(Press-News.org) Diabetes rates continue to rise, with 11.7 million Canadians living with diabetes or pre-diabetes. At UBC, scientists have created a pain-free drug delivery method to help people with diabetes manage the disease and maintain their health more easily.
Researchers at the Li Lab have developed oral insulin drops that when placed under the tongue are quickly and efficiently absorbed by the body, potentially replacing the need for insulin injections.
The drops contain a mixture of insulin and a unique cell-penetrating peptide (CPP) developed by Dr. Shyh-Dar Li and colleagues.
A little help from a peptide guide
“Insulin is a complicated molecule,” explains lead researcher Dr. Li, a professor in the faculty of pharmaceutical sciences. “In pill form, it’s easily destroyed in the stomach. Insulin also needs to be rapidly available in the blood, but as a large molecule, it cannot get through cells easily on its own.” The peptide, sourced from fish byproducts, opens a pathway for insulin to cross over.
Pre-clinical tests showed that insulin with the peptide effectively reaches the bloodstream whereas without the peptide, insulin remains stuck in the inside lining of the mouth.
“Think of it as a guide that helps insulin navigate through a maze to reach the bloodstream quickly. This guide finds the best routes, making it easier for insulin to get where it needs to go,” said Dr. Jiamin Wu, a postdoctoral researcher in the Li Lab.
Two versions of the peptide are described in recent articles in the Journal of Controlled Release (here and here). The UBC team is working to license the technology to a commercial partner.
Keeping medications on track
Healthy people get their insulin naturally from the pancreas to regulate glucose after a meal. Diabetes patients cannot produce sufficient insulin and need to get it from an outside source.
Unregulated glucose can be very dangerous, so diabetes patients must monitor their glucose levels and take insulin to lower it when necessary. While injections are the fastest way to get insulin into the blood, patients typically need at least three to four injections per day, which can affect their quality of life. Adherence to this regimen is challenging, and over time this can cause severe complications such as eye, kidney and nerve damage, potentially leading to limb amputations.
“My lab has been working on needle-free insulin alternatives these past three years,” said Dr. Li. “We tried nasal sprays before landing on oral drops, which are easy and convenient. Hopefully, the oral drops open up a new possibility for diabetes patients – making it easier to take their medications and regulate their blood glucose to maintain their health in the long run.”
Two inhalable insulin products (Exubera, Afrezza) were approved earlier but the effects were suboptimal and shown to increase the risk of lung cancer development. These products have been withdrawn. Dr. Li aims to achieve rapid, pain-free delivery of insulin without significant side effects. The new needle-free technology is expected to reduce the risk of cross-contamination, needle pricks, accidental infections and unsafe disposal of contaminated needles.
END
UBC-developed oral insulin drops offer relief for diabetes patients
Sublingual drops easily and efficiently absorbed by the body, potentially replacing insulin injections
2024-06-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Could taking certain drugs reduce risk of ruptured brain aneurysm?
2024-06-05
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, JUNE 5, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – A new study suggests that people who take a few common drugs may have a decreased risk of having a bleeding stroke due to a ruptured brain aneurysm. The study is published in the June 5, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The results do not prove that these drugs reduce the risk of this type of aneurysm; they only show an association.
“We urgently need new ways to prevent this type of stroke, which occurs at younger ages and with a higher death rate than other types of stroke,” said study author Jos Peter Kanning, ...
Fellowships will advance reporters’ coverage of aging in America
2024-06-05
The Gerontological Society of America (GSA) has received renewed grant support to welcome a 15th class of reporters for the Journalists in Aging Fellows Program. The 2024 funders to date include Silver Century Foundation, The John A. Hartford Foundation, and National Institute for Health Care Management Foundation (NIHCM).
Since its founding in 2010, this program has been responsible for more than 800 news stories produced by 231 alumni. It has two goals: to educate journalists about issues in aging, better allowing them to spread a new awareness to general-audience, ethnic, and other minority populations; and to disseminate information about new scientific findings, ...
Study shows AI-driven cyberattacks can inflict damage on GDP and supply chains for the world’s largest economies
2024-06-05
Cyberattacks driven by Artificial Intelligence (AI) pose unprecedented risks to global economies, supply chains, and trade. A forthcoming study from the journal Risk Analysis explores the cascading impacts of AI-driven cyberattacks.
