redox flow batteries (ICRFB), demonstrating outstanding improvements in performance and efficiency.
Iron-chromium redox flow batteries are pivotal in addressing the ...
Achieving a sustained fusion reaction is a delicate balancing act, requiring a sea of moving parts to come together to maintain a high-performing plasma: one that is dense enough, hot enough, and confined for long enough for fusion to take place.
Yet as researchers push the limits of plasma performance, they have encountered new challenges for keeping plasmas under control, including one that involves bursts of energy escaping from the edge of a super-hot plasma. These edge bursts negatively impact overall performance and even damage the plasma-facing ...
A compact, lightweight sensor system with infrared imaging capabilities developed by an international team of engineers could be easily fitted to a drone for remote crop monitoring.
This flat-optics technology has the potential to replace traditional optical lens applications for environmental sensing in a range of industries.
This innovation could result in cheaper groceries as farmers would be able to pinpoint which crops require irrigation, fertilisation and pest control, instead of taking a one-size-fits-all approach, thereby potentially boosting their harvests.
The sensor system can rapidly switch between edge ...
Car tires contain hundreds of chemical additives that can leach out of them. This is how they end up in crops and subsequently in the food chain. Researchers at the Center for Microbiology and Environmental Systems Science at the University of Vienna and the Hebrew University of Jerusalem have now detected these chemical residues in leafy vegetables for the first time. Although the concentrations were low, the evidence was clear, a finding that is also known for drug residues in plant-based foods. The study was published in the internationally renowned journal Frontiers in Environmental Science.
The presence of drug residues in commercially sold fruit ...
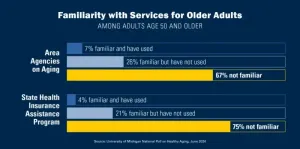
Older Americans may be missing out on a wide range of programs and services that could help them meet their needs or assist their aging loved ones, a new poll suggests.
The new findings from the National Poll on Healthy Aging, based at the University of Michigan, show most older adults don’t know about important public resources for older adults and their caregivers, either by name or general description.
The poll asked more than 4,000 adults over age 50 about their awareness and use of Area Agencies on Aging (AAAs), State Health Insurance Assistance ...