CCR4-NOT complex in stress resistance and longevity in C. elegans
2024-06-11
(Press-News.org)
“[...] it appears that the CCR4-NOT complex can influence longevity in a multitude of manners [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- June 11, 2024 – A new editorial paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 10, entitled, “CCR4-NOT complex in stress resistance and longevity in C. elegans.”
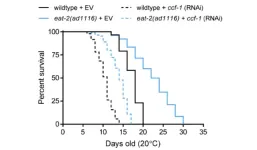
The ability to mount an adaptive response to environmental stress is crucial in organismal survival and overall fitness. In the context of aging, many genes that mediate resistance to stressors are also important in longevity, and aging has been shown to cause a decline in stress resistance. In their new editorial, researchers Cheng-Wei Wu and Hadi Tabarraei from the University of Saskatchewan wrote that recently, during a screening for genes that are required for the transcriptional response to heavy metal and oxidative stress in C. elegans, they found that depletion of subunits within the evolutionarily conserved CCR4-NOT protein complex compromises stress resistance and decreases lifespan.
“The CCR4-NOT (Carbon Catabolite Repression 4 – Negative On TATA-less) is a multi-protein complex tasked with regulating RNA metabolism across multiple steps including mRNA decay, transcription initiation and elongation, mRNA quality control and export, and mRNA translatability (reviewed in [3]).”
Studies in yeast have shown that CCR4-NOT is required for transcriptional elongation of stress responsive genes and that loss of function mutants of this protein complex have increased sensitivity to replication stress caused by DNA damaging agents [4, 5]. An expansive role for the CCR4-NOT complex in stress-induced transcriptional programming was demonstrated in C. elegans via whole-transcriptome sequencing analysis [2].
“Together, while the CCR4-NOT complex has been extensively studied for the past 3 decades, new studies in the model organism C. elegans have revealed an important new role for this protein complex in regulating normal aging as well as a requirement for many well-characterized and evolutionarily conserved pro-longevity pathways including reduced insulin signaling, mitochondrial suppression, enhanced stress response, and dietary restriction.”
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205918
Corresponding Author: Cheng-Wei Wu
Corresponding Email: michael.wu@usask.ca
Keywords: aging, oxidative stress, C. elegans, CCR4-NOT
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Aging:
Aging publishes research papers in all fields of aging research including but not limited, aging from yeast to mammals, cellular senescence, age-related diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer’s diseases and their prevention and treatment, anti-aging strategies and drug development and especially the role of signal transduction pathways such as mTOR in aging and potential approaches to modulate these signaling pathways to extend lifespan. The journal aims to promote treatment of age-related diseases by slowing down aging, validation of anti-aging drugs by treating age-related diseases, prevention of cancer by inhibiting aging. Cancer and COVID-19 are age-related diseases.
Aging is indexed by PubMed/Medline (abbreviated as “Aging (Albany NY)”), PubMed Central, Web of Science: Science Citation Index Expanded (abbreviated as “Aging‐US” and listed in the Cell Biology and Geriatrics & Gerontology categories), Scopus (abbreviated as “Aging” and listed in the Cell Biology and Aging categories), Biological Abstracts, BIOSIS Previews, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
Facebook
X, formerly Twitter
Instagram
YouTube
LinkedIn
Reddit
Pinterest
Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-06-11
Subscribe to UCSF News
Note to Editors: Speaker bios are available in our media kit
UCSF Health and UCSF Benioff Children’s Hospitals celebrated the signing of a Community Workforce Agreement (CWA) on June 11, agreeing to prioritize local union workers for the construction of a proposed landmark hospital building and related site improvements on its Oakland site.
The agreement, signed by the Building and Construction Trades Council of Alameda County (BTCA) and the project’s general contractor, Rudolph and Sletten, confirms a mutual understanding to hire union workers and follow union hiring practices. An additional agreement was signed by Overaa Construction, ...
2024-06-11
ITHACA, N.Y. – An artificial intelligence-powered virtual teammate with a female voice boosts participation and productivity among women on teams dominated by men, according to new Cornell University research.
The findings suggest that the gender of an AI’s voice can positively tweak the dynamics of gender-imbalanced teams and could help inform the design of bots used for human-AI teamwork, researchers said.
