(Press-News.org) Astronomers have captured what appears to be a snapshot of a massive collision of giant asteroids in Beta Pictoris, a neighboring star system known for its early age and tumultuous planet-forming activity.
The observations spotlight the volatile processes that shape star systems like our own, offering a unique glimpse into the primordial stages of planetary formation.
“Beta Pictoris is at an age when planet formation in the terrestrial planet zone is still ongoing through giant asteroid collisions, so what we could be seeing here is basically how rocky planets and other bodies are forming in real time,” said Christine Chen, a Johns Hopkins University astronomer who led the research.
The insights will be presented today at the 244th Meeting of the American Astronomical Society in Madison, Wisconsin.
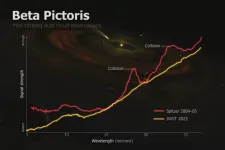
Chen’s team spotted significant changes in the energy signatures emitted by dust grains around Beta Pictoris by comparing new data from the James Webb Space Telescope with observations by the Spitzer Space Telescope from 2004 and 2005. With Webb’s detailed measurements, the team tracked the dust particles’ composition and size in the exact area previously analyzed by Spitzer.
Focusing on heat emitted by crystalline silicates—minerals commonly found around young stars as well as on Earth and other celestial bodies—the scientists found no traces of the particles previously seen in 2004–05. This suggests a cataclysmic collision occurred among asteroids and other objects about 20 years ago, pulverizing the bodies into fine dust particles smaller than pollen or powdered sugar, Chen said.
“We think all that dust is what we saw initially in the Spitzer data from 2004 and 2005,” said Chen, who is also an astronomer at the Space Telescope Science Institute. “With Webb’s new data, the best explanation we have is that, in fact, we witnessed the aftermath of an infrequent, cataclysmic event between large asteroid-size bodies, marking a complete change in our understanding of this star system.”
The new data suggests dust that was dispersed outward by radiation from the system’s central star is no longer detectable, Chen said. Initially, dust near the star heated up and emitted thermal radiation that Spitzer’s instruments identified. Now, dust that cooled off as it moved far away from the star no longer emits those thermal features.
When Spitzer collected the earlier data, scientists assumed something like small bodies grinding down would stir and replenish the dust steadily over time. But Webb’s new observations show the dust disappeared and was not replaced. The amount of dust kicked up is about 100,000 times the size of the asteroid that killed the dinosaurs, Chen said.
Beta Pictoris, located about 63 light years from Earth, has long been a focal point for astronomers because of its proximity and random processes where collisions, space weathering, and other planet-making factors will dictate the system’s fate.
At only 20 million years—compared to our 4.5-billion-year-old solar system—Beta Pictoris is at a key age where giant planets have formed but terrestrial planets might still be developing. It has at least two known gas giants, Beta Pic b and c, which also influence the surrounding dust and debris.
“The question we are trying to contextualize is whether this whole process of terrestrial and giant planet formation is common or rare, and the even more basic question: Are planetary systems like the solar system that rare?” said co-author Kadin Worthen, a doctoral student in astrophysics at Johns Hopkins. “We’re basically trying to understand how weird or average we are.”
The new insights also underscore the unmatched capability of the Webb telescope to unveil the intricacies of exoplanets and star systems, the team reports. They offer key clues into how the architectures of other solar systems resemble ours and will likely deepen scientists’ understanding of how early turmoil influences planets’ atmospheres, water content, and other key aspects of habitability.
“Most discoveries by JWST come from things the telescope has detected directly,” said co-author Cicero Lu, a former Johns Hopkins doctoral student in astrophysics. “In this case, the story is a little different because our results come from what JWST did not see.”
Other authors are Yiwei Chai and Alexis Li of Johns Hopkins; David R. Law, B.A. Sargent, G.C. Sloan, Julien H. Girard, Dean C. Hines, Marshall Perrin and Laurent Pueyo of the Space Telescope Science Institute; Carey M. Lisse of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory; Dan M. Watson of the University of Rochester; Jens Kammerer of the European Southern Observatory; Isabel Rebollido of the European Space Agency; and Christopher Stark of NASA Goddard Space Flight Center.
The research was supported by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration under Grant No. 80NSSC22K1752.
Journalists registered for the meeting can attend the presentation in person or virtually on Monday, June 10 at 10:15 a.m. Central Standard Time. Nonregistrants may watch the press conference on the AAS Press Office YouTube channel but will be unable to ask questions.
END
Webb telescope reveals asteroid collision in neighboring star system
2024-06-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
When is genome sequencing advisable?
