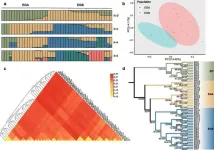
(Press-News.org) In a breakthrough that could redefine tea crop protection, a new study has shed light on the genetic makeup of the tea grey geometrid, Ectropis grisescens. Through the re-sequencing of 43 genomes, scientists have mapped out the pest's population structure and its remarkable adaptation to tea crops, offering new avenues for managing this agricultural adversary.
Amidst the lush tea plantations, a microscopic menace looms—the tea grey geometrid, a pest that can decimate tea yields with its insatiable appetite. The economic and qualitative havoc wreaked by this insect has prompted an urgent call for innovative pest control solutions. However, the genomic secrets of this species have remained largely unexplored, necessitating an in-depth genetic study to unravel its resilience and inform smarter pest management strategies.
Zhejiang University's research team has taken a monumental step forward with their latest publication (DOI: 10.1007/s44297-024-00026-z) in Crop Health on June 1, 2024. The study presents a detailed genomic analysis of the tea grey geometrid, unveiling a genetic variation atlas that may lead to the development of more precise and effective pest control tactics.
In a meticulous exploration of the tea grey geometrid's genome, the researchers have discovered a genetic mosaic that reveals the insect's evolutionary journey and its adeptness at exploiting tea crops. The distinction between two subpopulations, EGA and EGB, paints a more intricate picture of the species' adaptation across different regions. The identification of 627,569 SNPs is a testament to the insect's genetic diversity, hinting at a natural selection that favors traits enabling it to flourish in the presence of tea crops. The study's most captivating find is the presence of selected genes, such as those encoding P-glycoprotein and lactase, which suggest metabolic adaptations to the unique chemical milieu of tea plants. These genetic adaptations are likely crucial for the geometrid's successful invasion and survival in tea plantations, marking a significant leap in our comprehension of its biology and susceptibility.
Dr. Zhizhi Wang, the principal investigator of the study, underscores the significance of these genetic revelations. "Our research peels back the layers of the tea grey geometrid's evolutionary narrative and lays the groundwork for crafting pest management strategies that are rooted in genetic knowledge," Dr. Wang remarks.
The insights gleaned from this genomic study are poised to have a profound impact on the tea industry. With a clearer understanding of the genetic factors driving the tea grey geometrid's adaptation to tea crops, the scientific community is better equipped to devise eco-friendly and efficacious pest control measures. This could lead to a significant reduction in the use of chemical pesticides, thereby protecting the integrity and yield of tea crops, and fostering a more sustainable approach to agriculture.
###
References
DOI
10.1007/s44297-024-00026-z
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.1007/s44297-024-00026-z
Funding information
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Plan (Grant No.2019YFD1002101), the Guangdong Laboratory of Lingnan Modern Agriculture Project (Grant No. NT2021003), the Key Research and Development Program of Zhejiang Province (Grant No. 2021C02045) and the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. U22A20485 and 32272607).
About Crop Health
Crop Health serves as a comprehensive platform for disseminating the fundamental understanding and technological innovation in disease, pest and environmental pollution management, and resistance breeding and engineering. Aiming to be a leading academic journal, Crop Health is dedicated to publishing high-quality papers, covering all aspects connected to crop health with a particular interest in regards to cross-disciplinary research. Article types in this journal include original research articles, letters, short communications, reviews and perspectives.
END
Tea crop saviors: Genomic insights into the tea grey geometrid's survival strategy
2024-06-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cervical cancer screening rates among rural and urban females
2024-06-14
About The Study: This repeated cross-sectional study found that past-year Papanicolaou testing rates were lower in 2022 than 2019, pointing to a need to increase access to screenings to prevent an uptick in cervical cancer incidence. Rural-vs-urban differences in 2022 indicate a need to specifically target rural females.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Tyrone F. Borders, Ph.D., email ty.borders@uky.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.17094)
Editor’s ...
Tiny New Zealand bird delivers a lesson in birdsong evolution
2024-06-14
Parrots, songbirds, and hummingbirds can learn to make new sounds. No-one knew, but New Zealand’s smallest bird, the rifleman or titipounamu, may have a rudimentary version of the same talent.
University of Auckland research into the bird is part of a rethinking of how and when vocal learning evolved in birds.
