(Press-News.org) The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory will support three innovative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven science projects as part of the first round of awards from the National Artificial Intelligence Research Resource (NAIRR) Pilot.
Led by the National Science Foundation (NSF) in collaboration with DOE and several partners, the NAIRR Pilot aims to provide researchers and students with expanded access to key AI resources and data. NAIRR’s ultimate goal is to develop a shared national research infrastructure that will help advance safe, secure and trustworthy AI for science.
“Contributing to the NAIRR Pilot is a tremendous opportunity that aligns with our mission to provide world-class AI resources and expertise in support of open science.” — Katherine Riley, ALCF director of science
The three Argonne-supported NAIRR projects were among 35 total projects awarded computing time on NSF and DOE computing systems, including the Argonne Leadership Computing Facility’s (ALCF) AI Testbed. With advanced capabilities for AI and data-intensive tasks, the ALCF AI Testbed systems enable researchers to explore and advance the use of novel AI applications for science. The ALCF, a DOE Office of Science user facility, is currently offering access to its Cerebras, Graphcore, Groq and SambaNova systems through both the NAIRR Pilot and the ALCF Director’s Discretionary program, which accepts proposals year-round.
“Contributing to the NAIRR Pilot is a tremendous opportunity that aligns with our mission to provide world-class AI resources and expertise in support of open science,” said Katherine Riley, ALCF director of science. “By offering access to our AI Testbed, we’re excited to help grow and support the community of researchers who can harness the power of AI to solve challenges in science and engineering.”
Here are brief summaries of the three NAIRR projects using ALCF AI Testbed systems:
Building Reliable and Secure AI Surrogates for Large-Scale Scientific Applications with Portability Performance Analysis
Project lead: Wenqian Dong, Florida International University
This project will develop AI models to help speed up large-scale scientific simulations. Known as AI surrogates, these models are designed to replace the most time-intensive parts of simulations, enabling them to run more quickly and with less computing power. Their work aims to enhance simulations for diverse fields such as climate science and renewable energy systems.
Developing Trustworthy, Robust AI Models for Science Using Privacy Preserving Federated Learning
Project lead: Ravi Madduri, Argonne
With this project, researchers will explore the use of federated learning to advance the development of trustworthy AI models for science. Federated learning is a method that allows collaborators to train AI models together without having to share sensitive data. The NAIRR project will enable the team to evaluate various federation strategies, generate performance benchmarks and address policy issues related to federated learning.
Developing a Benchmark Hydrologic Dataset and a Fast AI Surrogate Model for Assessing Climate Impacts on Mountainous Hillslopes
Project lead: Lijing Wang, University of Connecticut
This project will simulate the movement and behavior of water across 2,000 mountain slopes under various climate scenarios. The team’s simulations will result in an AI-ready dataset that can be used for additional studies involving the water cycle’s impact on climate. They will also develop AI surrogate models to enable more rapid forecasting, supporting water resource management and climate impact assessments.
The Argonne Leadership Computing Facility provides supercomputing capabilities to the scientific and engineering community to advance fundamental discovery and understanding in a broad range of disciplines. Supported by the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) Office of Science, Advanced Scientific Computing Research (ASCR) program, the ALCF is one of two DOE Leadership Computing Facilities in the nation dedicated to open science.
Argonne National Laboratory seeks solutions to pressing national problems in science and technology by conducting leading-edge basic and applied research in virtually every scientific discipline. Argonne is managed by UChicago Argonne, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science.
The U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, visit https://energy.gov/science.
END
Argonne to support new AI for science projects as part of the National AI Research Resource Pilot
Three projects awarded access to the Argonne Leadership Computing Facility’s AI Testbed
2024-06-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Stress testing pension funds: Lithuanian researchers lead global innovation
2024-06-26
“We wanted to investigate how second pillar pension funds react to financial crises and how to protect them from the crises,” says Kaunas University of Technology (KTU) professor Dr Audrius Kabašinskas, who, together with his team, discovered a way to achieve this goal. The discovery in question is the development of stress tests for pension funds. Lithuanian researchers were the first in the world to come up with such an adaptation of the stress tests.
Stress tests are usually carried out on banks or other financial institutions to allow market regulators to determine and assess their ability to withstand adverse economic conditions.
According to the professor at ...
Multivitamin use and mortality risk in 3 prospective US cohorts
2024-06-26
About The Study: Multivitamin use was not associated with a mortality benefit in this cohort study of U.S. adults. Still, many adults report using multivitamins to maintain or improve health.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Erikka Loftfield, Ph.D., M.P.H., email erikka.loftfield@nih.gov.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.18729)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, ...
