New carbon nitride membrane revolutionizes lithium extraction from salt lakes
2024-06-14
(Press-News.org)
In a major breakthrough for lithium recovery technologies, researchers from the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, together with collaborators, have developed a crystalline carbon nitride membrane that could transform the lithium extraction industry.
The innovative design, which mimics biological ion channels, shows remarkable efficiency and durability in separating lithium ions from magnesium ions in salt-lake brine.
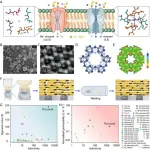
The study, published in Science Advances on June 14, introduces a "congener-welded" crystalline carbon nitride membrane with bio-inspired enhancements that significantly outperforms traditional polymer membranes. This innovative membrane achieves an impressive selectivity ratio of 1,708 for the extraction of highly dilute lithium ions (0.002 M) from concentrated magnesium ions (1.0 M), which is crucial for addressing the prevalent high magnesium content in various lithium sources.
The design of the membrane is inspired by nature’s own highly selective biological ion channels, which efficiently discriminate between different ions. "Our approach was to mimic these natural systems, creating a membrane with both high selectivity and enhanced stability, which are critical for practical applications," said ZHANG Yuanyuan, co-first author of the study from QIBEBT.
The exceptional performance of the membrane is due to its unique structure, which combines crystalline and amorphous forms of polymer carbon nitride. This structure not only provides the necessary pore uniformity and narrowness to exclude larger hydrated magnesium ions, but also facilitates smooth lithium-ion transport, similar to the barrier-free ion transport seen in natural ion channels.
"The dual functionality of our membrane opens up new possibilities for its use beyond lithium extraction," said Prof. GAO Jun, co-corresponding author of this study from QIBEBT. "These properties could make a significant contribution to environmental protection efforts, in addition to improving the efficiency of resource recovery."
This advancement comes at a crucial time, as the demand for lithium continues to grow, driven largely by the electric vehicle market and the renewable energy sector. Efficient and sustainable extraction methods are essential to meeting this demand and reducing the environmental impact of lithium mining.
"The advances achieved through this membrane technology offer new possibilities for efficient extraction of lithium, a crucial element in the transition to renewable energy and electric mobility," said Prof. LIU Jian, co-corresponding author of the study from QIBEBT.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-06-14
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Lung cancer is the most diagnosed cancer and the leading cause of cancer death globally, representing an urgent need for new and improved treatment options.
Researchers from Brigham and Women’s Hospital developed a new nanomedicine therapy that delivers anticancer drugs to lung cancer cells and enhances the immune system's ability to fight cancer.
The research must undergo rigorous toxicology studies before moving into clinical testing in patients but represents a potential treatment for patients who have failed to respond to traditional immunotherapy.
Researchers at Brigham and ...
2024-06-14
Atlanta, GA – June 14, 2024 – Antibiotics in the uppermost water surface, known as the sea surface microlayer, can significantly affect the number of bacteria present and contribute to the adaptation of marine bacteria against widely used antibiotics. In new research presented at ASM Microbe, scientists directly assessed the potential effects of antibiotics on bacterial diversity in Jade Bay, Southern North Sea, Germany.
The researchers tested the susceptibility and resistance of marine bacteria to ofloxacin, ...
2024-06-14
Atlanta, GA—Sepsis is a life-threatening infection complication and accounts for 1.7 million hospitalizations and 350,000 deaths annually in the U.S. Fast and accurate diagnosis is critical, as mortality risk increases up to 8% every hour without effective treatment. However, the current diagnostic standard is reliant on culture growth, which typically takes 2-3 days. Doctors may choose to administer broad-spectrum antibiotics until more information is available for an accurate diagnosis, but these can have limited efficacy and potential toxicity to the patient.
In a study presented at ASM Microbe, a team from Day Zero Diagnostics unveiled a novel approach to antimicrobial susceptibility ...
2024-06-14
A team of researchers led by Philip Walther at the University of Vienna carried out a pioneering experiment where they measured the effect of the rotation of Earth on quantum entangled photons. The work, just published in Science Advances, represents a significant achievement that pushes the boundaries of rotation sensitivity in entanglement-based sensors, potentially setting the stage for further exploration at the intersection between quantum mechanics and general relativity.
Optical Sagnac interferometers are the most sensitive devices to rotations. They have been pivotal in our understanding of fundamental physics since the early years of the last century, contributing to establish ...
2024-06-14
Atlanta, Ga. – June 14, 2023 – Researchers have demonstrated that a new technology could quickly and accurately diagnose bloodstream infections. The study findings were reported at ASM Microbe, the annual meeting of the American Society for Microbiology.
“There is a need to be able to rapidly and accurately diagnose bacteremia in newborn babies. They are especially susceptible to long-term morbidities and mortality the longer they go without treatment, or even with inaccurate treatment for bloodstream infections or sepsis,” said presenting study author April Aralar, Ph.D., a ...
2024-06-14
Background: We previously demonstrated the successful use of in vivo CRISPR gene editing to delete 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPD) to rescue mice deficient in fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase (FAH), a disorder known as hereditary tyrosinemia type 1 (HT1). The aim of this study was to develop an ex vivo gene-editing protocol and apply it as a cell therapy for HT1.
Methods: We isolated hepatocytes from wild-type (C57BL/6J) and Fah-/- mice and then used an optimized electroporation protocol to deliver Hpd-targeting CRISPR-Cas9 ribonucleoproteins into hepatocytes. Next, hepatocytes were transiently incubated in ...
2024-06-14
University of Georgia-based startup CyanVac LLC received federal funding to support a comparative Phase 2b clinical trial of CVXGA, the company’s intranasal vaccine candidates designed to protect against COVID-19.
As part of the award from Project NextGen, a federal initiative based in the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), CyanVac will sponsor a randomized, double-blind Phase 2b study with 10,000 participants to compare the efficacy and safety of the intranasal vaccine against an FDA-approved mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine.
The new vaccine is based on a viral delivery platform developed by He containing modified ...
2024-06-14
Patients are less likely to fill prescriptions for naloxone when they face increases in out-of-pocket costs, according to U-M researchers.
Patients are less likely to fill prescriptions for naloxone when they face increases in out-of-pocket costs, according to research by the University of Michigan.
Published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, the study utilized data from a national pharmacy transactions database from November 2020 to March 2021. Researchers found that about 1 in 3 naloxone ...
2024-06-14
New research by Swansea University and the University of Zurich has found that sharks retained high levels of functional diversity for most of the last 66 million years, before steadily declining over the last 10 million years to its lowest value in the present day.
Modern sharks are among the ocean’s most threatened species; yet have notably survived numerous environmental changes in their 250-million-year history. Today, their more than 500 species play many different ecological roles, from apex predators to nutrient transporters.
Ecological roles are determined by species’ traits such as body size, ...
2024-06-14
Periods of fasting reprogram the immune system’s natural killer cells to better fight cancer, according to a new study in mice from researchers at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK).
Fasting and other dietary regimens are increasingly being explored as ways to starve cancer cells of the nutrients they need to grow and to make cancer treatments more effective.
Now a team of researchers from MSK’s Sloan Kettering Institute and their collaborators have shown for the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New carbon nitride membrane revolutionizes lithium extraction from salt lakes