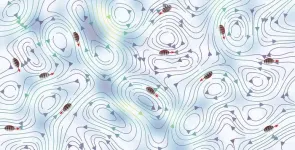
(Press-News.org) How do particles move in turbulent fluids? The answer to this question can be found in a new model presented in a thesis from the University of Gothenburg. The model could help speed up the development of new drugs.
When you stir a glass of water, it is easy to think that any particles in the water will end up in chaos and move completely randomly. But this is not always the case. For example, the so-called active micro-swimmers can move through flow on their own. Navid Mousavi, a PhD student at the University of Gothenburg, has created a model including various hydrodynamic factors to study how these particles handle and even utilise turbulence.
Micro-swimmers can be biological, such as plankton, or engineered particles such as nanomotors. Plankton contribute to global ecosystems by producing oxygen and they form the basis of the ocean food web.
Free-riding in the current
Navid Mousavi has created new methods for modelling and studying the navigation of micro-swimmers by combining active matter physics with machine learning principles. The thesis finds optimal behaviours for plankton to survive in their turbulent habitat.
“In the model, plankton use local information for navigation, reflecting the real-world conditions that these small swimmers encounter. Unlike previous models where navigation was based on global information,” says Navid Mousavi.
The research also showed that micro-swimmers can utilise the flow to move faster than they can on their own, which is an important insight for both biological and artificial applications.
Another exciting result of the study is the discovery of optimal behavior to avoid high turbulent strain. Surprisingly, it is observed that micro-swimmers tend to swim against the current to keep their position in low-strain regions.
“This behaviour seems to be crucial for survival and allows plankton to avoid predators and stay in nutrient-rich zones,” says Navid Mousavi.
Important knowledge for medicine development
All the strategies found were shown to work effectively in several different scenarios, meaning they can be applied to real-life situations.
The results of the study provide important knowledge that has several applications. An example is in medicine, where it could help develop smart micro-swimmers that can deliver drugs directly to specific areas of the body, making treatments more effective. Environmentally, these tiny swimmers could help clean up microplastics from our oceans and contribute to a healthier planet.
“In the future, we will need to validate the model in experiments, both with natural plankton and artificial micro-swimmers,” says Navid Mousavi.
The researchers also plan to investigate more complex models that deals with energy efficiency and the collective behaviour of multiple swimmers.
END
Model shows how plankton survive in a turbulent world
2024-06-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study: Teacher perceptions of chronically absent young students may add to the challenges of missing school
2024-06-25
Washington, June 25, 2024—A new study finds that early elementary school teachers report feeling less close to chronically absent students and view them less positively, even when those students do not cause trouble in the classroom. This “cooling down” in the relationship between teachers and their chronically absent students may exacerbate the academic challenges these children face.
The study—by Michael A. Gottfried and Phil H. Kim at the University of Pennsylvania, and Tina Fletcher at the ...
All-in-one method measures CO2 in concrete
2024-06-25
A new device can measure carbon dioxide captured in concrete more simply and in a third of the time of current methods. Researchers at the University of Tokyo worked with engineers in industry to create the boxlike device called the concrete thermal gravimetry and gas analyzer. The device heats concrete samples to almost 1,000 degrees Celsius, causing the CO2 within to be released so it can be measured. Compared to the current technique, which involves a time-consuming and complicated process of crushing concrete samples into powder for sampling, this new method is simpler, more accurate and user-friendly. The researchers hope it ...
Internet for billions in 100 countries with no current access and hope for transplant patients worldwide in new World Economic Forum emerging technologies report
2024-06-25
The World Economic Forum, in association with Frontiers, new Top 10 Emerging Technologies of 2024, released today (25 June), shows that among technologies emerging globally, reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS) and High-Altitude Platform Systems (HAPS) have the potential to connect billions worldwide who currently have no internet access.
The report also highlights how advances in genetically engineering animal organs for use in human transplantation gives hope to the millions on waiting lists worldwide. Other technologies in the top ten that that could transform lives and societies ...