Scientists traditionally assumed birds were split into two groups - those which can learn sounds (parrots, songbirds, and hummingbirds) and those which can’t - but the study published in the scientific journal Communications Biology ...
The phase transition of multi-component (TiZrVNb)C ceramics
2024-06-14
In recent years, high-entropy carbide ceramics have received extensive attention and become another research focus in the high entropy materials field, which are also known as multi-component carbide ceramics. The multi-component carbide ceramics not only inherit the special properties of high-entropy materials brought by complex compositions, but also keep the advantages of transition metal carbide ceramics as a kind of ultra-high temperature ceramics (UHTCs), such as high melting point, high-temperature stability, high Young's modulus, high hardness, and ...
Does endogenous technological change matter in model-based climate change narratives?
2024-06-14
Curbing the confirmed human influence on the climate system and mitigating climate change require profound transformation of global energy system. In this context, modeling technical progress and innovation within Integrated Assessment Models (IAMs) is crucial for providing insights about the consequences of long-term energy system transformation, and capturing the development of several interacting systems and technical evolution process.
A review of Endogenous Technological Change (ETC) written by Hongbo Duan ...
Bringing data to life: New interactive dashboard provides analysis and visualization of sickle cell disease prevalence and burden in an entire state
2024-06-14
INDIANAPOLIS – The Indiana Sickle Cell Dashboard, launching this month on the Regenstrief Institute website, presents a dynamic, panoptic picture of sickle cell disease throughout an entire state. The new dashboard uses de-identified data from throughout the state of Indiana, obtained from multiple clinical and administrative sources, to present easy-to-understand, interactive visualizations of the disease’s prevalence and burden.
The pioneering dashboard, created, developed and maintained by the Regenstrief Institute, is one of the first ...
Synthetic data holds the key to determining best statewide transit investments, new NYU Tandon School of Engineering study finds
2024-06-14
Synthetically generated population data can reveal the equity impacts of distributing transportation resources and funding across diverse regions, according to new research from NYU's Tandon School of Engineering that uses New York State as a case study.
Relying on an artificial dataset representing 19.5 million New York residents and over 120,000 modeled origin-destination trips, researchers from NYU Tandon's C2SMARTER, a Tier 1 U.S U.S. Department of Transportation-funded University Transportation Center, determined how best to invest in transportation services when equitable benefits are an objective.
They ...
New research finds biases encoded in language across cultures and history
2024-06-14
In a new study, published in Social Psychological and Personality Science, researchers share evidence that people’s attitudes are deeply woven into language and culture across the globe and centuries.
The researchers looked at connections between people’s attitudes and language from 55 different topics like rich vs. poor, dogs vs. cats, or love vs. money. They used four text sources: Current English writing and text, English books going back 200 years, and texts in 53 languages other than English. As a measure of people’s attitudes, they used data from over 100,000 Americans; first, direct self-reports, and second, an indirect ...
Mothers lower risk of caesarean births after COVID vaccination
2024-06-14
Pregnant women who have been vaccinated against Covid-19 are less likely to have a caesarean section or experience hypertension, according to a study.
A meta-analysis funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research Birmingham Biomedical Research Centre of 67 studies which included more than 1.8m women found that being fully vaccinated against COVID-19 had a protective benefit against infection and hospitalisation, while vaccination with at least one dose lowered the risk of adverse pregnancy-related and neonatal outcomes.
Drawing on ...
Ultrasensitive liquid biopsy tech spots cancer earlier than standard methods
2024-06-14
An artificial intelligence-powered method for detecting tumor DNA in blood has shown unprecedented sensitivity in predicting cancer recurrence, in a study led by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine, NewYork-Presbyterian, the New York Genome Center (NYGC) and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK). The new technology has the potential to improve cancer care with the very early detection of recurrence and close monitoring of tumor response during therapy.
In the study, which appears June 14 in Nature Medicine, the researchers showed that they could train a machine learning model, a type ...
New study emphasizes tradeoffs between arresting groundwater depletion and food security
2024-06-14
Washington DC, June 14, 2024: A study by authors from the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI), published today in Nature Sustainability, reaffirms the world’s growing dependence on depleting groundwater systems. Although efforts to slow down groundwater depletion need to be urgently accelerated, this study indicates that such efforts – in the absence of other accompanying measures – would likely lead to significant food security impacts. The study finds that ending groundwater depletion would lead to sharp declines in food production, ...