(Press-News.org) When stressed out, many of us turn to junk food for solace. But new University of Colorado Boulder research suggests this strategy may backfire.
The study found that in animals, a high-fat diet disrupts resident gut bacteria, alters behavior and, through a complex pathway connecting the gut to the brain, influences brain chemicals in ways that fuel anxiety.
“Everyone knows that these are not healthy foods, but we tend to think about them strictly in terms of a little weight gain,” said lead author Christopher Lowry, a professor of integrative physiology at CU Boulder. “If you understand that they also impact your brain in a way that can promote anxiety, that makes the stakes even higher.”
Lowry’s team divided adolescent rats into two groups: Half got a standard diet of about 11% fat for nine weeks; the others got a high-fat diet of 45% fat, consisting mostly of saturated fat from animal products.
The typical American diet is about 36% fat, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Throughout the study, the researchers collected fecal samples and assessed the animals’ microbiome, or gut bacteria. After nine weeks, the animals underwent behavioral tests.
When compared to the control group, the group eating a high-fat diet, not surprisingly, gained weight. But the animals also showed significantly less diversity of gut bacteria. Generally speaking, more bacterial diversity is associated with better health, Lowry explained. They also hosted far more of a category of bacteria called Firmicutes and less of a category called Bacteroidetes. A higher Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes ratio has been associated with the typical industrialized diet and with obesity.
The high-fat diet group also showed higher expression of three genes (tph2, htr1a, and slc6a4) involved in production and signaling of the neurotransmitter serotonin—particularly in a region of the brainstem known as the dorsal raphe nucleus cDRD, which is associated with stress and anxiety.
While serotonin is often billed as a “feel-good brain chemical,” Lowry notes that certain subsets of serotonin neurons can, when activated, prompt anxiety-like responses in animals. Notably, heightened expression of tph2, or tryptophan hydroxylase, in the cDRD has been associated with mood disorders and suicide risk in humans.
“To think that just a high-fat diet could alter expression of these genes in the brain is extraordinary,” said Lowry. “The high-fat group essentially had the molecular signature of a high anxiety state in their brain.”
Lowry suspects that an unhealthy microbiome compromises the gut lining, enabling bacteria to slip into the body’s circulation and communicate with the brain via the vagus nerve, a pathway from the gastrointestinal tract to the brain.
“If you think about human evolution, it makes sense,” Lowry said. “We are hard-wired to really notice things that make us sick so we can avoid those things in the future.”
Lowry stresses that not all fats are bad, and that healthy fats like those found in fish, olive oil, nuts and seeds can be anti-inflammatory and good for the brain.
His advice: Eat as many different kinds of fruits and vegetables as possible, add fermented foods to your diet to support a healthy microbiome and lay off the pizza and fries. Also, if you do have a hamburger, add a slice of avocado. Some research shows that good fat can counteract some of the bad.
END
Study shows a high-fat diet may fuel anxiety
2024-06-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Novel method for measuring nano/microplastic concentrations in soil using spectroscopy
2024-06-17
Nano and microplastics are a well-known menace, found practically everywhere in nature, including soil, oceans, drinking water, air, and even the human body. Studies show that soils in particular hold a significant portion of N/MPs. The problem with these N/MPs is their microscopic size, which allows them to easily migrate through soil into the ground or freshwater bodies due to rainwater leaching. From there, they enter the human body. Hence, it is imperative to understand the distribution and movement of the soil’s N/MPs to gauge their threat and mitigate it.
Current ...
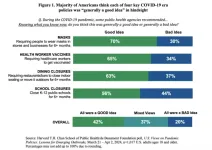
Poll: Majority of Americans say key COVID-19 policies were a good idea—but views of individual policies vary
2024-06-17
Embargoed for release: Monday, June 17, 6:00 AM ET
Boston, MA—A majority of Americans say that several key policies to stop the spread of COVID-19 were generally a good idea in hindsight, according to a new national poll by Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health and the de Beaumont Foundation. The poll also found, however, that views varied across policies, and many say the policies had negative impacts.
The poll, U.S. Views on Pandemic Policies: Lessons for Emerging Outbreaks, was conducted March 21 to April 2, 2024, among a nationally representative, probability-based sample of 1,017 adults ages 18 or older.
A majority of Americans say four key pandemic policies ...
Six distinct types of depression identified in Stanford Medicine-led study
2024-06-17
In the not-too-distant future, a screening assessment for depression could include a quick brain scan to identify the best treatment.
