(Press-News.org) NASA, on behalf of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), has selected Lockheed Martin Corp. of Littleton, Colorado, to build the spacecraft for NOAA’s Geostationary Extended Observations (GeoXO) satellite program.
This cost-plus-award-fee contract is valued at approximately $2.27 billion. It includes the development of three spacecraft as well as four options for additional spacecraft. The anticipated period of performance for this contract includes support for 10 years of on-orbit operations and five years of on-orbit storage, for a total of 15 years for each spacecraft. The work will take place at Lockheed Martin’s facility in Littleton and NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
The GeoXO constellation will include three operational satellites — east, west and central. Each geostationary, three-axis stabilized spacecraft is designed to host three instruments. The centrally-located spacecraft will carry an infrared sounder and atmospheric composition instrument and can also accommodate a partner payload. Spacecraft in the east and west positions will carry an imager, lightning mapper, and ocean color instrument. They will also support an auxiliary communication payload for the NOAA Data Collection System relay, dissemination, and commanding.
The contract scope includes the tasks necessary to design, analyze, develop, fabricate, integrate, test, evaluate, and support launch of the GeoXO satellites; provide engineering development units; supply and maintain the ground support equipment and simulators; and support mission operations at the NOAA Satellite Operations Facility in Suitland, Maryland.
NASA and NOAA oversee the development, launch, testing, and operation of all the satellites in the GeoXO program. NOAA funds and manages the program, operations, and data products. On behalf of NOAA, NASA and commercial partners develop and build the instruments and spacecraft and launch the satellites.
As part of NOAA’s constellation of geostationary environmental satellites to protect life and property across the Western Hemisphere, the GeoXO program is the follow-on to the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites – R (GOES-R) Series Program.
The GeoXO satellite system will advance Earth observations from geostationary orbit. The mission will supply vital information to address major environmental challenges of the future in support of weather, ocean, and climate operations in the United States. The advanced capabilities from GeoXO will help assess our changing planet and the evolving needs of the nation’s data users. Together, NASA and NOAA are working to ensure GeoXO’s critical observations are in place by the early 2030s when the GOES-R Series nears the end of its operational lifetime.
For more information on the GeoXO program, visit:
https://www.nesdis.noaa.gov/geoxo
END
NASA selects Lockheed Martin to build next-gen spacecraft for NOAA
2024-06-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
C-Path partners with FARA to fortify RDCA-DAP and further accelerate drug development with new Friedreich’s Ataxia Data
2024-06-18
TUCSON, Ariz., June 18, 2024 — Critical Path Institute (C-Path), a leader in accelerating drug development for rare diseases, today announced the targeted integration of additional Friedreich’s ataxia (FA) datasets into C-Path’s Rare Disease Cures Accelerator-Data and Analytics Platform (RDCA-DAP®) as part of a partnership with Friedreich’s Ataxia Research Alliance (FARA).
This update includes data from two natural history studies; the FA-CHILD study, which focuses on pediatric ...
Rigorous new study debunks misconceptions about anemia, education
2024-06-18
In low- and middle-income countries, anemia reduction efforts are often touted as a way to improve educational outcomes and reduce poverty. A new study, co-authored by a global health economics expert from the University of Notre Dame, evaluates the relationship between anemia and school attendance in India, debunking earlier research that could have misguided policy interventions.
Santosh Kumar, associate professor of development and global health economics at Notre Dame’s Keough School of Global Affairs, is co-author of the study, published in Communications ...
Existing high blood pressure drugs may prevent epilepsy, Stanford Medicine-led study finds
2024-06-18
A class of drugs already on the market to lower blood pressure appears to reduce adults’ risk of developing epilepsy, Stanford Medicine researchers and their colleagues have discovered. The finding comes out of an analysis of the medical records of more than 2 million Americans taking blood pressure medications.
The study, published June 17 in JAMA Neurology, suggests that the drugs, called angiotensin receptor blockers, could prevent epilepsy in people at highest risk of the disease, ...
