(Press-News.org) The ketogenic diet has its fanatics and detractors among dieters, but either way, the diet has a scientifically documented impact on memory in mice. Whlie uncovering how the high fat, low carbohydrate diet boosts memory in older mice, Buck scientists and a team from the University of Chile identified a new molecular signaling pathway that improves synapse function and helps explain the diet’s benefit on brain health and aging. Published in the June 5, 2024 issue of Cell Reports Medicine, the findings provide new directions for targeting the memory effects on a molecular level, without requiring a ketogenic diet or even the byproducts of it.
“Our work indicates that the effects of the ketogenic diet benefit brain function broadly, and we provide a mechanism of action that offers a strategy for the maintenance and improvement of this function during aging,” said the study’s senior author, Christian González-Billault, PhD, who is a professor at the Universidad de Chile and director of their Geroscience Center for Brain Health and Metabolism, and adjunct professor at the Buck Institute.
“Building off our previous work showing that a ketogenic diet improves healthspan and memory in aging mice, this new work indicates that we can start with older animals and still improve the health of the aging brain, and that the changes begin to happen relatively quickly,” said John Newman, MD, PhD, whose laboratory at Buck collaborated with Dr. González-Billault on the study. Newman is both an assistant professor at the Buck Institute, and a geriatrician at University of California, San Francisco. “It is the most detailed study to date of the ketogenic diet and aging brain in mice.”
More than a century ago, researchers observed that rats that consumed less food lived longer. “We now know that being able to manipulate lifespan is not about specifically eating less,” said Newman, but actually is related to signals inside cells that turn on and off specific pathways in response to available nutrients. Many of those pathways are related to aging, such as controlling protein turnover and metabolism.
Some of those signals are the ketone bodies, which consist of acetoacetate (AcAc), β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) and to a much lesser extent, acetone. These molecules are routinely produced in the liver. They ramp up when glucose is in short supply, whether due to caloric restriction, intense exercise or low carbohydrate intake, such as with a ketogenic diet.
Seven years ago, Newman led a team that published the first proof of the concept that if a ketogenic diet exposes mice to increased levels of ketone bodies over much of their adult life, it helps them to live longer and age in a more healthy way. “The most striking effect on their health as they aged was that their memory was preserved; it was possibly even better than when they were younger,” he said.
The current study, designed to answer what part of the ketogenic diet was having the effect and how it was affecting the brain on a molecular level to improve memory, was led by González-Billault in a collaboration with scientists at the Buck. Mice on a ketogenic diet are fed a ratio of 90 percent calories from fat and 10 percent from protein, while mice on a control diet received the same amount of protein but only 13 percent fat. The test mice, of “advanced age” of more than two years old, received one week of the ketogenic diet, cycled with one week of the control diet, to keep the mice from overeating and becoming obese.
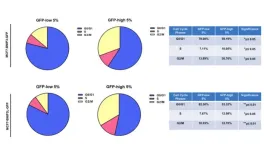
The benefits of the ketogenic diet, said, González-Billault, were demonstrated through neurophysiological and behavioral experiments with the mice that test how well the mechanisms involved in memory generation, storage, and retrieval function in aged animals. When these showed that the ketogenic diet appeared to benefit how well the synapses responsible for memory worked, they took a deep dive into the protein composition at these synapses in the hippocampus, in a collaboration with Buck professor Birgit Schilling, PhD, who directs the Proteomics and Mass Spectrometry Center.
“Surprisingly, we saw that the ketogenic diet caused dramatic changes in the proteins of the synapse,” said Schilling. Even more surprising, she said, was that the changes started after a relatively brief exposure to the diet (tested after only one week on the diet) and only became more pronounced over time (tested again after six weeks and a year).
Further testing indicated that in synapses, a particular signaling pathway (protein kinase A, which is critical to synapse activity) was activated by the ketogenic diet. In isolated cells, the team then showed that it appears that BHB, the main ketone body produced in a ketogenic diet, is activating this pathway. This leads to the idea, said González-Billault, that ketone bodies (specifically BHB) play a crucial role not only as an energy source, but also as a signaling molecule.
“BHB is almost certainly not the only molecule in play, but we think this is an important part of understanding how the ketogenic diet and ketone bodies work,” said Newman “This is the first study to really connect deep molecular mechanisms of ketone bodies all the way through to improving the aging brain.”
