(Press-News.org) Times of crises often call for strong and rapid action, but in polarized societies, strong top-down policies can backfire.
In a paper published on June 17, 2024, in Environmental Research Letters, SFI Applied Complexity Fellow Saverio Perri, SFI Science Board Fellow Simon Levin (Princeton University), and colleagues present a conceptual model of how these dynamics could play out in efforts to decarbonize our energy supply. The model illustrates the complex interplay between strong policies, people’s perception of risk, and the amount of polarization in a society. They show that in situations where the perception of risk is low — where the threat does not feel immediate or particularly dangerous — and opinion polarization is high, strong policy mandates can potentially worsen the long-term outcomes.
It’s a dynamic we saw play out in real-time throughout the COVID-19 pandemic. As policymakers took measures to slow transmission of the disease, the global perception of risk was very high. But as masks and lockdowns worked to curb the spread of the virus, our perceived risk declined; mandates lifted, individuals opted out, and case numbers rose again, often surpassing earlier surges.
Perri et. al’s new model suggests that a similar rebound could happen with policies to encourage a transition to low-carbon energy. Say the global community invested heavily in renewable-energy infrastructure in response to the damaging effects of climate change. If those investments were strong enough to reduce the damages, our human tendency would be to lower our guard. Perri and Levin’s model suggests that, in more polarized societies, this could trigger moves to reinvest in fossil fuels. “In this scenario, you have a very strong, effective policy, and that’s good,” says Perri. “But at the same time, in the long term, it’s ineffective.”
The model shows that, in highly polarized situations, social interactions — behaviors that reinforce dominant norms — can lead to a phase shift where an initial state-change can happen quickly, but subsequent transitions become harder. “It’s a double-edged sword. In one sense, it can accelerate a transition. But at the same time, it can make the threshold for that transition harder to meet,” says Perri. “It's beneficial if public opinion tends to favor a transition toward a sustainable state, but it’s clearly detrimental if there is a general consensus to maintain the unsustainable status quo or move toward a degraded state.”
These dynamic elements of human behavior aren’t included in climate models, but they should be, says Perri. “Our model is not predictive. But we can use it to understand how the dynamics of the system work,” he says. “What we find is that the perception of risk and the impact of opinions on climate mitigation actions are extremely important.” The authors hope that more climate models — and the policy decisions they might inspire — will consider these human–social feedbacks in the future.
Read the paper “Socio-political dynamics in clean energy transition” in Environmental Research Letters (June 17, 2024). DOI: 10.1088/1748-9326/ad5031
END
Polarization and risk perception could play important roles in climate-policy outcomes
When people's perception of risk is low and society is polarized, strong policy measures can backfire in the long run.
2024-06-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
AI shows how field crops develop
2024-06-17
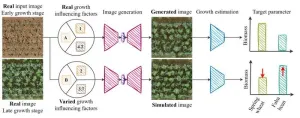
Researchers at the University of Bonn have developed software that can simulate the growth of field crops. To do this, they fed thousands of photos from field experiments into a learning algorithm. This enabled the algorithm to learn how to visualize the future development of cultivated plants based on a single initial image. Using the images created during this process, parameters such as leaf area or yield can be estimated accurately. The results have been published in the journal Plant Methods.
Which plants should I combine ...
African research funders in global spotlight through Dimensions indexing project
2024-06-17
African research is receiving a major visibility boost with the indexing of 10 national funders in Dimensions, the world’s largest linked research database.
This project is a collaboration with Digital Science, the Africa PID Alliance (APA), the Association of African Universities (AAU), the Training Centre in Communication (TCC Africa), and the Research Organization Registry (ROR).
“This project connects the research outputs from leading African funding bodies to the global research ecosystem,” said Joy Owango, Executive Director of TCC Africa ...
New study suggests cancer drug could be used to target protein connection that spurs Parkinson’s disease
2024-06-17
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
In studies with genetically engineered mice, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers say they have identified a potentially new biological target involving Aplp1, a cell surface protein that drives the spread of Parkinson’s disease-causing alpha-synuclein.