The findings mirror previous research that shows minority teammates are more likely to participate if the team adds members similar to them, said Angel Hsing-Chi Hwang, postdoctoral associate in information science and ...
2024-06-11
The human visual system is a dominant part of the brain’s processes and navigation of the world. To better understand an aspect of this system, researchers from Drexel University’s College of Nursing and Health Professions examined how life experiences impact a person’s perception of imagery – specifically decorated masks.
The study, published in Frontiers in Psychology, examined viewer responses to images of distressing and neutrally decorated masks and whether personal life history, particularly past ...
2024-06-11
TAMPA, Fla. — Leptomeningeal disease is a rare but lethal complication faced by late-stage melanoma patients. It occurs when cancer cells spread to the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, or the leptomeninges. This condition, which affects 5% to 8% of melanoma patients, often leads to rapid deterioration and is notoriously resistant to therapies. However, a new Moffitt Cancer Center study, published today in Cell Reports Medicine, uncovers the mechanisms that drive this drug resistance, offering new avenues ...
2024-06-11
Iran’s water policy is discriminatory and an example of environmental racism, with specific regions and ethnic groups deliberately impoverished, damaged and threatened by policymakers, a new study says.
Water scarcity lies at the core of Iran’s environmental crises. Approximately 28 million of Iran’s 85 million residents reside in water-stressed areas, a situation identified as ‘water bankruptcy’. This is particularly the case in the central, industrialised regions.
Other “donor basin” regions – which have ...
2024-06-11
The 2024 Warren Alpert Foundation Prize has been awarded to four scientists whose transformational discoveries led to the creation of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells, a treatment that modifies patients’ immune cells and optimizes their ability to eliminate cancer cells.
CAR T-cell therapy, the first successful example of synthetic biology used in clinical medicine, has saved the lives of tens of thousands of adults and children with blood cancers, including leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma.
The award recipients are:
Renier Brentjens, Katherine Anne Gioia Endowed Chair of Medicine and deputy director of Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center
Zelig ...
2024-06-11
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is a health condition characterized by a group of risk factors: high blood pressure, high blood sugar, unhealthy cholesterol levels, and abdominal fat. These factors increase the risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and other serious health problems.
Previous studies have shown that both genetics and lifestyle influence MetS. But human studies have found it challenging to pinpointing the disease’s exact genetic factors and how they interact with our environment – the differences between people’s diets and lifestyles have proven impossible to control.
Now, scientists led by Johan Auwerx at EPFL have addressed ...
2024-06-11
WhatsApp can be a highly effective tool to help older people overcome loneliness and depression, according to the findings of a study conducted in Guarulhos, the second-largest city in São Paulo state, Brazil.
An article on the study is published in the journal Nature Medicine. The co-corresponding author is Marcia Scazufca, a scientific researcher at Hospital das Clínicas (HC), the hospital complex run by the University of São Paulo’s Medical School (FM-USP), and a professor at the school.
“This was a randomized controlled trial involving 603 participants aged more than 60 and registered ...
2024-06-11
The ocean, rich in mineral resources such as oil, natural gas, polymetallic nodules, cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts, polymetallic sulfides, and rare earth ore, plays an increasingly important role in resource development and economic growth. It is also regarded as an essential strategic space for sustainable development with abundant wind, wave, tidal, and solar energy. Compared with onshore structures, however, offshore structures, being complex, bulky, and expensive, have to endure various random loads that change over time and space, including wind, waves, currents, tides, sea ice, and even coupled with ...
2024-06-11
When college athletes are evaluated for a possible concussion, the diagnosis is based on an athletic trainer or team physician’s assessment of three things: the player’s symptoms, physical balance and cognitive skills.
Research published today suggests that almost half of athletes who are ultimately diagnosed with a concussion will test normally on the recommended cognitive-skills test.
“If you don’t do well on the cognitive exam, it suggests you have a concussion. But many people who are concussed do fine on the exam,” said Dr. Kimberly Harmon, the study’s lead author. She is a professor of family medicine ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] CCR4-NOT complex in stress resistance and longevity in C. elegans