Looking forward, he said, the next step would be to see if the same memory protection could be achieved by using BHB alone, or possibly going even more targeted than that by manipulating the protein kinase A signaling pathway directly. “If we could recreate some of the big-picture effects on synapse function and memory just by manipulating that signaling pathway in the right cells,” he said, “we wouldn’t even need to eat a ketogenic diet in the end.”
CITATION: “Ketogenic diet administration later in life improves memory by modifying the synaptic cortical proteome via the PKA signaling pathway in aging mice”
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101593
Other Buck researchers involved in the study are: Samah Shah, Cameron Wehrfritz, Mitsunori Nomura and Joanna Bons.
Acknowledgements: This work was supported in part through funds from the National Institutes of Health, the Chilean National Fund for Scientific and Technological Development (FONDECYT), the Center of Interventional Medicine for Precision and Advanced Cellular Therapy (IMPACT) at Universidad de Los Andes, and the Chilean National Research and Development Agency (ANID).
COI: The authors declare no competing interests.
About the Buck Institute for Research on Aging
At the Buck, we aim to end the threat of age-related diseases for this and future generations. We bring together the most capable and passionate scientists from a broad range of disciplines to study mechanisms of aging and to identify therapeutics that slow down aging. Our goal is to increase human health span, or the healthy years of life. Located just north of San Francisco, we are globally recognized as the pioneer and leader in efforts to target aging, the number one risk factor for serious diseases including Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, cancer, macular degeneration, heart disease, and diabetes. The Buck wants to help people live better longer. Our success will ultimately change healthcare. Learn more at: https://buckinstitute.org
END
How the ketogenic diet improves healthspan and memory in aging mice
The insight into mechanisms provides new targets for improving memory that may not even require a ketogenic diet
2024-06-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Brazilian scientists develop functional bread to help prevent asthma
2024-06-17
Brazilian researchers have developed functional bread with the potential to prevent asthma, a respiratory disorder responsible for some 350,000 hospitalizations per year in the SUS (Sistema Único de Saúde), the nation’s public healthcare network.
The formulation, for which a patent application has been filed in Brazil (BR1020210266465), is described in an article published in the journal Current Developments in Nutrition. It contains Saccharomyces cerevisiae UFMG A-905, ...
Potential new treatment option for diabetic retinopathy
2024-06-17
Potential New Treatment Option for Diabetic Retinopathy
OU researcher developing potential new treatment for diabetic retinopathy that could address the problem much earlier.
OKLAHOMA CITY, OKLA. – Patients with diabetes face a host of potential health problems as they work to manage the chronic disease. Still, one concern that seems to weigh heavily is the risk of losing their sight through a condition known as diabetic retinopathy.
Researchers at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences and Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK) Cancer Center are studying a new, revolutionary treatment for diabetic retinopathy that could change the prognosis ...
Paternal use of metformin during sperm production not associated with major birth defects
2024-06-17
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 17 June 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not ...
American diets have a long way to go to achieve health equity
2024-06-17
Poor diet continues to take a toll on American adults. It’s a major risk factor for obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain cancers, and more than one million Americans die every year from diet-related diseases, according to the Food and Drug Administration. Poor diet and food insecurity is also costly, attributing to an estimated $1.1 trillion in healthcare expenditures and lost productivity. These burdens also contribute to major health disparities by income, education, zip code, race, and ethnicity.
In a study from the Food is Medicine Institute at the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University published today in ...
New ‘aging atlas’ provides a detailed map of how cells and tissues age
2024-06-17
A new aging atlas gives scientists an in-depth view of how individual cells and tissues in worms age and how different lifespan-extending strategies might stop the clock.
Aging impacts all the tissues in our body – from our muscles to our skin. Figuring out how individual tissues and cells age could help researchers better understand the aging process and aid in the development of anti-aging treatments.
Due to their short lifespans, simple body plans, and genetic similarity to humans, many researchers study aging in roundworms. To look at aging at the level of tissues and cells, a team of researchers from HHMI's Janelia ...
New technology allows researchers to precisely, flexibly modulate brain
2024-06-17
By Beth Miller
Human brain diseases, such as Parkinson’s disease, involve damage in more than one region of the brain, requiring technology that could precisely and flexibly address all affected regions simultaneously. Researchers at Washington University in St. Louis have developed a noninvasive technology combining a holographic acoustic device with genetic engineering that allows them to precisely target affected neurons in the brain, creating the potential to precisely modulate selected cell ...
Origins of cumulative culture in human evolution
2024-06-17
Each of us individually is the accumulated product of thousands of generations that have come before us in an unbroken line. Our culture and technology today are also the result of thousands of years of accumulated and remixed cultural knowledge.
