Could taking certain drugs reduce risk of ruptured brain aneurysm?
2024-06-05
(Press-News.org)
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, JUNE 5, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – A new study suggests that people who take a few common drugs may have a decreased risk of having a bleeding stroke due to a ruptured brain aneurysm. The study is published in the June 5, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The results do not prove that these drugs reduce the risk of this type of aneurysm; they only show an association.
“We urgently need new ways to prevent this type of stroke, which occurs at younger ages and with a higher death rate than other types of stroke,” said study author Jos Peter Kanning, MSc, of University Medical Center Utrecht in the Netherlands. “Our current surgical treatments for brain aneurysms have a risk of permanent disability and death that often outweighs the potential benefits, so preventing rupture with a non-invasive drug would be very beneficial.”
For the study, researchers looked at 4,879 people who had ruptured brain aneurysms, called aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhages. Those people were each compared to nine people of the same age and sex, for a total of 43,911 people who did not have ruptured brain aneurysms.
Then researchers looked at electronic health records to see what prescription drugs people took.
They found that four drugs were associated with a decreased risk of having a ruptured brain aneurysm: the high blood pressure drug lisinopril; the cholesterol drug simvastatin; the diabetes drug metformin; and the drug tamsulosin, prescribed for enlarged prostate.
After adjusting for other factors that could affect the risk of stroke, such as high blood pressure, smoking, alcohol abuse and total number of other health conditions, researchers found that people currently taking lisinopril were 37% less likely to have a ruptured brain aneurysm than those not taking the drug. People taking simvastatin were 22% less likely to have a stroke. Those taking metformin were 42% less likely to have a stroke and those taking tamsulosin were 45% less likely.
Researchers also found an increased risk of having a ruptured brain aneurysm for people taking four drugs: the blood thinner warfarin; the antidepressant venlafaxine; the antipsychotic and antiemetic drug prochlorperazine; and the painkiller co-codamol.
“Future research is needed to investigate these associations and determine whether these drugs are effective in reducing the risk of hemorrhagic stroke,” Kanning said. “This work could also help us identify additional risk factors for subarachnoid hemorrhage, potentially leading to new therapies to manage aneurysms.”
A limitation of the study was that researchers looked at drug prescriptions. It is possible that people may not take their drugs or may take them incorrectly.
The study was supported by the European Research Council.
Learn more about stroke at BrainandLife.org, home of the American Academy of Neurology’s free patient and caregiver magazine focused on the intersection of neurologic disease and brain health. Follow Brain & Life® on Facebook, X and Instagram.
When posting to social media channels about this research, we encourage you to use the hashtags #Neurology and #AANscience.
The American Academy of Neurology is the world's largest association of neurologists and neuroscience professionals, with over 40,000 members. The AAN’s mission is to enhance member career fulfillment and promote brain health for all. A neurologist is a doctor with specialized training in diagnosing, treating and managing disorders of the brain and nervous system such as Alzheimer's disease, stroke, concussion, epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, headache and migraine.
For more information about the American Academy of Neurology, visit AAN.com or find us on Facebook, X, Instagram, LinkedIn and YouTube.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-06-05
The Gerontological Society of America (GSA) has received renewed grant support to welcome a 15th class of reporters for the Journalists in Aging Fellows Program. The 2024 funders to date include Silver Century Foundation, The John A. Hartford Foundation, and National Institute for Health Care Management Foundation (NIHCM).
Since its founding in 2010, this program has been responsible for more than 800 news stories produced by 231 alumni. It has two goals: to educate journalists about issues in aging, better allowing them to spread a new awareness to general-audience, ethnic, and other minority populations; and to disseminate information about new scientific findings, ...
2024-06-05
Cyberattacks driven by Artificial Intelligence (AI) pose unprecedented risks to global economies, supply chains, and trade. A forthcoming study from the journal Risk Analysis explores the cascading impacts of AI-driven cyberattacks.
