(Press-News.org) Alfred Hitchcock observed that “There is no terror in the bang, only in the anticipation of it.” A common way to build suspense in a movie scene is for the audience to know something bad is going to happen, but not when it is going to happen. But how does uncertainty work to ratchet up our anxiety? In a recent paper in the journal Computational Psychiatry, researchers at the University of California, Davis, Department of Psychology take a deeper look into what builds fear.
Not knowing when something will happen can cause anxiety, but until now we didn’t have any idea why, said Drew Fox, associate professor of psychology at UC Davis. The first step in addressing this problem is being more precise about how we define ‘uncertainty’, he said.
Fox and graduate student Dan Holley realized that when you are anticipating that a bad thing is going to happen, depending on how the scenario is set up, there can be big differences in the perception of hazard at different times, even if the probability of the bad thing happening is the same.
For example, if there is a ten second countdown to an electric shock, the hazard rate is low until the countdown ends. But if the shock could occur at any time in those ten seconds, the hazard rate should go up, they calculated.
“If you know something is going to happen, as time goes on the hazard rate goes up because you know it didn’t happen earlier,” Fox said. “The hazard rate is always going to be higher if you don’t know when it is going to happen.”
Hazard rate rising over time
Holley and Fox, working with Professor Erie Boorman and graduate student Erica Varga, set up an experiment to test their idea. Volunteers received a small cash incentive (one cent per second) to stay in a virtual environment but could also get a mild electric shock at some point unless they opted to leave first.
They found that as expected, the hazard rate rather than the actual probability of getting a shock drives anxiety.
“At each experimental time point, the threat hazard rate mapped almost perfectly to our participants’ behavior, whereas the momentary threat probabilities had no predictive value whatsoever,” Holley said. The volunteers also reported feeling significantly more anxious in the higher hazard rate environment.
Our brains have likely evolved to track rising hazard rates, Holley said.
“Imagine a gazelle on the Serengeti,” he said. “As a matter of survival, it could keep its head down and graze a little longer, but the tradeoff is that it’s a bit more likely to be attacked by a lion.”
The longer the gazelle grazes, the more the hazard rate increases.
“Something in its mind must be tracking the hazard rate and guiding its behavior accordingly,” Holley said.
By breaking down the concept of ‘uncertainty’ in anxiety-inducing situations, the researchers hope to get a better understanding of the mechanisms behind fear and anxiety, including ways to treat the millions of people who suffer from extreme anxiety disorders.
The work was supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health.
END
How uncertainty builds anxiety
2024-06-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Adolescents today are more satisfied with being single
2024-06-25
Young people aged 14 to 20 years are nowadays more satisfied with being single than their counterparts ten years ago. This is the conclusion of a study undertaken by the Institute of Psychology at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU). "It seems that today's adolescents are less inclined to pursue a romantic relationship. This could well be the reason for the increased singlehood satisfaction," said psychologist Dr. Tita Gonzalez Avilés, lead author of the recent study. Growing numbers of people are living as ...
Researchers discover new flat electronic bands, paving way for advanced quantum materials
2024-06-25
In a study published in Nature Communications June 19, a team of scientists led by Rice University’s Qimiao Si predicts the existence of flat electronic bands at the Fermi level, a finding that could enable new forms of quantum computing and electronic devices.
Quantum materials are governed by the rules of quantum mechanics, where electrons occupy unique energy states. These states form a ladder with the highest rung called the Fermi energy.
Electrons, being charged, repel each other and move in correlated ways. ...
Discovery of vast sex differences in cellular activity has major implications for disease treatment
2024-06-25
By Darrin S. Joy
“We discovered a pronounced ‘men are from Mars, women are from Venus’ pattern,” says marine and environmental biologist Suzanne Edmands.
She refers not to human psychology, but rather to mitochondria, the cell components responsible for generating energy.
Edmands, professor of biological sciences at the USC Dornsife College of Letter, Arts and Sciences, recently published research in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences that reveals vast differences in gene activity within the mitochondria of males compared to females.
