(Press-News.org) Tsukuba, Japan—Viruses are ubiquitous in the environment, and organisms have developed various mechanisms to counter their threat. However, the genome of actinomycetes contains a highly conserved gene set encoding virus-like nanoparticles, although its biological significance has remained unclear.
In this study, researchers examined Streptomyces davawensis, an actinomycete species, and discovered that it produces virus-like particles that facilitate host reproduction. Extracellular DNA, which serves as a scaffold for multicellular organization, was significantly reduced in the colonies of mutant S. davawensis strains lacking virus-like particle production and cells trapped in abnormal aggregates. Detailed analysis revealed that the virus-like particles contain a unique enzyme (effector) crucial to their function, which partially degrades genomic DNA. The effector is released from the particle and localizes at the host cell membrane. The proposed model suggests that the effector partially degrades genomic DNA, bridging the intracellular and extracellular environments, thereby facilitating extracellular DNA release and providing a scaffold and nutrients for host cell reproduction. These findings reveal the exploitation mechanism of virus-related nanoparticles for bacterial proliferation and offer a novel strategy to reprogram virus-related nanoparticle functionality through modulation of effector activity for various applications in biotechnology.
###
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japanese Society for the Promotion of Science (19K15726, 23K13863 and 23K26811), the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JPMJMI21G8 and JPMJGX23B2) and the Suntory Rising Stars Encouragement Program in Life Sciences (SunRiSE).
Original Paper
Title of original paper:
Contractile injections systems facilitate sporogenic differentiation of Streptomyces davawensis through the action of a phage tapemeasure protein-related effector
Journal:
Nature Communications
DOI:
10.1038/s41467-024-48834-9
Correspondence
Assistant Professor NAGAKUBO, Toshiki
Institute of Life and Environmental Sciences, University of Tsukuba
Assistant Professor NISHIYAMA, Tatsuya
Life Science Research Center, College of Bioresource Sciences, Nihon University
Related Link
Institute of Life and Environmental Sciences
END
Virus-like nanoparticles control the multicellular organization and reproduction of host bacteria
2024-06-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Origins of fast radio bursts come into focus through polarized light
2024-06-11
TORONTO, ON, June 11, 2024 — What scientists previously thought about where Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs) come from is just the tip of the iceberg, according to new research led by astronomers at the University of Toronto. The mysteries of the millisecond-long cosmic explosions are unfolding with a new way of analyzing data from the Canadian Hydrogen Intensity Mapping Experiment (CHIME).
Published today in The Astrophysical Journal, the study details the properties of polarized light from 128 non-repeating FRBs — those from sources that have ...
Press registration opens for ACS Fall 2024
2024-06-11
WASHINGTON, June 11, 2024 — Journalists who register for the fall meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS) will have access to about 10,000 presentations on topics including agriculture and food, energy and fuels, health and medicine, sustainability, and more. ACS Fall 2024 is a hybrid meeting being held virtually and in person in Denver on Aug. 18-22, with the theme “Elevating Chemistry.”
ACS considers requests for press credentials and complimentary meeting registration from reporters (staff and freelance) and public information officers at government, nonprofit and educational institutions. Please ...
New plasma escape mechanism could protect fusion vessels from excessive heat
2024-06-11
The furious exhaust heat generated by a fusing plasma in a commercial-scale reactor may not be as damaging to the vessel’s innards as once thought, according to researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL), Oak Ridge National Laboratory and the ITER Organization (ITER).
“This discovery fundamentally changes how we think about the way heat and particles travel between two critically important regions at the edge of a plasma during fusion,” said PPPL Managing Principal Research Physicist Choongseok Chang, who led ...
Endocrine Society urges passage of the Right to IVF Act
2024-06-11
WASHINGTON—The Endocrine Society endorses the Right to IVF Act, which was introduced by Senators Cory Booker (D-NJ), Patty Murray (D-WA) and Tammy Duckworth (D-IL) to protect and expand nationwide access to fertility treatment, including in vitro fertilization (IVF), and urges the Senate to pass the Right to IVF Act on June 12th to ensure that the freedom to start and grow a family is protected and accessible to everyone in the United States.
Infertility affects an increasing number of individuals. ...
FAU Harbor Branch launches ‘eConch’ to grow and conserve the queen conch
2024-06-11
The queen conch (Aliger gigas) is a prized delicacy long harvested for food and revered for its beautiful shell. With a lifespan between 25 to 40 years, the queen conch is second only to the spiny lobster fishery and is the most important molluscan fishery in the Caribbean region.
Deeply rooted in the way of life in the Caribbean, many island communities depend on queen conch for their livelihoods. However, intensive fishing and habitat degradation from urbanization and climate change have caused conch populations ...
Surprisingly high levels of toxic gas found in Louisiana
2024-06-11
The toxic gas ethylene oxide, at levels thousand times higher than what is considered safe, was detected across parts of Louisiana with a cutting-edge mobile air-testing lab. The concentrations found dwarfed Environmental Protection Agency estimates for the region.
The findings, led by Johns Hopkins University environmental engineers, suggest significantly higher cancer risks for people who live near facilities that manufacture and use ethylene oxide, as well as a need for more accurate and reliable tools to monitor emissions.
“I don’t think there’s any census track in the area that wasn’t at higher risk for cancer than we would deem acceptable,” said ...
Soil bacteria respire more CO2 after sugar-free meals
2024-06-11
When soil microbes eat plant matter, the digested food follows one of two pathways. Either the microbe uses the food to build its own body, or it respires its meal as carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere.
Now, a Northwestern University-led research team has, for the first time, tracked the pathways of a mixture of plant waste as it moves through bacteria’s metabolism to contribute to atmospheric CO2. The researchers discovered that microbes respire three times as much CO2 from lignin carbons (non-sugar aromatic units) compared to cellulose carbons (glucose sugar units), which both add structure and support ...
Human evolution and online morality
2024-06-11
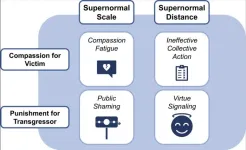
In a Review article, Claire Robertson and colleagues explore how human morality, which evolved in the context of small in-person groups, functions on the internet with over five billion users. Evolved human responses, such as compassion for victims and urges to punish transgressors, operate differently online, the authors argue. The internet exposes users to large quantities of extreme morally relevant stimuli in the form of 24-hour news and intentionally outrageous content from sometimes physically distant locations. Subjecting human brains to this ...
Price sensitivity to unhealthy foods
2024-06-11
Consumer data shows people with obesity are more price-sensitive than others when it comes to buying unhealthy foods, suggesting a food tax could be an effective public health measure. Taxes on sugar-sweetened beverages have become a commonly employed policy to improve public health. Less common are taxes on unhealthy foods, such as candy, cookies, or potato chips--and there is little data on whether such taxes would improve public health. Ying Bao and colleagues examined whether individuals of various ...
Book bans as political action
2024-06-11
In the 2021–2022 school year, schools banned books more often than ever before in United States history. Katie Spoon, Isabelle Langrock, and colleagues analyzed data from PEN America on 2,532 book bans that occurred during the year, in combination with county-level administrative data, book sales data, and a novel crowd-sourced dataset of author demographic information. The research team found that people of color are several times more likely to be the authors of banned books than White authors and that a considerable proportion of banned books, both fictional and historical, feature characters of color. About 37% of banned books were children’s ...