ACM recognizes innovators who solve real world problems
2024-06-18
ACM, the Association for Computing Machinery, today announced the recipients of four prestigious technical awards. These four awards in diverse categories celebrate the hard work and creativity which underpin many of today’s most important technologies.
Prateek Mittal, Princeton University, is the recipient of the 2023 ACM Grace Murray Hopper Award for foundational contributions to safeguarding Internet privacy and security using a cross-layer approach.
The unifying theme in Mittal’s ...
Wooden surfaces may have natural antiviral properties
2024-06-18
Viruses, including the coronavirus that causes COVID-19, can get passed from person to person via contaminated surfaces. But can some surfaces reduce the risk of this type of transmission without the help of household disinfectants? As reported in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, wood has natural antiviral properties that can reduce the time viruses persist on its surface — and some species of wood are more effective than others at reducing infectivity.
Enveloped viruses, like the coronavirus, can live up to five days on surfaces; nonenveloped viruses, including enteroviruses linked to the common cold, can live for weeks, in some cases even if the ...
For sustainable livestock farming bordering the Amazon Rainforest, look to the women
2024-06-18
When trees and livestock compete for land, the trees usually lose. It doesn’t have to be this way. But centrally designed plans to implement tree-livestock coexistence in deforested areas don’t always work on faraway farmland.
The ineffectiveness can be due to trying to accomplish too much too quickly. Transforming hundreds of thousands of hectares of treeless or degraded pastures into sustainable landscapes for livestock, nature and people should be a gradual, low-disruption process. And it should start ...
Dr. Felice J. Levine to step down as AERA Executive Director in June 2025
2024-06-18
AERA President Janelle T. Scott and Executive Director Felice J. Levine issued the following joint letter on June 18, 2024.
Dear AERA Members, Colleagues in the Field, and Leaders in Research and Education:
We are writing this joint letter to announce that Felice has decided to step down as Executive Director (ED) effective June 15, 2025. As she entered her fifth consecutive term, she signaled that she wished to move to an Emerita status next June and would not seek a further term of office. We both want to communicate this news now to provide sufficient lead time to conduct a search and ensure a smooth transition.
As ...
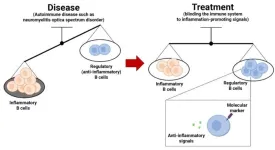
Treatment for autoimmune disorder acts on balance of immune cell types
2024-06-18
Autoimmune diseases cannot currently be cured, only treated, and this is also true for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder, which affects the central nervous system. A Kobe University study of how the treatment acts on the immune system shows that it shifts the balance of types of immune cells. This finding may represent a step toward the development of personalized medicine for autoimmune diseases.
An autoimmune disease is the body’s immune system turning against parts of the body itself. Neuromyelitis optica disorder spectrum, or NMOSD, is one of them and it causes inflammation of the central nervous system, leading to vision and sensory loss, weakness ...
Anti-inflammatory drug celecoxib could reduce risk of colon cancer recurrence for a subset of patients
2024-06-18
Boston – An analysis of data from a randomized clinical trial for patients with stage 3 colon cancer found that those with PIK3CA mutations who took celecoxib, an anti-inflammatory drug, after surgery lived significantly longer and had longer disease-free survival compared to those without the mutation. The study, highlighting a potential breakthrough in personalized cancer treatment, was led by clinical investigators at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
These findings are ...
Social inequalities widen after a breast cancer
2024-06-18
When it comes to health, inequalities can be seen at every level for women with breast cancer: prevention, screening, diagnosis, treatment, and survival. But what about their quality of life? A team from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), the University Hospitals of Geneva (HUG), Inserm, and Gustave Roussy has tracked nearly 6,000 women diagnosed with breast cancer over a 2-year period, showing that socioeconomic status has a major and lasting impact on their quality of life, despite identical medical treatment. These results from the UNICANCER-sponsored CANTO study, published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, call ...