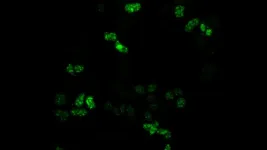
(Press-News.org) Bodybuilders and cellular mechanisms agree generating protein is a heavy lift. To complete the task, cells rely on complexes called spliceosomes. These molecular machines snip extra bits out of our genes’ RNA copies and piece together precise instructions for protein-building. When the splicing process goes awry, it can result in diseases like cancer or spinal muscular atrophy. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor Adrian Krainer helped develop the first FDA-approved treatment for this devastating genetic disorder. Now, his team has discovered that two important regulator proteins work together to keep the splicing process on track.
One of those regulators, a protein called SRSF1, has been a focus of Krainer’s lab since 1990. It was then that he discovered cells need SRSF1 for splicing to occur. His team has since found that too much SRSF1 can prompt cells to grow cancerous. Given this link to human disease, Krainer has been trying to determine just how SRSF1 works.
In his latest study, Krainer and graduate student Danilo Segovia set out to identify proteins that commingle with SRSF1 inside cells. They turned to a new technique that lets researchers track any protein that comes close to their molecule of interest—no matter how briefly. That’s important, Segovia says, because splicing is a dynamic process. Many molecules come and go quickly as the spliceosome assembles and does its work. With the new method, “You get the history of all the proteins that were within close range of SRSF1,” Segovia says.
‘History’ is the right word, as the list turned out quite long. It included known splicing regulators as well as some surprises. Segovia and Krainer were particularly interested in SRSF1’s interaction with a protein called DDX23. This enzyme helps newly built spliceosomes get themselves into shape for RNA splicing.
Next, Krainer and Segovia teamed with CSHL Director of Research Leemor Joshua-Tor. Together, they confirmed a strong interaction between SRSF1 and DDX23. Segovia proposes that their connection might be important for ensuring DDX23 is in the right place at the right time or in the right form to promote splicing.
“SRSF1 seems to be pretty central here,” Krainer says. He explains that in addition to its interaction with DDX23, the regulator protein is needed for an earlier step in spliceosome assembly. “It seems to be at this pivotal point between spliceosome transitions.” With his group’s list of SRSF1-interacting proteins, researchers now have a new set of clues into how this critical regulator does its work. That could help reduce the lift that comes with looking for new insights into cancer and other devastating diseases.
END
RNA splicing’s spotters
2024-06-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Clinical trial shows promising results in a two-drug combination that curbs methamphetamine use
2024-06-10
A clinical trial on a two-drug therapy for methamphetamine use disorder reduced use of the highly addictive drug for up to 12 weeks after initiation of treatment, UCLA-led research suggests.
Participants in the ADAPT-2 clinical trial who received a combination of injectable naltrexone plus extended-release oral bupropion (NTX+BUPN) had a 27% increase in methamphetamine-negative urine tests, indicating reduced usage. By contrast, the placebo group had an 11% increase in negative tests.
The study will be published in the peer-reviewed journal Addiction.
“These ...
Gut microbes from aged mice induce inflammation in young mice, study finds
2024-06-10
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — When scientists transplanted the gut microbes of aged mice into young “germ-free” mice — raised to have no gut microbes of their own — the recipient mice experienced an increase in inflammation that parallels inflammatory processes associated with aging in humans. Young germ-free mice transplanted with microbes from other young mice had no such increase.
The findings suggest that changes to the gut microbiome play a role in the systemwide inflammation that often occurs ...
Valentin Fuster, MD, Ph.D., received 2024 Distinguished Award from European Society for Clinical Investigation (ESCI)
2024-06-10
The European Society for Clinical Investigation (ESCI) is awarding Valentin Fuster, MD, PhD, President of Mount Sinai Heart and Physician-in-Chief of The Mount Sinai Hospital, its ESCI Distinguished Medal for 2024. He received this honor during the ESCI Annual Scientific Meeting in Barcelona, Spain, during a special ceremony on Friday, June 7.
The ESCI Medal is awarded yearly for outstanding achievements in clinical investigation and for the teaching of young scientists and medical specialists.
