(Press-News.org) In the 2023 update of their recommendations for osteoarthritis management, EULAR – The European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology – recognise osteoarthritis as a severe disease, and one with important implications for both the individual and society.3 However, most people with osteoarthritis do not receive optimal management,4,5 and this represents an important unmet need – especially when considering additional systemic comorbidities. To explore this further, ComOA6 has combined case-control and cohort studies for over 3 million people in primary care in the UK, Netherlands, Sweden, and Spain. The analyses – shared at the 2024 EULAR congress in Vienna – examines associations between osteoarthritis and 61 different comorbidities identified before and after the first osteoarthritis diagnosis. The researches then tested the similarity of their findings across the four countries – where congruency was determined to be present if the results of all centres were significant and favoured in one direction.
Across the four databases there were 845,373 osteoarthritis cases and 2,556,243 controls. Pooled prevalence data showed several conditions that were more common in people with osteoarthritis than in matched controls. The conditions with leading prevalence were chronic back pain, hypertension, allergy, cataract, vertigo, depression, and diabetes. Of 33 comorbidities studied, 10 such as fibromyalgia, polymyalgia, and chronic back pain showed congruent evidence of association with osteoarthritis during the diagnosis across the four countries. The three major comorbidities developed after the diagnosis of osteoarthritis were fibromyalgia, rheumatoid arthritis, and polymyalgia. No congruent evidence of association with either before or after the diagnosis of osteoarthritis was found for 14 chronic conditions, including heart failure, diabetes, dementia, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
These are important findings to consider for planning management of people with osteoarthritis, and suggest further research is warranted to establish the causal association between osteoarthritis and its comorbidities.
Source
Swain S, et al. Comorbidities in people with osteoarthritis in four European primary care settings - comprehensive evidence from the ComOA study. Presented at EULAR 2024; OP0230.
Ann Rheum Dis 2024; DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2024-eular.3327.
References
1. EULAR RheumaMap. A research roadmap to transform the lives of people with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases; 2019.
2. Hunter DJ, Bierma- Zeinstra S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet 2019;393:1745–59.
3. Moseng T, et al. EULAR recommendations for the non- pharmacological core management of hip and knee osteoarthritis: 2023 update. Ann Rheum Dis 2024; doi:10.1136/ard-2023-225041.
4. Basedow M, Esterman A. Assessing appropriateness of osteoarthritis care using quality indicators: a systematic review. J Eval Clin Pract 2015;21:782–9.
5. Hagen KB, et al. Quality of community- based osteoarthritis care: a systematic review and meta- analysis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2016;68:1443–52.
6. Swain S, et al. Comorbidities in osteoarthritis (ComOA): a combined cross-sectional, case–control and cohort study using large electronic health records in four European countries. BMJ Open 2022;12:e052816.
About EULAR
EULAR is the European umbrella organisation representing scientific societies, health professional associations and organisations for people with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs). EULAR aims to reduce the impact of RMDs on individuals and society, as well as improve RMD treatments, prevention, and rehabilitation. To this end, EULAR fosters excellence in rheumatology education and research, promotes the translation of research advances into daily care, and advocates for the recognition of the needs of those living with RMDs by EU institutions.
Contact
EULAR Communications, communications@eular.org
Notes to Editors
EULAR Recommendations
EULAR School of Rheumatology
EULAR Press Releases
END
Osteoarthritis: associations and comorbidities
Data from the multi-centre ComOA study
2024-06-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
High-precision measurements challenge our understanding of Cepheids
2024-06-14
“Classical Cepheids” are a type of pulsating star that rhythmically brightens and dims over time. These pulsations help astronomers measure vast distances across space, which makes Cepheids crucial “standard candles” that help us understand the size and scale of our universe.
Despite their importance, studying Cepheids is challenging. Their pulsations and potential interactions with companion stars create complex patterns that are difficult to measure accurately. Different instruments and methods used over the years have led to inconsistent data, ...
New approach to identifying altermagnetic materials
2024-06-14
Magnetic materials have traditionally been classified as either ferromagnetic, like the decorative magnets on iron refrigerator doors that are seemingly always magnetic, or antiferromagnetic, like two bar magnets placed end-to-end with opposite poles facing each other, canceling each other out so that the material has no net magnetism. However, there appears to be a third class of magnetic materials exhibiting what in 2022 was dubbed altermagnetism.
Microscopically, magnetism arises from a collection of tiny magnets associated with electrons, ...
Is magnesium the sleeping potion that enables sandhoppers to survive cold winters?