But when did our earliest ancestors begin to make connections and start to build on the knowledge of others, setting us apart from other primates? Cumulative culture — the accumulation of technological modifications and improvements over generations — allowed humans to adapt to a diversity of environments and challenges. But, it is unclear when cumulative culture first developed during hominin evolution.
A study published ...
Mitophagy and cancer: BNIP3/BNIP3L’s role in stemness, ATP production, proliferation, and cell migration
2024-06-17
“[...] our current work has provided a novel strategy to enrich for a sub-population of cancer cells, with high basal levels of mitophagy.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 17, 2024 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 11, entitled, “Mitophagy and cancer: role of BNIP3/BNIP3L as energetic drivers of stemness features, ATP production, proliferation, and cell migration.”
Mitophagy is a selective form of autophagy which permits ...
Breakthrough approach enables bidirectional BCI functionality
2024-06-17
Brain-computer interfaces or BCIs hold immense potential for individuals with a wide range of neurological conditions, but the road to implementation is long and nuanced for both the invasive and noninvasive versions of the technology. Bin He of Carnegie Mellon University is highly driven to improve noninvasive BCIs, and his lab uses an innovative electroencephalogram (EEG) wearable to push the boundaries of what’s possible. For the first time on record, the group successfully integrated a novel focused ultrasound stimulation to realize bidirectional BCI that both encodes and decodes brain waves using machine learning in a study with 25 human subjects. This work opens ...
Polarization and risk perception could play important roles in climate-policy outcomes
2024-06-17
Times of crises often call for strong and rapid action, but in polarized societies, strong top-down policies can backfire.
In a paper published on June 17, 2024, in Environmental Research Letters, SFI Applied Complexity Fellow Saverio Perri, SFI Science Board Fellow Simon Levin (Princeton University), and colleagues present a conceptual model of how these dynamics could play out in efforts to decarbonize our energy supply. The model illustrates the complex interplay between strong policies, people’s perception of risk, and the amount of polarization in a society. They show that in situations where the perception of risk is low — where the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Machine learning reveals Raman signatures of liquid-like ion conduction in solid electrolytes
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia researchers emphasize benefits and risks of generative AI at different stages of childhood development
Why conversation is more like a dance than an exchange of words
With Evo 2, AI can model and design the genetic code for all domains of life
Discovery of why only some early tumors survive could help catch and treat cancer at very earliest stages
Study reveals how gut bacteria and diet can reprogram fat to burn more energy
Mayo Clinic researchers link Parkinson's-related protein to faster Alzheimer's progression in women
Trends in metabolic and bariatric surgery use during the GLP-1 receptor agonist era
Loneliness, anxiety symptoms, depressive symptoms, and suicidal ideation in the all of us dataset
A decision-support system to personalize antidepressant treatment in major depressive disorder
Thunderstorms don’t just appear out of thin air - scientists' key finding to improve forecasting
Automated CT scan analysis could fast-track clinical assessments
New UNC Charlotte study reveals how just three molecules can launch gene-silencing condensates, organizing the epigenome and controlling stem cell differentiation
Oldest known bony fish fossils uncover early vertebrate evolution
High‑performance all‑solid‑state magnesium-air rechargeable battery enabled by metal-free nanoporous graphene
Improving data science education using interest‑matched examples and hands‑on data exercises
Sparkling water helps keep minds sharp during long esports sessions
Drone LiDAR surveys of abandoned roads reveal long-term debris supply driving debris-flow hazards
UGA Bioinformatics doctoral student selected for AIBS and SURA public policy fellowship
Gut microbiome connected with heart disease precursor
Nitrous oxide, a product of fertilizer use, may harm some soil bacteria
FAU lands $4.5M US Air Force T-1A Jayhawk flight simulator
SimTac: A physics-based simulator for vision-based tactile sensing with biomorphic structures
Preparing students to deal with ‘reality shock’ in the workplace
Researchers develop beating, 3D-printed heart model for surgical practice
Black soldier fly larvae show promise for safe organic waste removal
People with COPD commonly misuse medications
How periodontitis-linked bacteria accelerate osteoporosis-like bone loss through the gut
Understanding how cells take up and use isolated ‘powerhouses’ to restore energy function
Ten-point plan to deliver climate education unveiled by experts
[Press-News.org] How the ketogenic diet improves healthspan and memory in aging miceThe insight into mechanisms provides new targets for improving memory that may not even require a ketogenic diet