Unlike traditional cyberattacks, which are typically manual or scripted, AI-driven cyberattacks utilize AI and machine learning algorithms to enhance their effectiveness, stealthiness and adaptability. AI-driven cyberattacks can autonomously learn and evolve their tactics, techniques and procedures based on real-time feedback and environmental changes.
Through simulation scenarios, the researchers discovered the potential ...
Allison Institute announces appointment of two immunobiology experts as associate members
2024-06-05
HOUSTON ― The James P. Allison Institute at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center today announced the appointment of its newest members, Susan Bullman, Ph.D., and Xi Chen, Ph.D., to further the institute’s ongoing work of impactful immunobiology research. These accomplished researchers, joining as associate members, bring valuable expertise in studying how the intratumoral microbiome and the immune microenvironment influence patient responses to immunotherapy.
As Allison Institute members, Bullman and Chen will lead impactful research programs aligned with the institute’s ...
Focused Ultrasound Foundation designates Virginia Tech as a Center of Excellence
2024-06-05
The Focused Ultrasound Foundation has designated Virginia Tech as a Focused Ultrasound (FUS) Center of Excellence, making it the sixth such center in the United States and one of only 12 in the world.
“Virginia Tech possesses significant strengths in the FUS field, and it is an honor to recognize them as a Center of Excellence,” said Neal F. Kassell, founder and chairman of the Focused Ultrasound Foundation. “With distinguished experts across the colleges of engineering, science, veterinary medicine, and medicine, ...
US public opinion on social media is warming to nuclear energy, but concerns remain
2024-06-05
Images
The U.S. public displays more positive than negative sentiment toward nuclear energy but concerns remain about waste, cost and safety, according to an analysis of 300,000 posts on X (formerly Twitter) by University of Michigan researchers.
The study was recently published in Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews.
Identifying public concerns and misconceptions about nuclear energy can target efforts to bridge these gaps as nuclear energy will play a large role in goals to decarbonize ...
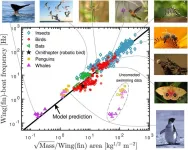
Flapping frequency of birds, insects, bats and whales described by universal equation
2024-06-05
A single universal equation can closely approximate the frequency of wingbeats and fin strokes made by birds, insects, bats and whales, despite their different body sizes and wing shapes, Jens Højgaard Jensen and colleagues from Roskilde University in Denmark report in a new study in the open-access journal PLOS ONE, publishing June 5.
The ability to fly has evolved independently in many different animal groups. To minimize the energy required to fly, biologists expect that the frequency that animals flap their wings should be determined by the natural resonance frequency of the wing. However, finding a universal mathematical description of flapping flight has proved ...
Pro-inflammatory diets are associated with higher levels of the heart failure biomarker NT-proBNP, with potential implications for cardiovascular risk, per study of more than 10,000 US adults
2024-06-05
Pro-inflammatory diets are associated with higher levels of the heart failure biomarker NT-proBNP, with potential implications for cardiovascular risk, per study of more than 10,000 US adults
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0304289
Article Title: Association between dietary inflammatory index and NT-proBNP levels in US adults: A cross-sectional analysis
Author Countries: China
Funding: The study was funded by the Yan'an Science and Technology Plan Project (Grant No. 2022SLSFGG-025).The funders ...
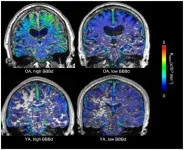
Normal ageing might be associated with increased blood-brain barrier permeability in regions also vulnerable in Alzheimer's Disease, in small study comparing healthy brains of the young and old
2024-06-05
Normal ageing might be associated with increased blood-brain barrier permeability in regions also vulnerable in Alzheimer's Disease, in small study comparing healthy brains of the young and old
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0299764
Article Title: Associations between regional blood-brain barrier permeability, aging, and Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers in cognitively normal older adults
Author Countries: USA
Funding: Research reported in this publication was supported ...
Evidence-based design or Feng Shui in hospital rooms might benefit patients
2024-06-05
In an online study, virtual hospital rooms designed according to the principles of evidence-based design or the principles of Feng Shui were associated with greater potential benefit for viewers than virtual representations of standard hospital rooms. Emma Zijlstra of Hanze University of Applied Sciences in the Netherlands and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on June 5.
Hospital designers might consider employing specific design principles in an effort to improve patients’ experiences. Growing evidence suggests ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
[Press-News.org] UBC-developed oral insulin drops offer relief for diabetes patientsSublingual drops easily and efficiently absorbed by the body, potentially replacing insulin injections