Brain imaging combined with machine learning can reveal subtypes of depression and anxiety, according to a new study led by researchers at Stanford Medicine. The study, to be published June 17 in the journal Nature Medicine, sorts depression into six biological subtypes, or “biotypes,” and identifies treatments that are more likely or less likely to work ...
Chronic high blood pressure during pregnancy doubled between 2008 and 2021 in the U.S.
2024-06-17
Research Highlights:
The number of individuals in the United States who had chronic hypertension or chronic high blood pressure during pregnancy doubled between 2008 and 2021, according to a nationwide review of private health insurance claims.
Treatment rates for chronic hypertension during pregnancy remained relatively low but stable during the same time, with only about 60% of the individuals receiving (filling prescriptions for) antihypertensive medications.
The researchers say these findings underscore the need to adhere to clinical guidelines for accurate diagnosis and treatment of high blood pressure before and during pregnancy.
Embargoed until 4 ...
Pancreatic cancer’s cellular amnesia
2024-06-17
Things aren’t always as they seem. Take pancreatic cancer, for example. In up to one in 10 cases, researchers have documented a peculiar characteristic. Some of the pancreatic cells appear to have lost their identity. It’s as if they forget what they are.
“This is very bizarre. You see pancreatic cancer, which usually somewhat resembles the original organ, losing those features and basically becoming akin to skin or esophagus—these other very unrelated tissues, " explains ...
An earthquake changed the course of the Ganges. Could it happen again?
2024-06-17
A major earthquake 2,500 years ago caused one of the largest rivers on Earth to abruptly change course, according to a new study. The previously undocumented quake rerouted the main channel of the Ganges River in what is now densely populated Bangladesh, which remains vulnerable to big quakes. The study was just published in the journal Nature Communications.
Scientists have documented many river-course changes, called avulsions, including some in response to earthquakes. However, “I don’t think we have ever seen such a big ...
New study reveals urgent need for region-specific models to improve brain health in diverse settings
2024-06-17
A pioneering study published today in the journal Nature Aging has unveiled significant heterogeneity in the risk factors affecting healthy aging in Latin America and emphasised the limitations of current models of brain health, which are primarily based on data from high-income countries. The research was conducted by researchers from Trinity College Dublin (Ireland), and by colleagues in Universidad Adolfo Ibanez (Chile) and Pontificia Universidad Javeriana (Colombia) among others.
The study developed a metanalytical approach with 146,000 participants and findings emphasise how current models of brain health may not apply ...
Treatment of stress-induced exhaustion disorder has wrong focus
2024-06-17
A new thesis at Uppsala University questions the traditional view of stress-induced exhaustion disorder. A new model is proposed in its place that puts more focus on meaningfulness rather than recovery.
“There are no established evidence-based models for the psychological treatment of stress-induced exhaustion disorder. The concepts of ‘recovery’ and ‘stress’ are so widely accepted in our current era that it is difficult to examine them critically. It’s easy to think that patients with stress-related exhaustion should prioritise rest and relaxation, but an overly one-sided focus on recovery ...
Bedtime battles: 1 in 4 parents say their child can’t go to sleep because they’re worried or anxious
2024-06-17
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – Many bedtime battles stem from children’s after dark worries, suggests a new national poll.
And while most families have bedtime rituals to help their little ones ease into nighttime, many rely on strategies that may increase sleep challenges long term, according to the University of Michigan Health C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital National Poll on Children’s Health.
Overall, one in four parents describe getting their young child to bed as difficult – and these parents are less likely to have a bedtime routine, more likely to leave on a video or TV show, and more likely to stay with their child until they’re ...
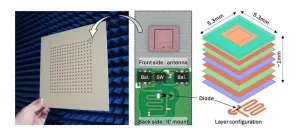
Towards wider 5G network coverage: novel wirelessly powered relay transceiver
2024-06-17
A novel 256-element wirelessly powered transceiver array for non-line-of-sight 5G communication, featuring efficient wireless power transmission and high-power conversion efficiency, has been designed by scientists at Tokyo Tech. The innovative design can enhance the 5G network coverage even to places with link blockage, improving flexibility and coverage area, and potentially making high-speed, low-latency communication more accessible.
Millimeter wave 5G communication, which uses extremely high-frequency radio signals (24 to 100 GHz), is a promising technology for next-generation wireless ...