(Press-News.org) Key Takeaways
The introduction of a standardized handoff protocol substantially improved communication among OR staff, ensuring critical information was transferred consistently.
The enhanced communication reduced potential patient safety risks and highlighted the importance of standardized handoff tools in improving surgical outcomes.
CHICAGO (June 19, 2024) — A new study showcases a successful quality improvement program that significantly enhances surgical safety. By implementing a standardized handoff protocol, known as SHRIMPS, the study demonstrates how effective communication in operating rooms (OR) can reduce the risk of errors and improve patient care. The findings are published in the Journal of the American College of Surgeons (JACS).
"This study is a prime example of how quality improvement initiatives can lead to better patient outcomes," said study co-author Madeline Anderson, DO, a surgery resident at the University of Kentucky. "By standardizing communication during surgical procedures, we can ensure that all team members are informed, and that critical information is consistently conveyed, reducing the risk of errors."
Prompted by a frontline stakeholder’s concerns about inadequate quality surgical technician handoffs, the quality improvement (QI) team at the Lexington VA Medical Center, affiliated with the University of Kentucky hospital, developed an audit tool to evaluate handoffs across various surgical cases from May 2022 to February 2024. Initial audits revealed handoffs occurred in 82.6% of cases, but with only 34.4% of critical elements being communicated.
In response, the team, in collaboration with OR staff, developed a standardized communication checklist with the acronym “SHRIMPS” (Sharps, Sponges, Hidden or held items, Replaced items, Instruments & Implants, Medications, Procedure overview, Specimens). Although it has nothing to do with the crustacean, the team chose the SHRIMPS acronym to be a helpful mnemonic device for surgical teams. This checklist was displayed prominently in all ORs at the Lexington VA Medical Center.
Key Findings
Before implementing SHRIMPS, handoffs occurred in 82.6% of cases, with only 34.4% of critical elements communicated.
After implementing SHRIMPS, 100% of cases included handoffs, with 98.2% of critical elements addressed.
The duration of handoffs averaged 69.4 seconds post-implementation, ensuring thorough communication without significantly increasing handoff time.
Announcements of handoffs to the entire OR team increased to 97.1%, ensuring all staff were aware of personnel changes.
“Part of the success of SHRIMPS comes from the QI team engaging with both topline and frontline OR stakeholders, including surgical technicians and circulating nurses,” said Dr. Anderson. “This approach ensures the tool is more effective and garners buy-in from the people ultimately using it.”
The success of the SHRIMPS protocol highlights the significant impact quality improvement programs can have in health care – by implementing standardized handoff protocols, operating rooms can achieve better communication, fewer errors, and enhanced patient care, the authors note. The study authors advocate for the widespread adoption of such tools to ensure reliable and efficient information transfer in surgical environments.
The study is published as an article in press on the JACS website.
Citation: Stephens WS, Anderson MJ, Levy BE, et al. Surgical Intraoperative Handoff Initiative: Standardizing Operating Room Communication using SHRIMPS. Journal of the American College of Surgeons, 2024. DOI: 10.1097/XCS.0000000000001115
# # #
About the American College of Surgeons
The American College of Surgeons (ACS) is a scientific and educational organization of surgeons that was founded in 1913 to raise the standards of surgical practice and improve the quality of care for all surgical patients. The ACS is dedicated to the ethical and competent practice of surgery. Its achievements have significantly influenced the course of scientific surgery in America and have established it as an important advocate for all surgical patients. The ACS has approximately 90,000 members and is the largest organization of surgeons in the world. “FACS” designates that a surgeon is a Fellow of the ACS.
Follow the ACS on social media: X | Instagram | YouTube | LinkedIn | Facebook
CONTACT:
Sheila Evans | 312-202-5386
Dan Hamilton | 312-202-5328
Email: pressinquiry@facs.org
END
Standardized OR handoffs significantly improve surgical communication and patient safety
SHRIMPS can save lives in the operating room
2024-06-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Immune response study explains why some people don't get COVID-19
2024-06-19
Scientists have discovered novel immune responses that help explain how some individuals avoid getting COVID-19.
Using single-cell sequencing, researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, University College London (UCL), Imperial College London, the Netherlands Cancer Institute and their collaborators, studied immune responses against SARS-CoV-2 infection in healthy adult volunteers, as part of the world's first COVID-19 human challenge study1. Not all exposed participants went on to develop a COVID-19 infection, ...
New research illuminates the ecological importance of gray wolves in the American West
2024-06-19
Corvallis, OR — A study published today in the journal BioScience sheds light on the importance of gray wolves in western United States. Led by William Ripple, a scientist at Oregon State University and the Conservation Biology Institute, the research delves into the implications of large predator absence on plant and animal communities, and ecosystem functions. It calls attention to “shifting baselines” wherein increasingly degraded conditions are viewed as reflecting the historical state of a system.
"By the 1930s, wolves were largely absent from the American West, including its national parks. Most published ecological ...