Although the study looks at tiny marine organisms called copepods, ...
nTIDE June 2024 Deeper Dive: Employment trends for people with disabilities highlight continued gains for those with vision impairments
2024-06-25
East Hanover, NJ – June 25, 2024 – The employment-to-population ratio for individuals with vision impairments continues to show marked improvement, according to data shared during the according to last Friday’s National Trends in Disability Employment (nTIDE) Deeper Dive Lunch & Learn Webinar. nTIDE is a joint effort by Kessler Foundation and the University of New Hampshire’s Institute on Disability (UNH-IOD).
Director of Research Arielle Silverman, PhD, and Research Specialist Sarahelizabeth Baghun, PhD, from the ...
WVU refining at-home sleep apnea detection device to help with more efficient diagnosis, treatment
2024-06-25
West Virginia University researchers will put a sleep apnea detection device at the fingertips or wrists of patients facilitating early diagnosis and treatment of the disease with support from a National Science Foundation grant.
Dr. Sunil Sharma, N. Leroy Lapp Professor and division chief of the Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine Fellowship Program in the WVU School of Medicine, received the award after working with other WVU researchers to develop prototypes and secure a patent.
“It’s about taking technology from the lab to the bedside,” Sharma said. ...
UC San Diego receives $5 million to support geriatrics workforce enhancement program
2024-06-25
The University of California San Diego has been selected for the third time to participate in the Geriatrics Workforce Enhancement Program (GWEP). This highly selective program comes with a $5 million grant from the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA). These funds will be used over the next five years to support the San Diego Imperial Geriatric Education Center (SDIGEC), which provides geriatric educational programming to health workers and other care providers across both San Diego and ...
Got prunes? Prunes may preserve bone density and strength in older women
2024-06-25
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Dairy isn’t the only food that’s good for bone health. Prunes may also protect bone structure and strength in postmenopausal women, according to a new study led by Penn State researchers. The findings, published in Osteoporosis International, suggest that daily prune consumption slows the progression of age-related bone loss and reduces the risk of fracture.
“This is the first randomized controlled trial to look at three-dimensional bone outcomes with respect to bone structure, geometry and estimated strength,” said Mary Jane ...
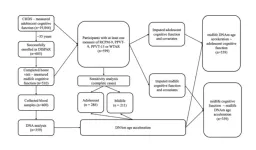
Associations of childhood, adolescence, and midlife cognitive function with DNA methylation age acceleration in midlife
2024-06-25
“[...] our study brings attention to the potential influence of adolescent crystalized intelligence on age-related DNAm at older age.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 25, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 11, entitled, “Associations of childhood, adolescence, and midlife cognitive function with DNA methylation age acceleration in midlife.”
Prior studies showed increased age acceleration (AgeAccel) is associated with worse cognitive function among ...
Think you might have COVID? Wait two days to test
2024-06-25
Peek in medicine cabinets across the U.S. and you’ll find stacks of leftover COVID-19 tests.
When symptoms arise, so do questions: When should I test? How accurate is it really? And what should I do if I test positive?
In a paper published June 14 in the journal Science Advances, CU Boulder researchers unveil a new mathematical model to quickly answer such questions, not only for COVID but also for emerging rapid tests for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), the flu and other infectious diseases.
One key takeaway: Advice can differ ...
Researchers develop new training technique that aims to make AI systems less socially biased
2024-06-25
CORVALLIS, Ore. – An Oregon State University doctoral student and researchers at Adobe have created a new, cost-effective training technique for artificial intelligence systems that aims to make them less socially biased.
Eric Slyman of the OSU College of Engineering and the Adobe researchers call the novel method FairDeDup, an abbreviation for fair deduplication. Deduplication means removing redundant information from the data used to train AI systems, which lowers the high computing costs of the training.
Datasets gleaned from the internet often contain biases present in society, the researchers said. When those biases are codified in trained AI models, they can serve to perpetuate ...