(Press-News.org) As space travel becomes more frequent, a new biomarker tool was developed by an international team of researchers to help improve the growing field of aerospace medicine and the health of astronauts.
Dr. Guy Trudel (Professor in the Faculty of Medicine), Odette Laneuville (Associate Professor, Faculty of Science, and Director of the Biomedical Sciences) and Dr. Martin Pelchat (Associate Professor in the Department of Biochemistry, Microbiology and Immunology) are among the contributors to an international study led by Eliah Overbey of Weill Cornell Medicine and the University of Austin. Published today in Nature it introduces the Space Omics and Medical Atlas (SOMA), a database of integrated data and sample repository from a diverse range of space missions, including from SpaceX and NASA.
Space travel creates cellular, molecular, and physiological shifts in astronauts. SOMA is expected to provide a much necessary biomedical profiling that can help tease out the short and long-term health impacts of spaceflight. This will bring needed health monitoring, risk mitigation, and countermeasures baseline data for upcoming lunar, Mars, and exploration-class missions. It is meant to help keep astronauts and space travelers alive and healthy.
It may also have some intended use here on Earth.
“This represents a breakthrough in the study of human adaptation and life in space. Since many of the changes in astronaut in space resemble those of people who are immobile in bed, these studies can be clinically relevant. The data are therefore important for future space exploration while also providing a correlation to people on Earth with limited mobility or who are bedridden before their rehabilitation,” says Dr. Trudel, a rehabilitation physician and researcher at The Ottawa Hospital who has focused on space travel and its effects on the human immune system.
Highlights of the study, include:
The Atlas includes extensive molecular and physiological profiles encompassing genomics, epigenomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and microbiome data sets, which reveal some consistent features across missions.
Samples were taken pre-flight, during, post-flight and throughout the recovery period.
Comprehensive profile of the physiological changes of the I4 crew (ages 29, 38, 42, 51) and 13 unique biospecimen sample types were collected and processed.
2,911 samples were banked with over 1,000 samples processed for sequencing, imaging, and biochemical analysis creating the first-ever aerospace medicine biobank.
The SOMA resource represents an over 10-fold increase in total publicly available human space omics data.
“The University of Ottawa’s Faculty of Medicine, its Faculty of Science, and The Ottawa Hospital’s Bone and Joint Research laboratory have a long history of contributions and successes in studying human adaptation to space. They also involve students from different programs, providing a unique learning experience in both bone and joint health, and in the rapidly developing field of aerospace medicine,” adds Dr. Trudel.
END
New biomarker database designed to improve astronaut health may also be useful to earthlings
The Space Omics and Medical Atlas (SOMA) includes samples from space missions, providing insight into short and long-term health impacts of spaceflight
2024-06-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Haiku may shine a light on humans’ relationship with insects, study suggests
2024-06-11
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Haiku poems have reflected humans’ experiences in nature for hundreds of years, including observations of bugs and other wildlife. Recently, Penn State researchers analyzed which insects were mentioned the most in haiku — with butterflies, fireflies and singing insects such as crickets topping the list.
Haiku are three-line poems with five syllables in the first and third lines, and seven syllables in the second line.
In their study of nearly 4,000 haiku, recently published in the journal PLOS ONE, the researchers also found that aquatic arthropods — such as caddisflies, stoneflies and fishflies — were mentioned the ...
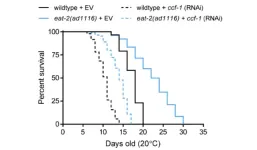
CCR4-NOT complex in stress resistance and longevity in C. elegans
2024-06-11
“[...] it appears that the CCR4-NOT complex can influence longevity in a multitude of manners [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- June 11, 2024 – A new editorial paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 10, entitled, “CCR4-NOT complex in stress resistance and longevity in C. elegans.”
The ability to mount an adaptive response to environmental stress is crucial in organismal survival and overall fitness. In the context of aging, many genes that mediate resistance to stressors are also important in longevity, and aging has been shown to cause ...
Workforce agreement supports local labor for Oakland Hospital
2024-06-11
Subscribe to UCSF News
Note to Editors: Speaker bios are available in our media kit
UCSF Health and UCSF Benioff Children’s Hospitals celebrated the signing of a Community Workforce Agreement (CWA) on June 11, agreeing to prioritize local union workers for the construction of a proposed landmark hospital building and related site improvements on its Oakland site.