Forgotten predators: Ecological understanding is often marred by the exclusion of extirpated species
2024-06-19
New research published in the journal BioScience describes how the removal large predators is often unrecognized in ecological scholarship, creating an issue of "shifting baselines," with profound implications for restoration efforts.
A team led by researchers from Oregon State University, including co-lead authors William J. Ripple and Christopher Wolf, reviewed 96 published studies from 1955 to 2021 that were conducted in 11 national parks where gray wolves had been extirpated. Their analysis found that ...
Inclusive care: Strategies to support infant feeding for parents with disabilities through WIC
2024-06-19
Philadelphia, June 19, 2024 – Infant feeding, involving breastfeeding, formula feeding, and the introduction of solid foods, is crucial for parenting. Pregnant and postpartum individuals with intellectual and developmental disabilities face challenges in infant feeding compared to parents without intellectual and developmental disabilities, often due to ableism and inaccessible care. The Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) program, a federal nutrition initiative, can address these disparities by offering inclusive and accessible support and counseling.
A recent research article in the Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior, published ...
Computer modelling shows where Arizona’s winter precipitation originates
2024-06-19
The Sun Corridor in Arizona in the semi-arid Southwestern U.S. is a land of seeming unlimited growth that is constantly colliding with physical constraints. It is mountainous but also home to a large valley that includes one of the fastest growing metropolitan areas in the U.S.
While experiencing explosive growth, the Phoenix metropolitan area faces an uncertain future due to prolonged drought and fluctuating seasonal water availability. Planning for the future, especially in terms of water, ...
STUDY: Sourcing genomically diverse seedlings to create climate-change resilient forests brings optimism for partnerships between science and practice
2024-06-19
The roots of the project formed during a CASRI conference in 2018 when experts from various organizations learned about red spruce genetic research being conducted by Keller’s lab and collaborators at University of Maryland with funding by the National Science Foundation. The group saw an opportunity to join forces to take an on-the-ground approach to utilizing the genetic data for red spruce restoration. In 2019, funding from the Wildlife Conservation Society’s Climate Adaptation Fund enabled this group to pursue science-informed restoration at scale.
“Science-informed ...
Could auto-antibodies be linked to severe COVID-19?
2024-06-19
Even though COVID-19 manifests as a mild and short-lived disease in most people, some suffer extremely severe symptoms; in the worst cases, these patients die due to complications such as respiratory failure or thromboembolism. It is well-known that factors such as age and underlying medical conditions like diabetes or immunodeficiencies increase vulnerability to severe COVID-19. However, some patients still experience severe COVID-19 without any apparent reason.
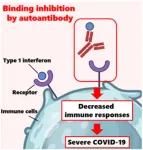
One possible explanation may lie in auto-antibodies, which are antibodies that erroneously target specific proteins produced by one’s own body. In normal circumstances, type I interferons ...
Breakthrough UC San Diego brain recording device receives FDA approval for a clinical trial
2024-06-19
Video: https://youtu.be/-7ggs6e2UXI?si=lnFqEscjJh-91n64
B-roll: https://youtu.be/pvNBa733ICw?si=DotUuQkxVgMQ0jY7
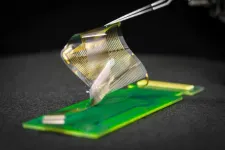
The Federal Drug Administration approved a clinical trial to test the effectiveness of an electronic grid that records brain activity during surgery, developed by engineers at the University of California San Diego.
The device with nanoscale sensors records electrical signals directly from the surface of the human brain in record-breaking detail. The grid’s breakthrough resolution could provide better guidance for planning and performing surgeries to remove brain tumors and treat drug-resistant epilepsy.
The grid’s higher resolution ...
A study led by ISGlobal and IDIAPJGol recommends strengthening immunity against COVID-19 in people with cancer
2024-06-19
Researchers from the Institut d’Investigació en Atenció Primària Jordi Gol (IDIAPJGol) and the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a center promoted by “la Caixa” Foundation, have led a study on the effectiveness of vaccines against COVID-19 among cancer patients in Catalonia. The research, published in the journal Nature Communications, recommends administering additional doses of the vaccine among this risk population.
Cancer patients are at increased risk of death from COVID-19, especially ...
A railroad of cells
2024-06-19
Looking under the microscope, a group of cells slowly moves forward in a line, like a train on the tracks. The cells navigate through complex environments. A new approach by researchers involving the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) now shows how they do this and how they interact with each other. The experimental observations and the following mathematical concept are published in Nature Physics.
The majority of the cells in the human body cannot move. Some specific ones, however, can go to different places. For example, in wound healing, cells move through the body to repair damaged tissue. They sometimes ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
Predicting extreme rainfall through novel spatial modeling
The Lancet: First-ever in-utero stem cell therapy for fetal spina bifida repair is safe, study finds
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Eric Moore, M.D., elected to Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees
NYU named “research powerhouse” in new analysis
New polymer materials may offer breakthrough solution for hard-to-remove PFAS in water
[Press-News.org] Standardized OR handoffs significantly improve surgical communication and patient safetySHRIMPS can save lives in the operating room