2024-06-10
Genetic mutations in human DNA can prevent proteins that perform important functions in the body from being formed correctly. This can lead to serious disorders that cause disease or even disability. Many of these diseases are already known and can be attributed to specific genes. To diagnose them, clinicians use a standard procedure known as exome sequencing. This involves analysing those segments of human DNA that are directly responsible for the correct formation of proteins. This coding part, the exome, makes up only around ...
Association found between media diet and science-consistent beliefs about climate change
2024-06-10
In a paper titled “The Politicization of Climate Science: Media Consumption, Perceptions of Science and Scientists, and Support for Policy,” published May 26, 2024, in the Journal of Health Communication, researchers probed the associations between media exposure and science-consistent beliefs about climate change and the threat it posed to the respondent.
Expanding on earlier work associating Fox News consumption with doubts about the existence of human-caused climate change, a team of scholars affiliated with the Annenberg Public Policy ...
Older, poorer, Black, Medicaid beneficiaries less likely to be placed on liver transplant lists
2024-06-10
INDIANAPOLIS – A new, healthy liver offers the best survival for patients with early-stage liver cancer. But a new study, led by Katie Ross-Driscoll, PhD, MPH, of Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Surgery, has identified disparities in liver transplant referral and evaluation, which must precede waitlisting, for these potentially lifesaving procedures.
While other studies have demonstrated disparities in placement on organ waitlists, the new study is one of the first to examine the transplant ...
Imposing cost-efficient trade sanctions
2024-06-10
By Alistair Jones
SMU Office of Research – Global condemnation of Russia over its invasion of Ukraine has prompted the imposition of trade sanctions. Such measures are a form of economic coercion, commonly used for reasons of foreign policy.
Trade sanctions can be put in place in an attempt to alter objectionable behaviour – in Russia's case, waging a war – or to punish an offending state through the disruption of economic exchange.
"Sanctions can be in many forms and raising ...
Statins for heart disease prevention could be recommended for far fewer Americans if new risk equation is adopted
2024-06-10
PITTSBURGH – If national guidelines are revised to incorporate a new risk equation, about 40% fewer people could meet criteria for cholesterol-lowering statins to prevent heart disease, according to a study by researchers at the University of Pittsburgh, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and University of Michigan. Published today in JAMA Internal Medicine, the study examines the potential impact of widespread adoption of the PREVENT equations, which were released by the American Heart Association ...
Multicenter clinical study supports safety of deep general anesthesia
2024-06-10
General anesthesia makes it possible for millions of patients each year to undergo lifesaving surgeries while unconscious and free of pain. But the 176-year-old medical staple uses powerful drugs that have stoked fears of adverse effects on the brain — particularly if used in high doses.
New findings published June 10 in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), however, support an earlier study that indicates that anesthesia is no more hazardous for the brain at higher doses than at lower doses, ...
Cancer incidence trends in successive social generations in the US
2024-06-10
About The Study: In this model-based cohort analysis of incident invasive cancer in the general population, decreases in lung and cervical cancers in Generation X may be offset by gains at other sites. Generation X may be experiencing larger per-capita increases in the incidence of leading cancers than any prior generation born in 1908 through 1964. On current trajectories, cancer incidence could remain high for decades.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Philip S. Rosenberg, Ph.D., email rosenbep@mail.nih.gov.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
Global prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents
2024-06-10
About The Study: This study’s findings indicated 1 of 5 children or adolescents experienced excess weight and that rates of excess weight varied by regional income and Human Development Index. Excess weight among children and adolescents was associated with a mix of inherent, behavioral, environmental, and sociocultural influences that need the attention and committed intervention of primary care professionals, clinicians, health authorities, and the general public.
Corresponding Author: To ...
Severe pediatric neurological manifestations with SARS-CoV-2 or MIS-C hospitalization and new morbidity
2024-06-10
About The Study: The results of this study suggest that children and adolescents with acute SARS-CoV-2 or multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) and severe neurological manifestations may be at high risk for long-term impairment and may benefit from screening and early intervention to assist recovery.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Ericka L. Fink, M.D., M.S., email finkel@ccm.upmc.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.14122)
Editor’s ...
Elephants have names for each other like people do, new study shows
2024-06-10
Colorado State University scientists have called elephants by their names, and the elephants called back.
Wild African elephants address each other with name-like calls, a rare ability among nonhuman animals, according to a new study published in Nature Ecology and Evolution.
Researchers from CSU, Save the Elephants and ElephantVoices used machine learning to confirm that elephant calls contained a name-like component identifying the intended recipient, a behavior they suspected based on observation. When the researchers played back recorded calls, elephants responded affirmatively ...