(Press-News.org) A first-of-its-kind study found high rates of food insecurity, housing insecurity, financial strain, and/or a lack of transportation among patients at federally qualified health centers, particularly patients who were low-income or from racial/ethnic minority populations.
Federally qualified health centers (FQHCs) offer primary care services to 1 in 11 Americans, the majority of whom are low-income and/or underinsured and may not otherwise receive this care. While prior research has shown that 70 percent of FQHCs screen for social risk factors such as food and housing insecurity, no studies have quantified the extent to which FQHC patients are experiencing these challenges nationwide.
For the first time, a study led by Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH) researchers obtained data from all US FQHCs that reported positive screening rates of food insecurity, housing insecurity, financial strain, and lack of transportation, and found that more than 1 in 10 FQHC patients reported experiencing at least one of these social risk factors in 2022.
Published in the journal JAMA Internal Medicine, the findings also showed that rates of these risk factors were significantly higher among FQHCs with greater proportions of patients from historically disenfranchised groups.
“Federally qualified health centers are crucial safety-net providers for millions of low-income families in the US,” says study lead and corresponding author Dr. Kevin Nguyen, assistant professor of health law, policy & management at BUSPH. “In addition to delivering health services, these centers often provide assistance to patients seeking support for housing, food, and transportation. Our findings likely reflect the structural barriers to equity that many patients from marginalized populations continue to face.”
For the study, Dr. Nguyen and colleagues at BUSPH and Brown University School of Public Health (Brown University SPH) utilized 2022 federal data from 1,338 FQHCs across the country, representing 30 million patients in total, including 21.7 million patients among the FQHCs that reported positive screening rates. Among the patients that were screened, the average positive screening rates were 27.6 percent for financial strain, 16.3 percent for food insecurity, 15.4 percent for housing insecurity, and 14.1 percent for lack of transportation. Many of the patients who experienced some or all of the social risk factors also reported that they had income under the federal poverty level, lacked insurance, identified as Black, identified as a sexual minority, were currently or previously unhoused, and/or lived in urban settings.
The researchers hope these findings spur additional support for FQHCs, particularly those with higher proportions of marginalized patients. Many FQHCs are experiencing several barriers to meeting the clinical and social needs of these patients, including limited training and limited ability to integrate screening into care processes.
“Funding specifically allocated for integrating social risk screening, as well as community-informed processes for addressing unmet social needs, may help mitigate these barriers,” Dr. Nguyen says. “National policies are shifting toward incentivizing the measurement of social risk factors, so identifying the payment and care delivery models that equip providers to sustainably address unmet social needs among patients who want assistance may be critical.”
The study’s senior author was Megan Cole, associate professor of health law, policy & management at BUSPH. The study was coauthored by Nicole Giron, doctoral candidate in health services research at Brown University SPH.
END
More than 1 in 10 patients at FQHCs experience major social risk factors
A first-of-its-kind study found high rates of food insecurity, housing insecurity, financial strain, and/or a lack of transportation among patients at federally qualified health centers.
2024-06-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Artificial intelligence accurately screens heart failure patients for clinical trial eligibility
2024-06-17
Generative Artificial Intelligence (Gen AI) can rapidly and accurately screen patients for clinical trial eligibility, according to a new study from Mass General Brigham researchers. Such technology could make it faster and cheaper to evaluate new treatments and, ultimately, help bring successful ones to patients.
Investigators assessed the accuracy and cost of a Gen AI process they named RAG-Enabled Clinical Trial Infrastructure for Inclusion Exclusion Review (RECTIFIER), that identifies patients who meet criteria for enrollment in ...
Unlocking the mystery behind the performance decline in a promising cathode material
2024-06-17
The first generation of lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles has been a remarkable success story. Yet, the question arises: What changes to battery materials will spur further advances to extend driving range and lower costs?
A better positive electrode, or cathode, for lithium-ion batteries has been the focus of intense past research. The cathode is one of the main components in batteries. Several candidates for cathode materials offer the prospect of batteries with much higher energy storage, leading to longer driving range. However, the capacity, or amount of current flowing out within a given time, tends to decline rapidly with charge-discharge cycling for reasons ...
A call for renaming clinical research partnerships
2024-06-17
PHILADELPHIA (June 17, 2024) - In a recently published opinion piece in BMJ Open, “Rhetoric of Research: A Call for Renaming the Clinical Research Partnership,” authors from Penn Nursing and Georgetown University School of Nursing, present a compelling argument for rethinking the language used to describe participants in clinical research. The opinion calls for a shift from the traditional term “patient participant” to “participant partner,” emphasizing the crucial role of participants in ...