2024-06-14
Magnesium compounds are a common ingredient of many remedies designed to help people wind down and escape the stresses of modern life.
However, a new study has shown it is not only humans that are using forms of the chemical as a way to help them survive challenging conditions.
In tests conducted on beaches in Cornwall, and in the laboratory at the University of Plymouth, scientists confirmed the findings of previous studies which showed large sandhoppers (Talitrus saltator) increase the levels of magnesium ions in their bodies as temperatures fall. This slows them down so they are less active than they would be during the warmer months.
However, the new study has shown for the first time ...
Report highlights trajectory challenges for women in elite football
2024-06-14
Report highlights trajectory challenges for women in elite football
A new report commissioned by the Fédération Internationale de Football Association (FIFA) and Fédération Internationale des Associations de Footballeurs Professionnels (FIFPRO), undertaken by Edith Cowan University (ECU), surveyed footballers across 12 countries in six confederations. More than 700 players participated in the survey, with 71.5% classifying themselves as professional, with a further ...
How men can better support each other’s mental health
2024-06-14
Men are often urged to talk about their mental health with friends, but what does that involve?
This week, researchers from the Men’s Health Research Program at UBC introduced In Good Company, a website and podcast series aimed at answering precisely that question. The website provides practical advice for men seeking to make new connections, strengthen existing relationships and provide mutual support. The podcast series interviews men’s health experts and psychologists to explore the nuances and benefits of authentic male connection. Both ...
Low-sodium alternatives can lead to major health gains in Indonesia
2024-06-14
Excess sodium intake and a lack of potassium are major contributing factors towards high blood pressure in Indonesia, prompting calls for low-sodium potassium-rich salt substitutes (LSSS) to be readily available to improve health and curb health costs.
New Griffith University research has looked at the impact of switching out current table salt (100 per cent sodium chloride) with a low-sodium alternative in Indonesia.
Lead author Dr Leopold Aminde from the School of Medicine and Dentistry said the World Health Organisation has recommended a population-wide reduction in sodium consumption to tackle the burden of high blood pressure and ...
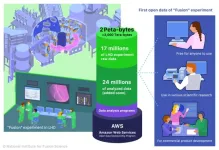
25 years of massive fusion energy experiment data completely open on the “cloud”, to be available to everyone
2024-06-14
Background
High-temperature fusion plasma experiments conducted in the Large Helical Device (LHD) of the National Institute for Fusion Science (NIFS), have renewed the world record for an acquired data amount, 0.92 terabytes (TB) per experiment, in February 2022, by using a full range of state-of-the-art plasma diagnostic devices*1. The International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER), which is currently under construction in France through the international collaboration of seven parties, is expected to generate ...
Rice lab achieves major gains in perovskite solar cell stability
2024-06-14
EMBARGOED for release until 1pm U.S. Central Time (2pm Eastern) on June 13, 2024
HOUSTON – (June 13, 2024) – Solar power is not only the fastest growing energy technology in recent history but also one of the cheapest energy sources and the most impactful in terms of reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
A Rice University study featured on the cover of today’s issue of Science describes a way to synthesize formamidinium lead iodide (FAPbI3) ⎯ the type of crystal currently used to make the highest-efficiency perovskite solar cells ⎯ into ultrastable, high-quality photovoltaic films. The overall efficiency of the resulting ...
New mechanisms in the development of stroke were discovered
2024-06-14
A group of researchers from the University of Tartu and international scientists discovered new mechanisms of how stroke occurs by studying changes in mouse and human cells. The study lays the foundation for new, more precise treatment methods and better diagnostics, which could improve cardiovascular health in the future.
One of the authors of the study, a PhD student of Faculty of Medicine of University of Tartu Katyayani Sukhavasi said that affecting people of all ages, every fifth minute, someone suffers a stroke resulting in brain bleeding or ischemia. „Consequently, many people die ...
The BMJ Commission sets out manifesto for a healthier UK
2024-06-14
Long term thinking and stable, consistent policies are key to improving our nation’s financial prosperity and wellbeing, say experts on The BMJ Commission on the Future of the NHS as they set out their manifesto for a healthier UK.
The BMJ Commission brings together leading experts from medicine and healthcare to identify the key challenges and priorities and make recommendations aimed at ensuring that the vision of the NHS is realised.
Their key pledges of what they would do if they were in government are:
Reaffirming ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
[Press-News.org] Osteoarthritis: associations and comorbiditiesData from the multi-centre ComOA study