A new paradigm in photothermal therapy! DGIST developed “ultrasound-assisted photothermal therapy (ULTRA-PTT)” technology!
2024-06-25
□ Professor Jin-ho Chang’s research team from the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at DGIST (President Kun-woo Lee) developed “Ultrasound-assisted photothermal therapy (ULTRA-PTT)” technology that significantly enhances the performance of conventional photothermal therapy. This technology was developed in collaboration with Senior Researcher Hye-min Kim from the Advanced Photonics Research Institute at GIST (President Ki-chul Lim) using the team’s proprietary “ultrasound-induced optical clearing” technology.
□ Phototherapy, using light, ...
Nanowires create elite warriors to enhance T cell therapy
2024-06-25
Adoptive T-cell therapy has revolutionized medicine. A patient’s T-cells — a type of white blood cell that is part of the body’s immune system — are extracted and modified in a lab and then infused back into the body, to seek and destroy infection, or cancer cells.
Now Georgia Tech bioengineer Ankur Singh and his research team have developed a method to improve this pioneering immunotherapy.
Their solution involves using nanowires to deliver therapeutic ...
Plant-sourced nitrate proves positive to human health
2024-06-25
Plant-sourced nitrate proves positive to human health
New research from Edith Cowan University (ECU) has found that nitrate from plant sources is associated with a lower risk of mortality while nitrate from other sources such as animal-based foods, processed meat and tap water, is linked to a higher risk of mortality.
Nitrate, a compound found in vegetables, meat, and drinking water, has been the subject of debate due to its potential impact on health. Emerging evidence suggests that dietary nitrate may play a role in preventing cardiovascular disease (CVD), dementia, and ...
DGIST-POSTECH joint research team developed next-generation impact-resistant stretchable electronic component
2024-06-25
□ Professor Kyung-In Jang’s research team from the Department of Robotics and Mechatronics Engineering at DGIST (President Kunwoo Lee) has succeeded in developing a highly stable stretchable electronic device, which overcomes the mechanical limitations of conventional inorganic materials and enhances their stretchability and durability. In collaboration with Professor Taeho Park’s team from the Department of Chemical Engineering at POSTECH (President Seong-Keun Kim), the research team has developed a stretchable hybrid polymer and applied it to electronic devices, enabling them to operate stably even under deformation ...
Robots help put brakes on inflammatory diseases
2024-06-25
Fully automated diagnostic techniques, including liquid handling robots, are poised to improve the lives of millions of people living with inflammatory diseases worldwide.
A landmark WEHI study has revealed new methods in detecting necroptosis, a key factor in many inflammatory diseases like psoriasis, arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
The findings mark a huge leap forward in our ability to diagnose necroptosis accurately. They also offer practical methods that can be easily reproduced in hospitals worldwide, giving hope for new ways to treat inflammatory diseases.
At a glance
Necroptosis is a form of cell death, one of the body’s natural ...
Chronic loneliness may increase stroke risk among older adults
2024-06-25
Embargoed for release: Monday, June 24, 7:30 PM ET
Key points:
In a study of loneliness and stroke risk over time among adults ages 50+, those who experienced chronic loneliness had a 56% higher risk of stroke than those who consistently reported not being lonely.
Those who experienced situational loneliness did not have an elevated risk of stroke—suggesting that the impact of loneliness on stroke risk occurs over the longer term.
Boston, MA—Chronic loneliness may significantly raise older adults’ risk of stroke, according to a new study led by Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
“Loneliness is increasingly considered a ...
Risk of Parkinson’s more than double for people with anxiety
2024-06-25
The risk of developing Parkinson’s is at least twice as high in people with anxiety compared to those without, finds a new study by UCL researchers.
The research, published in the British Journal of General Practice, investigated whether there was a link between people over the age of 50 who had recently developed anxiety and a later diagnosis of Parkinson’s.
The team used UK primary care data between 2008 and 2018 and assessed 109,435 patients who had developed anxiety after the age of 50 and compared them to 878,256 matched ...