(Press-News.org) People with higher weight, and those who have high-quality experiences with higher-weight people, report less weight bias, per social psychology study of US adults
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0305080
Article Title: The role of social norms, intergroup contact, and ingroup favoritism in weight stigma
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work.
END
People with higher weight, and those who have high-quality experiences with higher-weight people, report less weight bias, per social psychology study of US adults
2024-06-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
In two separate clinical studies, combined immunotherapy approach enhances cancer patient response
2024-06-20
Because not all cancer patients respond to a leading type of cancer immunotherapy drug, known as an immune checkpoint inhibitor, scientists explored whether adding janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors – drugs that treat chronic inflammation – could help. In two separate clinical studies, researchers found that adding JAK inhibitors did improve patients’ responses to cancer checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapies. “Aside from the exciting findings of the early phase trials reported by [both groups], they provide a great deal of data with complex analyses of immune ...
Airborne mapping reveals roles for biogenic sources and temperature in air pollution emissions in Los Angeles
2024-06-20
Airborne observations over California have revealed that biogenic sources of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) – blooming trees and growing plants – dominate summertime air pollutant formation in Los Angeles, in a way that increases with temperature. Future air pollution regulations thus need to consider that only 40% of urban VOC emissions (those not tied to biogenic sources) can be mitigated through regulations, say the authors. Ambient air pollution – the fourth-leading global ...
Old bombs reveal new insights: Plants store more carbon, but for a shorter time frame, than we thought
2024-06-20
Analysis of radiocarbon produced during nuclear bomb testing in the 1960s suggests that current Earth system models underestimate carbon uptake into terrestrial vegetation and soils. But, say the study’s authors, this storage is more short-lived than previously thought. The findings suggest that anthropogenic carbon dioxide will not reside as long in the terrestrial biosphere as models currently predict. Accurate climate predictions, crucial for developing effective climate policies, require a robust representation of the global carbon cycle. It’s thought that vegetation and soils account for taking up approximately 30% of anthropogenic carbon dioxide (CO2) ...
The time it takes a person to decide can predict their preference
2024-06-20
Researchers led by Sophie Bavard at the University of Hamburg, Germany, found that people can infer hidden social preferences by observing how fast others make social decisions. Publishing June 20th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology, the study shows that when someone knows the options being considered by another person, and they know how long it takes them to reach their decisions, they can use this information to predict the other person’s preference, even if they do not know what the actual choices were.
How do we know what someone’s social preferences ...
Hurricane changed ‘rules of the game’ in monkey society
2024-06-20
A devastating hurricane transformed a monkey society by changing the pros and cons of interacting with others, new research shows.
Hurricane Maria hit Puerto Rico in 2017, killing more than 3,000 people. It also destroyed 63% of vegetation on Cayo Santiago (also known as Monkey Island), which is home to a population of rhesus macaques.
Even now, tree cover remains far below pre-hurricane levels and – in this hot part of the world – that makes shade a scarce and precious resource for the macaques.
The new study, led by the universities of Pennsylvania and Exeter and published in the journal Science, shows the storm ...
Researchers widely observe yet seldom publish about same-sex sexual behavior in primates and other mammals - often because it is perceived to be rare
2024-06-20
Researchers widely observe yet seldom publish about same-sex sexual behavior in primates and other mammals - often because it is perceived to be rare
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0304885
Article Title: Same-sex sexual behaviour among mammals is widely observed, yet seldomly reported: Evidence from an online expert survey
Author Countries: Canada, USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Wild chimpanzees seek out medicinal plants to treat illness and injuries
2024-06-20
Chimpanzees appear to consume plants with medicinal properties to treat their ailments, according to a study publishing on June 20 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Elodie Freymann from the University of Oxford, UK, and colleagues.
Many plants produce compounds that have medicinal effects on humans and other animals. Wild chimpanzees eat a variety of plant matter, including some that is nutritionally poor but may treat or lessen the symptoms of illness. However, it is hard to determine whether chimpanzees self-medicate, by intentionally seeking out plants with properties that help their specific ailments, or passively consume plants ...
New catalyst unveils the hidden power of water for green hydrogen generation
2024-06-20
Hydrogen is a promising chemical and energy vector to decarbonize our society. Unlike conventional fuels, hydrogen utilization as a fuel does not generate carbon dioxide in return. Unfortunately, today, most of the hydrogen that is produced in our society comes from methane, a fossil fuel. It does so in a process (methane reforming) that leads to substantial carbon dioxide emissions. Therefore, the production of green hydrogen requires scalable alternatives to this process.
Water electrolysis offers a path to generate green hydrogen which can be ...
Supermassive black hole appears to grow like a baby star
2024-06-20
Supermassive black holes pose unanswered questions for astronomers around the world, not least “How do they grow so big?” Now, an international team of astronomers, including researchers from Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden, has discovered a powerful rotating, magnetic wind that they believe is helping a galaxy’s central supermassive black hole to grow. The swirling wind, revealed with the help of the ALMA telescope in nearby galaxy ESO320-G030, suggests that similar processes are involved both in black hole growth and the birth of stars.
Most galaxies, including our own Milky Way have a supermassive black hole at their centre. How ...
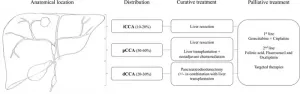
Early detection crucial in bile duct cancer for patients with rare liver disease
2024-06-20
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a rare progressive liver disease that damages bile ducts and significantly increases the risk of bile duct cancer, particularly a type called cholangiocarcinoma (CCA). This cancer is aggressive, and curative surgery is uncommon. Liver transplantation is a potential treatment option for some PSC-CCA patients, especially if the cancer is caught early. Early diagnosis is essential for successful treatment.
PSC can affect people of all ages but primarily strikes men in their 30s and 40s. It is often accompanied by inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The disease can progress to liver failure and increase the risk of colorectal cancer ...