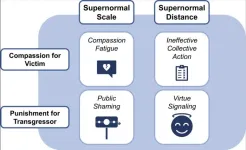
(Press-News.org) In a Review article, Claire Robertson and colleagues explore how human morality, which evolved in the context of small in-person groups, functions on the internet with over five billion users. Evolved human responses, such as compassion for victims and urges to punish transgressors, operate differently online, the authors argue. The internet exposes users to large quantities of extreme morally relevant stimuli in the form of 24-hour news and intentionally outrageous content from sometimes physically distant locations. Subjecting human brains to this new morally oversaturated environment has caused compassion fatigue, public shaming, ineffective collective action and virtue signaling, according to the authors. Compassion fatigue arises because empathy is a costly cognitive resource, easily overtaxed by the demands of round-the-clock information about suffering. Public shaming arises because the internet makes it all too easy for very large numbers of people to indulge in the universal human desire to punish wrongdoers, thought to be an evolved adaptation to living in groups—but small groups. As posting a condemnation is nearly costless, it becomes a tempting way to signal moral virtue and group membership. Real aid may in some cases be replaced by non-costly forms of compassion, such as “liking” or “sharing” a post, which does little to help but makes people feel they have fulfilled their moral responsibilities. In addition, the ease of organizing online leads to massive—but ephemeral—social movements with shallow roots and little staying power. The authors call for research into platform design features that sustain attention or engagement without inducing negative externalities on individuals and society, and for greater public access to platform algorithms so that research can proceed.
END
Human evolution and online morality
2024-06-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Price sensitivity to unhealthy foods
2024-06-11
Consumer data shows people with obesity are more price-sensitive than others when it comes to buying unhealthy foods, suggesting a food tax could be an effective public health measure. Taxes on sugar-sweetened beverages have become a commonly employed policy to improve public health. Less common are taxes on unhealthy foods, such as candy, cookies, or potato chips--and there is little data on whether such taxes would improve public health. Ying Bao and colleagues examined whether individuals of various ...
Book bans as political action
2024-06-11
In the 2021–2022 school year, schools banned books more often than ever before in United States history. Katie Spoon, Isabelle Langrock, and colleagues analyzed data from PEN America on 2,532 book bans that occurred during the year, in combination with county-level administrative data, book sales data, and a novel crowd-sourced dataset of author demographic information. The research team found that people of color are several times more likely to be the authors of banned books than White authors and that a considerable proportion of banned books, both fictional and historical, feature characters of color. About 37% of banned books were children’s ...
New study shows metabolic and bariatric surgery prevents pre-diabetes from developing into type 2 diabetes in most patients
2024-06-11
Patients with pre-diabetes and severe obesity who had metabolic and bariatric surgery were 20-times less likely to develop full-blown type 2 diabetes over the course of 15 years than patients with the condition who did not have surgery, according to a new study* presented today at the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting.
Only 1.8% of patients progressed to a diagnosis of diabetes in five years after metabolic surgery (Roux-en-Y gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy), which rose to 3.3% in 10 years and 6.7% after 15 years. The protective effect against diabetes was higher ...
New studies suggest benefit of total robotic metabolic and bariatric surgery over conventional laparoscopy
2024-06-11
SAN DIEGO – June 11, 2024 – Two new studies* presented today at the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting suggest total robotic metabolic and bariatric surgery may result in shorter operative times, reduced lengths of stay and lower complications compared to laparoscopic approaches.
In one study, researchers from AdventHealth in Celebration, FL examined the outcomes of a single surgeon who performed 809 metabolic and bariatric operations – 498 totally robotic and 311 laparoscopic -- between 2020 and 2023. They found total robotic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) resulted in significantly shorter ...
Bariatric surgery more effective and durable than new obesity drugs and lifestyle intervention
2024-06-11
SAN DIEGO – June 11, 2024 – Systematic reviews* of medical literature between 2020 to 2024 show bariatric surgery, also known as metabolic or weight-loss surgery, produces the greatest and most sustained weight loss compared to GLP-1 receptor agonists and lifestyle interventions. The study was presented today at the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting.
Researchers found lifestyle interventions such as diet and exercise resulted in an average weight loss of 7.4% but that weight was generally regained within 4.1 years. GLP-1s and metabolic ...
For Republican men, environmental support hinges on partisan identity
2024-06-11
PULLMAN, Wash. – Who proposes a bill matters more to Republican men than what it says—at least when it comes to the environment, a recent study found.
In an experiment with 800 adults, researchers used an article describing a hypothetical U.S. Senate bill about funding state programs to reduce water pollution to test partisan preferences, changing only the political affiliation of the proposal’s sponsors. Democrats in the study who favored the proposal supported the legislation no matter who proposed it and at higher levels than the Republican participants. Republicans’ support varied, however, dropping about 18% when it was described as being ...
Research signals major milestone in cutting harmful gases that deplete ozone and worsen global warming
2024-06-11
A new study has revealed significant progress in the drive to reduce levels in the atmosphere of chemicals that destroy Earth’s ozone layer, confirming the success of historic regulations limiting their production.
The findings, led by the University of Bristol and published today in Nature Climate Change, show for the first time a notable decline in the atmospheric levels of potent ozone-depleting substances (ODS), called hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs). These HCFCs are also harmful greenhouse gases, so a reduction should also lessen global warming.
The Montreal Protocol was agreed to internationally in 1987 to introduce controls on the production and usage of ODS, which were once ...
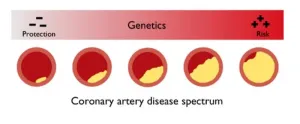
New AI tool finds rare variants linked to heart disease in 17 genes
2024-06-11
New York, NY [June 11, 2024]—Using an advanced artificial intelligence tool, researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have identified rare coding variants in 17 genes that shed light on the molecular basis of coronary artery disease (CAD), the leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide.
The discoveries, detailed in the June 11 online issue of Nature Genetics [DOI: 10.1038/s41588-024-01791-x], reveal genetic factors impacting heart disease that open new avenues for targeted treatments and personalized approaches to cardiovascular care.
The investigators used an in silico, or computer-derived, score for coronary artery disease (ISCAD) ...
New discovery reveals unexpected ocean algae help cool the Earth
2024-06-11
Peer-reviewed – observational study - cells
A common type of ocean algae plays a significant role in producing a massively abundant compound that helps cool the Earth’s climate, new research has discovered.
The findings of the study by the University of East Anglia (UEA) and Ocean University of China (OUC) could change our understanding of how these tiny marine organisms impact our planet.
The team identified the bloom-forming Pelagophyceae algae as potentially abundant and important producers ...
New computer vision method helps speed up screening of electronic materials
2024-06-11
Boosting the performance of solar cells, transistors, LEDs, and batteries will require better electronic materials, made from novel compositions that have yet to be discovered.
To speed up the search for advanced functional materials, scientists are using AI tools to identify promising materials from hundreds of millions of chemical formulations. In tandem, engineers are building machines that can print hundreds of material samples at a time based on chemical compositions tagged by AI search algorithms.
But to date, there’s been no similarly speedy way to confirm that these printed materials actually perform as expected. ...