SwRI breaks ground on new hypersonic engine research facility
2024-06-17
SAN ANTONIO — June 17, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) today celebrated the groundbreaking of the Center for Accelerating Materials and Processes (CAMP), a new facility that will support research and development for tomorrow’s high-speed aerospace engines.
“This project will help ensure the U.S. is a leader in high-speed propulsion research and development,” said Dr. Barron Bichon, director of SwRI’s Materials Engineering Department. “SwRI is committed to advancing this vital technology on behalf of Texas and the nation.”
Market forces including growth in global defense, air travel, ...
International Gemini Observatory and Subaru combine forces to discover first ever pair of merging quasars at cosmic dawn
2024-06-17
Since the very first instant after the Big Bang the Universe has been expanding. This means that the early Universe was considerably smaller and early-formed galaxies were more likely to interact and merge. Galaxy mergers fuel the formation of quasars — extremely luminous galactic cores where gas and dust falling into a central supermassive black hole emit enormous amounts of light. So when looking back at the early Universe astronomers would expect to find numerous pairs of quasars in close proximity to each other as their host galaxies undergo mergers. However, they have been surprised ...
Repurposed drug may help stabilize vision in rare disease
2024-06-17
Roughly 50 families scattered across the world share ultra-rare variants in a particular gene. Silent for years, the inherited mutations make themselves known when patients reach the fourth decade of life. Changes in vision start a cascade of symptoms. Five to 20 years later, the illness is fatal.
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have dedicated many years to understanding the rare condition known as retinal vasculopathy with cerebral leukoencephalopathy and systemic manifestations, or RVCL-S, with the aim of developing a treatment ...
Face screening tool detects stroke in seconds
2024-06-17
A new smartphone face-screening tool could help paramedics to identify stroke in seconds – much sooner and more accurately than is possible with current technologies.
Strokes, which affect millions of people globally, occur when the blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, which prevent brain tissue from getting oxygen and nutrients. A few minutes of delay can result in permanent damage to the brain cells.
A team of biomedical engineers at RMIT University developed the AI capabilities behind the software technology and has published their results ...
Making this Parkinson's drug is just turtles all the way down (video)
2024-06-17
WASHINGTON, June 17, 2024 — L-DOPA is the best drug we have for Parkinson’s disease, but its molecular mirror image, D-DOPA, causes dangerous side effects. Making L-DOPA without also making D-DOPA is surprisingly hard and requires a specific kind of molecule to pull off. But that specific molecule must be made from a different and equally specific molecule. In this video, our host, George Zaidan, explains how one of the winners of the 2001 Nobel Prize in Chemistry pulled it off, and why "chiral synthesis," as it's called, is really just turtles all the way down. https://youtu.be/_cb09XB07LQ?si=BuMEI5fOuHmuQlkZ
Reactions is a video series ...
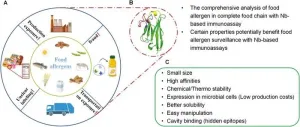
Camelid nanobodies: Transforming food allergen analysis
2024-06-17
Recent advancements show nanobodies from camelid antibodies excel in food allergen detection with superior stability, specificity, and cost-effectiveness. This innovative approach aims to improve accuracy and efficiency, crucial for preventing severe allergic reactions. The study highlights nanobodies' potential in reliable immunoassays, addressing rising food allergies and enhancing safety measures.
Food allergies pose significant health risks, affecting millions worldwide, with the prevalence rising over the past decades. Traditional detection methods, such as monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies, are often costly, labor-intensive, and prone to cross-reactions. The need for ...
Federal study examines care following nonfatal overdose among Medicare beneficiaries; identifies effective interventions and gaps in care
2024-06-17
Researchers from the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), the National Institutes of Health’s (NIH) National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) found that among a cohort of 137,000 Medicare beneficiaries who experienced a nonfatal overdose in 2020, almost 24,000 (17.4%) experienced a subsequent nonfatal overdose, and about 1,300 (1%) died from overdose in the following year. Results were published today in JAMA Internal Medicine, identifying both effective interventions and significant gaps in care.
“People who have experienced ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
[Press-News.org] More than 1 in 10 patients at FQHCs experience major social risk factorsA first-of-its-kind study found high rates of food insecurity, housing insecurity, financial strain, and/or a lack of transportation among patients at federally qualified health centers.