(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this cohort study of World Trade Center responders who survived these unique exposures and participated in a longitudinal follow-up study of cognition from 2014 through 2022, when compared with responders with the lowest exposure levels or responders who used personalized protective equipment (PPE), more severe exposure to dust or debris was significantly associated with a higher risk of dementia before 65 years of age. This study suggests that the reliable use of PPE might help prevent the onset of dementia before age 65 years among individuals exposed to an uncontrolled building collapse. Future research is warranted to determine cerebral biomarkers for individuals with exposure-associated dementia.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Sean A. P. Clouston, Ph.D., email sean.clouston@stonybrookmedicine.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.16504)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.16504?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=061224
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Incidence of dementia before age 65 years among World Trade Center attack responders
JAMA Network Open
2024-06-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Neighborhood deprivation and breast cancer mortality among Black and white women
2024-06-12
About The Study: Neighborhood deprivation was associated with increased breast cancer mortality among non-Hispanic white women in this cohort study. Neighborhood racial composition, residential mobility, and rurality did not explain the lack of association among non-Hispanic Black women, suggesting that factors beyond those explored here may contribute to breast cancer mortality in this racial group.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Lauren E. Barber, Ph.D., email lauren.barber@emory.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.16499)
Editor’s ...
Hybrid work is a “win-win-win” for companies, workers
2024-06-12
It is one of the most hotly debated topics in today’s workplace: Is allowing employees to log in from home a few days a week good for their productivity, careers, and job satisfaction?
Nicholas Bloom, a Stanford economist and one of the foremost researchers on work-from-home policies, has uncovered compelling evidence that hybrid schedules are a boon to both employees and their bosses.
In a study, newly published in the journal Nature, of an experiment on more than 1,600 workers at Trip.com — a Chinese company that is one of the world’s largest online travel agencies — Bloom finds that employees who work from home ...
Inherited genetic factors may predict the pattern of X chromosome loss in older women
2024-06-12
hat: Researchers have identified inherited genetic variants that may predict the loss of one copy of a woman’s two X chromosomes as she ages, a phenomenon known as mosaic loss of chromosome X, or mLOX. These genetic variants may play a role in promoting abnormal blood cells (that have only a single copy of chromosome X) to multiply, which may lead to several health conditions, including cancer. The study, co-led by researchers at the National Cancer Institute, part of the National Institutes of Health, was published ...
Study on fruit flies could benefit eggs of older women
2024-06-12
A Dartmouth study conducted on fruit flies reports the first evidence in any organism that oocytes—the cells that become eggs—regularly rejuvenate the critical protein linkages that bind chromosomes together. The findings are a potentially important step toward helping women reduce their risk of pregnancy complications as they age, the researchers report in the journal Current Biology.
Women are born with the oocytes they will have for life, and the cohesive linkages that connect chromosomes are established in those cells prenatally. When they reach childbearing age, ovulation triggers the ...
Climate change-related disturbances linked to worse cardiovascular health, researchers show
2024-06-12
BOSTON – Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for approximately one in every three deaths, with more than 20 million deaths reported in 2021 according to a 2024 World Heart Federation report. Improvements in heart disease prevention, treatment and intervention have led to substantial declines in cardiovascular deaths in recent decades, but climate change caused by the continued combustion of fossil fuels may undermine this progress. Over the last century, NASA confirms the average global temperature has risen by more than two degrees Fahrenheit, leading to long-term shifts in average weather patterns, disturbance ...
Groundbreaking study uncovers new insights into alternative splicing and disease associations
2024-06-12
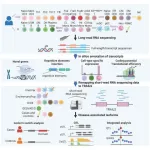
Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) researchers harness long-read RNA sequencing to decode genetic intricacies and disease links.
Tokyo, Japan – Alternative splicing, a process where a single gene can give rise to multiple different proteins via inclusion or exclusion of certain segments of the gene sequence, is known to occur in over 90% of human genes. This leads to the production of numerous transcript isoforms (splice variants of an expressed gene) crucial for protein function and cellular processes. Despite previous research on mechanisms underlying alternative splicing ...
A review of high-performance cementitious composites in bridge deck durability
2024-06-12
Many modern bridges use orthotropic steel bridge decks (OSBD), the decks being the surface sections of the bridge. OSBDs were designed to be lightweight and economical. However, this design has shown increasing issues with pavement cracking and fatigue damage at the welds that connect the bridge deck to the bridge superstructure. Fatigue damage is damage that accrues over time with use.
To ameliorate these problems, a new bridge deck was designed. The composite bridge deck system (CBD) added a layer of concrete to decrease the probability of damage due to fatigue. More recently the use of high-performance materials, such as ultra-high-performance ...
Boron nitride microribbons strengthened and toughened alumina composite ceramics with excellent mechanical, dielectric, and thermal conductivity properties
2024-06-12
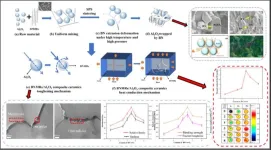
In recent years, the high complexity of integrated devices has made heat accumulation increasingly critical and has resulted in higher heat dissipation requirements for substrates and packaging materials. In this study, boron nitride microribbon (BNMR)/Al2O3 composite ceramics are prepared using spark plasma sintering (SPS). This study examines the effect of varying the amount of toughened phase BNMR on the density, mechanical properties, dielectric constant, and thermal conductivity of BNMR/Al2O3 composite ceramics while also exploring the mechanisms behind the toughening and increased ...
New perspectives of perovskites-based ferroelectric ceramics for energy storage applications
2024-06-12
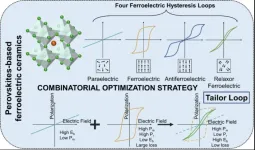
With the escalating impacts of climate change and depletion of resources, dielectric capacitors are emerging as promising high-demanded candidates for high-performance energy storage devices. However, due to the shortcomings of various dielectric ceramics (e.g., paraelectrics, ferroelectrics, and antiferroelectrics), their low polarizability, low breakdown strength, and large hysteresis loss limit their standalone use in the advancing of energy storage ceramics. Therefore, synthesizing novel perovskite-based materials that exhibit high energy density, high energy efficiency, and low loss is crucial in achieving superior energy ...
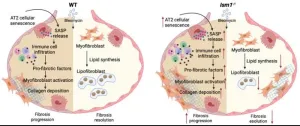
Ism1 deficiency in mice exacerbates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis with enhanced cellular senescence and delayed fibrosis resolution
2024-06-12
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic and progressive lung disease marked by the thickening and scarring of lung tissue with unclear etiology. Affecting around five million people worldwide, IPF causes severe respiratory problems and greatly diminishes the quality of life. Despite ongoing medical research, the exact cause of IPF is still unknown, and treatment options are limited. The prognosis for IPF is grim, with only about 20% of patients surviving five years post-diagnosis, highlighting the critical need for better therapies and a deeper understanding ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
[Press-News.org] Incidence of dementia before age 65 years among World Trade Center attack respondersJAMA Network Open