(Press-News.org) A Surrey mathematician is the first ever UK-based winner of a prestigious international prize for his work to better understand patterns which contribute to a diverse range of phenomena, including stop-and-go traffic jams, weather fronts, sunspots and crime hotspots.
The T Brooke Benjamin Prize is awarded every two years by the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (SIAM) – the world's largest applied mathematics society – for outstanding work in the field of nonlinear waves.
Professor David Lloyd from the University of Surrey's School of Mathematics and Physics said:
"The emergence of patterns that occur around crime hotspots, weather fronts and stop-and-go traffic jams are governed by complex mathematical explanations. My research develops mathematical theories for how and when these patterns occur and what their behaviours are. These are fundamental problems across science, engineering, and nature.
"I feel very honoured to win this prestigious prize, and I'm delighted that it offers an opportunity to share the elegant beauty of this field of mathematics with a wider audience. I hope someone somewhere has their curiosity piqued by these intriguing patterns and is inspired to find out more."
Professor Lloyd will receive his prize at the SIAM Conference on Nonlinear Waves and Coherent Structures in Baltimore, USA, on Wednesday 26 June.
ENDS
END
From sunspots to traffic jams: Explaining real-world patterns scoops major maths prize for Surrey professor
2024-06-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Orchid awakening: Unveiling the hormonal choreography behind flower development
2024-06-25
A cutting-edge study has uncovered the complex hormonal and genetic interactions that dictate the seasonal flowering cycle of Cymbidium sinense, the Chinese orchid. This research sheds light on the enigmatic mechanisms of floral bud dormancy and its subsequent activation, offering new perspectives on the control of flowering times in plants.
Flower development in plants is a complex process influenced by various intrinsic and extrinsic factors. Hormones like gibberellin (GA) and abscisic acid (ABA) play pivotal roles in regulating this process. In many orchids, including the Chinese Cymbidium, flower bud dormancy ...
EMBO Gold Medal awarded to Elvan Böke
2024-06-25
EMBO awards the EMBO Gold Medal 2024 to Elvan Böke, group leader at the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) in Barcelona, Spain. The award recognizes researchers under the age of 40 for outstanding contributions to the life sciences in Europe. The awardee receives a gold medal and a bursary of 10,000 euros.
Early-stage oocytes are exposed to biological and environmental factors for decades, which can make them susceptible to cumulative damage. At the same time, the growth phases associated with oocyte maturation ...
Battling anthracnose: Unearthing the plant's arsenal against pathogenic fungi
2024-06-25
A pivotal study has shed light on the intricate mechanisms of nonhost resistance (NHR) in plants, a critical defense against a broad spectrum of pathogens. By identifying and characterizing four novel core effectors from the pathogen Colletotrichum fructicola, researchers have unveiled key players in the plant Nicotiana benthamiana's immune response. This discovery is set to transform approaches to plant disease management, offering a pathway to bolster crops against devastating fungal infections.
Plant diseases caused by pathogens like Colletotrichum ...
Robots face the future
2024-06-25
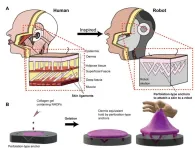
Researchers have found a way to bind engineered skin tissue to the complex forms of humanoid robots. This brings with it potential benefits to robotic platforms such as increased mobility, self-healing abilities, embedded sensing capabilities and an increasingly lifelike appearance. Taking inspiration from human skin ligaments, the team, led by Professor Shoji Takeuchi of the University of Tokyo, included special perforations in a robot face, which helped a layer of skin take hold. Their research could be useful in the cosmetics industry and to help train plastic surgeons.
Takeuchi is a pioneer in the field of biohybrid ...
Physical, sexual, and intimate partner violence among transgender and gender-diverse individuals
2024-06-25
About The Study: In this survey study of adults in California, results showed that transgender and gender-diverse individuals, especially transgender men, are at higher risk of experiencing all forms of violence relative to cisgender women. Results highlight the need for gender-affirming violence prevention and intervention services as well as policies that protect transgender and gender-diverse individuals from discriminatory violence.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Sabrina ...
Bone health after exercise alone, GLP-1 receptor agonist treatment, or combination treatment
2024-06-25
About The Study: The combination of exercise and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA) (liraglutide) was the most effective weight loss strategy while preserving bone health in this randomized clinical trial. Liraglutide treatment alone reduced bone mineral density at clinically relevant sites more than exercise alone despite similar weight loss.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Signe Sorensen Torekov, Ph.D., email torekov@sund.ku.dk.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.16775)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
Penn study finds better survival rates for recipients of lungs from hospital-based donor care units compared to independent donor care units
2024-06-25
PHILADELPHIA— A new study by Penn researchers examined, for the first time, the differences in lung transplant graft outcomes from organs recovered from the two types of deceased organ donor care facilities operating in the United States. The research, published today in JAMA Network Open, offers insights that could improve the organ donation and transplantation process for patients across the nation.
In the U.S., deceased organ donors are traditionally cared for in hospitals, which provide intensive care and testing needed to rehabilitate organs, identify transplant ...
3D-printed chip sensor detects foodborne pathogens for safer products
2024-06-25
WASHINGTON, June 25, 2024 – Every so often, a food product is recalled because of some sort of contamination. For consumers of such products, a recall can trigger doubt in the safety and reliability of what they eat and drink. In many cases, a recall will come too late to keep some people from getting ill.
In spite of the food industry’s efforts to fight pathogens, products are still contaminated and people still get sick. Much of the problem stems from the tools available to screen for harmful pathogens, which are often not effective enough at protecting the public.
In AIP Advances, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Guangdong University of Technology and Pudong ...
A model of Collaborative Ethics to guide translational research from fundamental discoveries to real-world applications
2024-06-25
By Benjamin Boettner
(BOSTON) — In sciences, disruptive research that is breaking new ground often raises new and not-yet-explored ethical questions. Although new scientific breakthroughs can have the power to change how we understand and live in the world, the ethical implications of technologies that will emerge based on these new insights can affect an emerging field’s public acceptance and have moral implications for society at large. They can also impact the process of translating discoveries into real-world products, sometimes requiring new regulation.
Historically, ethicists – who form the branch of philosophy that is concerned with morality and studies ...
Frauke Gräter appointed new director at the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research
2024-06-25
How can artificial intelligence and machine learning be used for innovative research in the field of soft matter? Frauke Gräter, the current Head of the Molecular Biomechanics group at the Heidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies (HITS) and Professor of Molecular Biomechanics at Heidelberg University, will research these and other topics as the new Director at the MPI for Polymer Research starting July 1, 2024.
Frauke Gräter has made an international name for herself through her outstanding scientific contributions, particularly in the field of molecular biomechanics. Her academic ...