This prestigious recognition highlights Dr. Fuster’s significant contributions to the worldwide field of cardiology. Dr. Fuster’s work has been ...
Planetary Health Diet associated with lower risk of premature death, lower environmental impact
2024-06-10
Embargoed for release: Monday, June 10, 7:00 AM ET
Key takeaways:
People whose diets most closely adhered to the Planetary Health Diet (PHD) had 30% lower risk of premature death compared to those with the lowest adherence.
Every major cause of death, including cancer, heart disease, and lung disease, was lower with greater adherence to this dietary pattern.
Diets adhering to the PHD pattern had substantially lower environmental impact, including 29% lower greenhouse gas emissions and 51% less land use.
Boston, MA—People who eat a healthy, sustainable diet may ...
Improved prime editing system makes gene-sized edits in human cells at therapeutic levels
2024-06-10
Scientists at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard have improved a gene-editing technology that is now capable of inserting or substituting entire genes in the genome in human cells efficiently enough to be potentially useful for therapeutic applications.
The advance, from the lab of Broad core institute member David Liu, could one day help researchers develop a single gene therapy for diseases such as cystic fibrosis that are caused by one of hundreds or thousands of different mutations in a gene. Using this new approach, they would insert a healthy copy of the gene at its native location in the genome, rather than having to create a different ...
Lung organoids unveil secret: How pathogens infect human lung tissue
2024-06-10
How do pathogens invade the lungs? Using human lung microtissues, a team at the Biozentrum of the University of Basel has uncovered the strategy used by a dangerous pathogen. The bacterium targets specific lung cells and has developed a sophisticated strategy to break through the lungs’ line of defense.
Earlier this year, the WHO published a list of twelve of the world’s most dangerous bacterial pathogens that are resistant to multiple antibiotics and pose a grave threat to human health. This list includes Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a much-feared nosocomial pathogen ...
The solar system may have passed through dense interstellar clouds 2 million years ago, altering Earth’s climate
2024-06-10
Around two million years ago, Earth was a very different place, with our early human ancestors living alongside saber-toothed tigers, mastodons, and enormous rodents. And, depending on where they were, they may have been cold: Earth had fallen into a deep freeze, with multiple ice ages coming and going until about 12,000 years ago. Scientists theorize that ice ages occur for a number of reasons, including the planet’s tilt and rotation, shifting plate tectonics, volcanic eruptions, and carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere. ...
Miniaturizing a laser on a photonic chip
2024-06-10
Lasers have revolutionized the world since the 60’s and are now indispensable in modern applications, from cutting-edge surgery and precise manufacturing to data transmission across optical fibers.
But as the need for laser-based applications grows, so do challenges. For example, there is a growing market for fiber lasers, which are currently used in industrial cutting, welding, and marking applications.
Fiber lasers use an optical fiber doped with rare-earth elements (erbium, ytterbium, neodymium etc) as their optical gain source (the part that produces the laser’s light). They emit high-quality beams, they have high power output, and they are efficient, ...
Study: Physical activity in the evening lowers blood sugar levels
2024-06-10
ROCKVILLE, Md.— New research reveals that moderate to vigorous physical activity in the evening for sedentary adults with overweight and obesity is most beneficial in lowering daily blood sugar levels, according to a study published in Obesity, The Obesity Society’s (TOS) flagship journal.
Experts explain that it has been well established that moderate to vigorous physical activity enhances glucose homeostasis in adults with overweight and obesity who are at higher risk of developing insulin resistance. ...
Experts develop nutritional recommendations for patients treated with anti-obesity medications
2024-06-10
ROCKVILLE, Md.— Individuals treated with anti-obesity medications generally experience reduced appetite, which typically leads to reduced food intake. As a result, dietary quality becomes more important because nutritional needs must be met within the context of eating less. To improve this process, medical experts have developed a list of evidence-based nutritional recommendations to assist clinicians treating patients with anti-obesity medications, according to a review published in the journal Obesity, The Obesity Society’s (TOS) flagship journal.
“Our evidence-based review aims to equip clinicians with knowledge ...