The agreement, signed by the Building and Construction Trades Council of Alameda County (BTCA) and the project’s general contractor, Rudolph and Sletten, confirms a mutual understanding to hire union workers and follow union hiring practices. An additional agreement was signed by Overaa Construction, ...
Female AI ‘teammate’ generates more participation from women
2024-06-11
ITHACA, N.Y. – An artificial intelligence-powered virtual teammate with a female voice boosts participation and productivity among women on teams dominated by men, according to new Cornell University research.
The findings suggest that the gender of an AI’s voice can positively tweak the dynamics of gender-imbalanced teams and could help inform the design of bots used for human-AI teamwork, researchers said.
The findings mirror previous research that shows minority teammates are more likely to participate if the team adds members similar to them, said Angel Hsing-Chi Hwang, postdoctoral associate in information science and ...
Do traumatic life experiences impact perception of distressing imagery?
2024-06-11
The human visual system is a dominant part of the brain’s processes and navigation of the world. To better understand an aspect of this system, researchers from Drexel University’s College of Nursing and Health Professions examined how life experiences impact a person’s perception of imagery – specifically decorated masks.
The study, published in Frontiers in Psychology, examined viewer responses to images of distressing and neutrally decorated masks and whether personal life history, particularly past ...
Moffitt study reveals new mechanism of drug resistance in melanoma leptomeningeal disease
2024-06-11
TAMPA, Fla. — Leptomeningeal disease is a rare but lethal complication faced by late-stage melanoma patients. It occurs when cancer cells spread to the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, or the leptomeninges. This condition, which affects 5% to 8% of melanoma patients, often leads to rapid deterioration and is notoriously resistant to therapies. However, a new Moffitt Cancer Center study, published today in Cell Reports Medicine, uncovers the mechanisms that drive this drug resistance, offering new avenues ...
Iran’s war policy is discriminatory and an example of “environmental racism”, study says
2024-06-11
Iran’s water policy is discriminatory and an example of environmental racism, with specific regions and ethnic groups deliberately impoverished, damaged and threatened by policymakers, a new study says.
Water scarcity lies at the core of Iran’s environmental crises. Approximately 28 million of Iran’s 85 million residents reside in water-stressed areas, a situation identified as ‘water bankruptcy’. This is particularly the case in the central, industrialised regions.
Other “donor basin” regions – which have ...
2024 Warren Alpert Foundation Prize honors four pioneers in CAR T-cell therapy
2024-06-11
The 2024 Warren Alpert Foundation Prize has been awarded to four scientists whose transformational discoveries led to the creation of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells, a treatment that modifies patients’ immune cells and optimizes their ability to eliminate cancer cells.
CAR T-cell therapy, the first successful example of synthetic biology used in clinical medicine, has saved the lives of tens of thousands of adults and children with blood cancers, including leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma.
The award recipients are:
Renier Brentjens, Katherine Anne Gioia Endowed Chair of Medicine and deputy director of Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center
Zelig ...
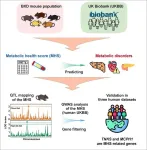
Building a blueprint of metabolic health – from mouse to human
2024-06-11
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is a health condition characterized by a group of risk factors: high blood pressure, high blood sugar, unhealthy cholesterol levels, and abdominal fat. These factors increase the risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and other serious health problems.
Previous studies have shown that both genetics and lifestyle influence MetS. But human studies have found it challenging to pinpointing the disease’s exact genetic factors and how they interact with our environment – the differences between people’s diets and lifestyles have proven impossible to control.
Now, scientists led by Johan Auwerx at EPFL have addressed ...
Use of WhatsApp messages by public health service to treat depression in older people produces results, study shows
2024-06-11
WhatsApp can be a highly effective tool to help older people overcome loneliness and depression, according to the findings of a study conducted in Guarulhos, the second-largest city in São Paulo state, Brazil.
An article on the study is published in the journal Nature Medicine. The co-corresponding author is Marcia Scazufca, a scientific researcher at Hospital das Clínicas (HC), the hospital complex run by the University of São Paulo’s Medical School (FM-USP), and a professor at the school.
“This was a randomized controlled trial involving 603 participants aged more than 60 and registered ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] New biomarker database designed to improve astronaut health may also be useful to earthlingsThe Space Omics and Medical Atlas (SOMA) includes samples from space missions, providing insight into short and long-term health impacts of spaceflight