Unlike traditional cyberattacks, which are typically manual or scripted, AI-driven cyberattacks utilize AI and machine learning algorithms to enhance their effectiveness, stealthiness and adaptability. AI-driven cyberattacks can autonomously learn and evolve their tactics, techniques and procedures based on real-time feedback and environmental changes.
Through simulation scenarios, the researchers discovered the potential ...
2024-06-05
HOUSTON ― The James P. Allison Institute at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center today announced the appointment of its newest members, Susan Bullman, Ph.D., and Xi Chen, Ph.D., to further the institute’s ongoing work of impactful immunobiology research. These accomplished researchers, joining as associate members, bring valuable expertise in studying how the intratumoral microbiome and the immune microenvironment influence patient responses to immunotherapy.
As Allison Institute members, Bullman and Chen will lead impactful research programs aligned with the institute’s ...
2024-06-05
The Focused Ultrasound Foundation has designated Virginia Tech as a Focused Ultrasound (FUS) Center of Excellence, making it the sixth such center in the United States and one of only 12 in the world.
“Virginia Tech possesses significant strengths in the FUS field, and it is an honor to recognize them as a Center of Excellence,” said Neal F. Kassell, founder and chairman of the Focused Ultrasound Foundation. “With distinguished experts across the colleges of engineering, science, veterinary medicine, and medicine, ...
2024-06-05
Images
The U.S. public displays more positive than negative sentiment toward nuclear energy but concerns remain about waste, cost and safety, according to an analysis of 300,000 posts on X (formerly Twitter) by University of Michigan researchers.
The study was recently published in Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews.
Identifying public concerns and misconceptions about nuclear energy can target efforts to bridge these gaps as nuclear energy will play a large role in goals to decarbonize ...
2024-06-05
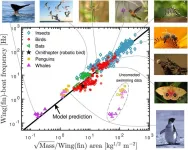
A single universal equation can closely approximate the frequency of wingbeats and fin strokes made by birds, insects, bats and whales, despite their different body sizes and wing shapes, Jens Højgaard Jensen and colleagues from Roskilde University in Denmark report in a new study in the open-access journal PLOS ONE, publishing June 5.
The ability to fly has evolved independently in many different animal groups. To minimize the energy required to fly, biologists expect that the frequency that animals flap their wings should be determined by the natural resonance frequency of the wing. However, finding a universal mathematical description of flapping flight has proved ...
2024-06-05
Pro-inflammatory diets are associated with higher levels of the heart failure biomarker NT-proBNP, with potential implications for cardiovascular risk, per study of more than 10,000 US adults
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0304289
Article Title: Association between dietary inflammatory index and NT-proBNP levels in US adults: A cross-sectional analysis
Author Countries: China
Funding: The study was funded by the Yan'an Science and Technology Plan Project (Grant No. 2022SLSFGG-025).The funders ...
2024-06-05
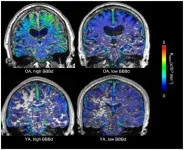
Normal ageing might be associated with increased blood-brain barrier permeability in regions also vulnerable in Alzheimer's Disease, in small study comparing healthy brains of the young and old
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0299764
Article Title: Associations between regional blood-brain barrier permeability, aging, and Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers in cognitively normal older adults
Author Countries: USA
Funding: Research reported in this publication was supported ...
2024-06-05
In an online study, virtual hospital rooms designed according to the principles of evidence-based design or the principles of Feng Shui were associated with greater potential benefit for viewers than virtual representations of standard hospital rooms. Emma Zijlstra of Hanze University of Applied Sciences in the Netherlands and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on June 5.
Hospital designers might consider employing specific design principles in an effort to improve patients’ experiences. Growing evidence suggests ...
2024-06-05
The formation of relationships within violent US Islamist extremist groups is highly driven by mutual contacts and the tendency for people to bond with others similar to themselves, according to new research. Anina Schwarzenbach, formally of Harvard University and the University of Maryland (currently affiliated with the University of Bern) and Michael Jensen of the University of Maryland present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on June 5, 2024.
Prior research on social structures within extremist networks have primarily ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Could taking certain drugs reduce risk of ruptured brain aneurysm?