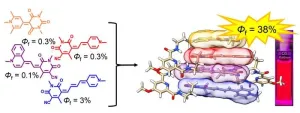
Solar technology: Innovative light-harvesting system works very efficiently
2024-06-26
In order to convert sunlight into electricity or other forms of energy as efficiently as possible, the very first step is an efficient light-harvesting system. Ideally, this should be panchromatic, i.e. absorb the entire spectrum of visible light.
The light-collecting antennae of plants and bacteria are a model for this. They capture a broad spectrum of light for photosynthesis, but are very complex in structure and require many different dyes to transmit the energy of the absorbed light and focus it on a central point.
The light-harvesting systems developed by humans to date also have disadvantages:
Although ...
Brain’s ‘escape switch’ controlled by threat sensitivity dial
2024-06-26
Neuroscientists have discovered how the brain bidirectionally controls sensitivity to threats to initiate and complete escape behaviour in mice. These findings could help unlock new directions for discovering therapies for anxiety and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
The study, published today in Current Biology, outlines how researchers at the Sainsbury Wellcome Centre at UCL studied a region of the brain called the periaqueductal gray (PAG), which is known to be hyperactive in people with anxiety and PTSD. Their ...
Improving prostate cancer screening for transgender women
2024-06-26
Transgender women are still at risk for prostate cancer. A new study led by Cedars-Sinai Cancer investigators, published in the peer-reviewed Journal of the American Medical Association, concludes that current screening guidelines could miss early-stage prostate cancer in transgender women on hormone therapy.
The prostate, a small gland that helps make semen, also produces a protein called prostate-specific antigen, or PSA. Blood levels of PSA tend to be elevated in people who have prostate cancer, and the PSA test, which measures those levels, is a common prostate ...
For healthy adults, taking multivitamins daily is not associated with a lower risk of death
2024-06-26
What: A large analysis of data from nearly 400,000 healthy U.S. adults followed for more than 20 years has found no association between regular multivitamin use and lower risk of death. The study, led by researchers at the National Institutes of Health’s National Cancer Institute, was published June 26, 2024, in JAMA Network Open.
Many adults in the United States take multivitamins with the hope of improving their health. However, the benefits and harms of regular multivitamin use remain unclear. ...
From takeoff to flight, the wiring of a fly's nervous system is mapped
2024-06-26
Work is underway on a wiring diagram of the motor circuits in the central nervous system that control muscles in fruit flies. This connectome, as the wiring diagram is called, is already providing detailed information on how the nerve coordination of leg movements differs from that controlling the wings.
Although fruit flies seem like simple creatures, the researchers said that their motor system contains “an unexpected level of complexity.”
“A typical fly motor neuron receives thousands of synapses from hundreds ...
A chip-scale Titanium-sapphire laser
2024-06-26
As lasers go, those made of Titanium-sapphire (Ti:sapphire) are considered to have “unmatched” performance. They are indispensable in many fields, including cutting-edge quantum optics, spectroscopy, and neuroscience. But that performance comes at a steep price. Ti:sapphire lasers are big, on the order of cubic feet in volume. They are expensive, costing hundreds of thousands of dollars each. And they require other high-powered lasers, themselves costing $30,000 each, to supply them with enough energy to function.
As a result, Ti:sapphire lasers ...
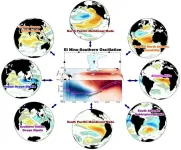
El Niño forecasts extended to 18 months with innovative physics-based model
2024-06-26
Across Asia, the Pacific Ocean, and the Americas, El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) brings variations in winds, weather, and ocean temperature that can cause droughts, floods, crop failures, and food shortages. Recently, the world has experienced a major El Niño event in 2023-2024, dramatically impacting weather, climate, ecosystems, and economies globally. By developing an innovative modeling approach, researchers from the School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST) at the University ...
Scientists discover genetic ‘off switch’ in legume plants that limits biological ability to source nutrients
2024-06-26
A genetic “off switch” that shuts down the process in which legume plants convert atmospheric nitrogen into nutrients has been identified for the first time by a team of international scientists.
Legumes like beans, peas and lentils are unique among crops for their ability to interact with soil bacteria to convert or “fix” nitrogen into a usable form of nutrients. However, this energy-intensive biological process is reduced when nitrogen is already abundant in the soil either through natural processes or through the application of synthetic ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
[Press-News.org] Argonne to support new AI for science projects as part of the National AI Research Resource PilotThree projects awarded access to the Argonne Leadership Computing Facility’s AI Testbed