The findings, published May 31 in Nature Communications, reveal how Aplp1 connects with Lag3, another cell surface receptor, in a key part of a process that helps spread harmful alpha-synuclein proteins to brain cells. Those protein buildups are hallmarks of Parkinson’s disease.
Notably, the researchers say, Lag3 is already the target of a combination ...
More than 1 in 10 patients at FQHCs experience major social risk factors
2024-06-17
A first-of-its-kind study found high rates of food insecurity, housing insecurity, financial strain, and/or a lack of transportation among patients at federally qualified health centers, particularly patients who were low-income or from racial/ethnic minority populations.
Federally qualified health centers (FQHCs) offer primary care services to 1 in 11 Americans, the majority of whom are low-income and/or underinsured and may not otherwise receive this care. While prior research has shown that 70 percent of FQHCs screen for social ...
Artificial intelligence accurately screens heart failure patients for clinical trial eligibility
2024-06-17
Generative Artificial Intelligence (Gen AI) can rapidly and accurately screen patients for clinical trial eligibility, according to a new study from Mass General Brigham researchers. Such technology could make it faster and cheaper to evaluate new treatments and, ultimately, help bring successful ones to patients.
Investigators assessed the accuracy and cost of a Gen AI process they named RAG-Enabled Clinical Trial Infrastructure for Inclusion Exclusion Review (RECTIFIER), that identifies patients who meet criteria for enrollment in ...
Unlocking the mystery behind the performance decline in a promising cathode material
2024-06-17
The first generation of lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles has been a remarkable success story. Yet, the question arises: What changes to battery materials will spur further advances to extend driving range and lower costs?
A better positive electrode, or cathode, for lithium-ion batteries has been the focus of intense past research. The cathode is one of the main components in batteries. Several candidates for cathode materials offer the prospect of batteries with much higher energy storage, leading to longer driving range. However, the capacity, or amount of current flowing out within a given time, tends to decline rapidly with charge-discharge cycling for reasons ...
A call for renaming clinical research partnerships
2024-06-17
PHILADELPHIA (June 17, 2024) - In a recently published opinion piece in BMJ Open, “Rhetoric of Research: A Call for Renaming the Clinical Research Partnership,” authors from Penn Nursing and Georgetown University School of Nursing, present a compelling argument for rethinking the language used to describe participants in clinical research. The opinion calls for a shift from the traditional term “patient participant” to “participant partner,” emphasizing the crucial role of participants in ...
SwRI breaks ground on new hypersonic engine research facility
2024-06-17
SAN ANTONIO — June 17, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) today celebrated the groundbreaking of the Center for Accelerating Materials and Processes (CAMP), a new facility that will support research and development for tomorrow’s high-speed aerospace engines.
“This project will help ensure the U.S. is a leader in high-speed propulsion research and development,” said Dr. Barron Bichon, director of SwRI’s Materials Engineering Department. “SwRI is committed to advancing this vital technology on behalf of Texas and the nation.”
Market forces including growth in global defense, air travel, ...
International Gemini Observatory and Subaru combine forces to discover first ever pair of merging quasars at cosmic dawn
2024-06-17
Since the very first instant after the Big Bang the Universe has been expanding. This means that the early Universe was considerably smaller and early-formed galaxies were more likely to interact and merge. Galaxy mergers fuel the formation of quasars — extremely luminous galactic cores where gas and dust falling into a central supermassive black hole emit enormous amounts of light. So when looking back at the early Universe astronomers would expect to find numerous pairs of quasars in close proximity to each other as their host galaxies undergo mergers. However, they have been surprised ...
Repurposed drug may help stabilize vision in rare disease
2024-06-17
Roughly 50 families scattered across the world share ultra-rare variants in a particular gene. Silent for years, the inherited mutations make themselves known when patients reach the fourth decade of life. Changes in vision start a cascade of symptoms. Five to 20 years later, the illness is fatal.
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have dedicated many years to understanding the rare condition known as retinal vasculopathy with cerebral leukoencephalopathy and systemic manifestations, or RVCL-S, with the aim of developing a treatment ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Polarization and risk perception could play important roles in climate-policy outcomesWhen people's perception of risk is low and society is polarized, strong policy measures can backfire in the long run.